Abstract
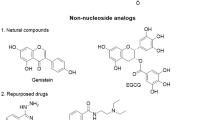
The epimutational event, i.e., ectopic methylation in tumor suppressor genes, can lead to gene silencing, thus promoting prognosis of cancer. The progression of DNA methylation is a cycle of demethