Abstract
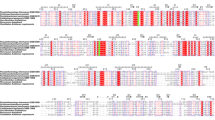
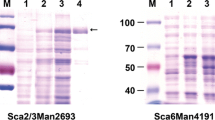
SCO0948 was found to be the single open reading frame annotated to encode an α-mannosidase (AM1) in Streptomyces coelicolor M145. To characterize the protein, we overexpressed SCO0948 in Escherichia coli BL21(DE3). Recombinant AM1, with a molecular weight of 110 kDa, exhibited α-mannosidase activity toward 4-nitrophenyl-α-d-mannopyranoside with a K m of 4.61 mM, a V max of 101.6 mM/min, and a specific activity of 47.96 U/mg. Treatment of ovalbumin, a glycoprotein, with AM1 resulted in partial deglycosylation, as assessed by glycostaining and matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry. The S. coelicolor deletion mutant for SCO0948 failed to produce α-mannosidase activity, confirming AM1 as the only α-mannosidase in S. coelicolor M145. Interestingly, the deletion mutant and a complementation strain produced lower levels of the antibiotics actinorhodin and undecylprodigiosin in glucose minimal media. The results indicate that AM1 as an α-mannosidase influences deglycosylation and antibiotic production in S. coelicolor M145.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cobucci-Ponzano, B., Conte, F., Strazzulli, A., Capasso, C., Fiume, I., Pocsfalvi, G., et al. (2010). The molecular characterization of a novel GH38 alpha-mannosidase from the crenarchaeon Sulfolobus solfataricus revealed its ability in de-mannosylating glycoproteins. Biochimie, 92, 1895–1907.
Cantarel, B. L., Coutinho, P. M., Rancurel, C., Bernard, T., Lombard, V., & Henrissat, B. (2009). The Carbohydrate-Active EnZymes database (CAZy): an expert resource for glycogenomics. Nucleic Acids Research, 37, D233–D238.
Zhu, Y., Suits, M. D., Thompson, A. J., Chavan, S., Dinev, Z., Dumon, C., et al. (2010). Mechanistic insights into a Ca2+-dependent family of alpha-mannosidases in a human gut symbiont. Nature Chemical Biology, 6, 125–132.
Mast, S. W., & Moremen, K. W. (2006). Family 47 alpha-mannosidases in N-glycan processing. Methods in Enzymology, 415, 31–46.
Venkatesan, M., Kuntz, D. A., & Rose, D. R. (2009). Human lysosomal alpha-mannosidases exhibit different inhibition and metal binding properties. Protein Science, 18, 2242–2251.
Numao, S., Kuntz, D. A., Withers, S. G., & Rose, D. R. (2003). Insights into the mechanism of Drosophila melanogaster Golgi alpha-mannosidase II through the structural analysis of covalent reaction intermediates. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 278, 48074–48083.
Foster, J. M., & Roberts, D. B. (1997). The soluble alpha-mannosidases of Drosophila melanogaster. Insect Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, 27, 657–661.
Suits, M. D., Zhu, Y., Taylor, E. J., Walton, J., Zechel, D. L., Gilbert, H. J., et al. (2010). Structure and kinetic investigation of Streptococcus pyogenes family GH38 alpha-mannosidase. PLoS One, 5, e9006.
Sampaio, M. M., Chevance, F., Dippel, R., Eppler, T., Schlegel, A., Boos, W., et al. (2004). Phosphotransferase-mediated transport of the osmolyte 2-O-alpha-mannosyl-d-glycerate in Escherichia coli occurs by the product of the mngA (hrsA) gene and is regulated by the mngR (farR) gene product acting as repressor. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 279, 5537–5548.
Rivera-Marrero, C. A., Ritzenthaler, J. D., Roman, J., & Moremen, K. W. (2001). Molecular cloning and expression of an alpha-mannosidase gene in Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Microbial Pathogenesis, 30, 9–18.
Nankai, H., Hashimoto, W., & Murata, K. (2002). Molecular identification of family 38 alpha-mannosidase of Bacillus sp. strain GL1, responsible for complete depolymerization of xanthan. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 68, 2731–2736.
Nakajima, M., Fushinobu, S., Imamura, H., Shoun, H., & Wakagi, T. (2006). Crystallization and preliminary X-ray analysis of cytosolic alpha-mannosidase from Thermotoga maritima. Acta Crystallographica Section F: Structural Biology and Crystallization Communications, 62, 104–105.
Angelov, A., Putyrski, M., & Liebl, W. (2006). Molecular and biochemical characterization of alpha-glucosidase and alpha-mannosidase and their clustered genes from the thermoacidophilic archaeon Picrophilus torridus. Journal of Bacteriology, 188, 7123–7131.
Baird, J. K., & Cunningham, W. L. (1970). Properties of an alpha-mannosidase from Streptomyces WL6. Biochemical Journal, 120, 18P.
Demain, A. L., & Inamine, E. (1970). Biochemistry and regulation of streptomycin and mannosidostreptomycinase (alpha-d-mannosidase) formation. Bacteriologial Reviews, 34, 1–19.
Shi, P., Yao, G., Cao, Y., Yang, P., Yuan, T., Huang, H., et al. (2011). Cloning and characterization of a new beta-mannosidase from Streptomyces sp. S27. Enzyme and Microbial Technology, 49, 277–283.
Han, A. R., Park, S. R., Park, J. W., Lee, E. Y., Kim, D. M., Kim, B. G., et al. (2011). Biosynthesis of glycosylated derivatives of tylosin in Streptomyces venezuelae. Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology, 21, 613–616.
Raty, K., Kunnari, T., Hakala, J., Mantsala, P., & Ylihonko, K. (2000). A gene cluster from Streptomyces galilaeus involved in glycosylation of aclarubicin. Molecular Genetics and Genomics, 264, 164–172.
Sasaki, J., Mizoue, K., Morimoto, S., & Omura, S. (1996). Microbial glycosylation of macrolide antibiotics by Streptomyces hygroscopicus ATCC 31080 and distribution of a macrolide glycosyl transferase in several Streptomyces strains. Journal of Antibiotics (Tokyo), 49, 1110–1118.
Cundliffe, E. (1992). Glycosylation of macrolide antibiotics in extracts of Streptomyces lividans. Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy, 36, 348–352.
Ramos, A., Lombo, F., Brana, A. F., Rohr, J., Mendez, C., & Salas, J. A. (2008). Biosynthesis of elloramycin in Streptomyces olivaceus requires glycosylation by enzymes encoded outside the aglycon cluster. Microbiology, 154, 781–788.
Nguyen, H. C., Karray, F., Lautru, S., Gagnat, J., Lebrihi, A., Huynh, T. D., et al. (2010). Glycosylation steps during spiramycin biosynthesis in Streptomyces ambofaciens: involvement of three glycosyltransferases and their interplay with two auxiliary proteins. Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy, 54, 2830–2839.
Sartain, M. J., & Belisle, J. T. (2009). N-Terminal clustering of the O-glycosylation sites in the Mycobacterium tuberculosis lipoprotein SodC. Glycobiology, 19, 38–51.
Fratti, R. A., Chua, J., Vergne, I., & Deretic, V. (2003). Mycobacterium tuberculosis glycosylated phosphatidylinositol causes phagosome maturation arrest. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences United States of America, 100, 5437–5442.
Dobos, K. M., Swiderek, K., Khoo, K. H., Brennan, P. J., & Belisle, J. T. (1995). Evidence for glycosylation sites on the 45-kilodalton glycoprotein of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Infection and Immunity, 63, 2846–2853.
Michell, S. L., Whelan, A. O., Wheeler, P. R., Panico, M., Easton, R. L., Etienne, A. T., et al. (2003). The MPB83 antigen from Mycobacterium bovis contains O-linked mannose and (1→3)-mannobiose moieties. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 278, 16423–16432.
Garbe, T., Harris, D., Vordermeier, M., Lathigra, R., Ivanyi, J., & Young, D. (1993). Expression of the Mycobacterium tuberculosis 19-kilodalton antigen in Mycobacterium smegmatis: immunological analysis and evidence of glycosylation. Infection and Immunity, 61, 260–267.
Cowlishaw, D. A., & Smith, M. C. (2001). Glycosylation of a Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2) cell envelope protein is required for infection by bacteriophage phi C31. Molecular Microbiology, 41, 601–610.
Wehmeier, S., Varghese, A. S., Gurcha, S. S., Tissot, B., Panico, M., Hitchen, P., et al. (2009). Glycosylation of the phosphate binding protein, PstS, in Streptomyces coelicolor by a pathway that resembles protein O-mannosylation in eukaryotes. Molecular Microbiology, 71, 421–433.
Espitia, C., Servin-Gonzalez, L., & Mancilla, R. (2010). New insights into protein O-mannosylation in actinomycetes. Molecular Biosystems, 6, 775–781.
Kieser, T., Bibb, M. J., Buttner, M. J., Chater, K., & Hopwood, D. A. (2000). Practical Streptomyces genetics. Norwich: John Innes Centre.
Sambrook, J., Fritsch, E., & Maniatis, T. (1998). Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual (2nd ed.). Cold Spring Harbor: Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory.
Bierman, M., Logan, R., O'Brien, K., Seno, E. T., Rao, R. N., & Schoner, B. E. (1992). Plasmid cloning vectors for the conjugal transfer of DNA from Escherichia coli to Streptomyces spp. Gene, 116, 43–49.
Bystrykh, L. V., Fernandez-Moreno, M. A., Herrema, J. K., Malpartida, F., Hopwood, D. A., & Dijkhuizen, L. (1996). Production of actinorhodin-related “blue pigments” by Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2). Journal of Bacteriology, 178, 2238–2244.
Gil, G. C., Kim, Y. G., & Kim, B. G. (2008). A relative and absolute quantification of neutral N-linked oligosaccharides using modification with carboxymethyl trimethylammonium hydrazide and matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry. Analytical Biochemistry, 379, 45–59.
Gonzalez, D. S., & Jordan, I. K. (2000). The alpha-mannosidases: phylogeny and adaptive diversification. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 17, 292–300.
Santos-Beneit, F., Rodriguez-Garcia, A., & Martin, J. F. (2013). Identification of different promoters in the absA1-absA2 two-component system, a negative regulator of antibiotic production in Streptomyces coelicolor. Molecular Genetics and Genomics, 288, 39–48.
D'Alia, D., Nieselt, K., Steigele, S., Muller, J., Verburg, I., & Takano, E. (2010). Noncoding RNA of glutamine synthetase I modulates antibiotic production in Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2). Journal of Bacteriology, 192, 1160–1164.
Rodriguez, E., Navone, L., Casati, P., & Gramajo, H. (2012). Impact of malic enzymes on antibiotic and triacylglycerol production in Streptomyces coelicolor. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 78, 4571–4579.
Rajesh, T., Song, E., Kim, J. N., Lee, B. R., Kim, E. J., Park, S. H., et al. (2012). Inactivation of phosphomannose isomerase gene abolishes sporulation and antibiotic production in Streptomyces coelicolor. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 93, 1685–1693.
Lu, Y. W., San Roman, A. K., & Gehring, A. M. (2008). Role of phosphopantetheinyl transferase genes in antibiotic production by Streptomyces coelicolor. Journal of Bacteriology, 190, 6903–6908.
Rajesh, T., Song, E., Lee, B. R., Park, S. H., Jeon, J. M., Kim, E., et al. (2013). Increased sensitivity to chloramphenicol by inactivation of manB in Streptomyces coelicolor. Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology, 22, 1324–1329.
Yang, Y. H., Song, E., Park, S. H., Kim, J. N., Lee, K., Kim, E., et al. (2010). Loss of phosphomannomutase activity enhances actinorhodin production in Streptomyces coelicolor. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 86, 1485–1492.
Yang, Y. H., Song, E., Kim, E. J., Lee, K., Kim, W. S., Park, S. S., et al. (2009). NdgR, an IclR-like regulator involved in amino-acid-dependent growth, quorum sensing, and antibiotic production in Streptomyces coelicolor. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 82, 501–511.
Acknowledgments
The work was partially supported by a National Research Foundation of Korea grant (NRF-2011-619-E0002), the Basic Science Research Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Education (NRF-2013R1A1A2A10004690), and the Polar Academic Program (PAP, PD13010) from KOPRI. This research was also partially supported by the Korea Ministry of Environment as a “Converging Technology Project (201-101-007)” and as an “Eco-Innovation Project (405-112-0382).”
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rajesh, T., Jeon, JM., Song, E. et al. Putative Role of a Streptomyces coelicolor-Derived α-Mannosidase in Deglycosylation and Antibiotic Production. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 172, 1639–1651 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-013-0635-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-013-0635-y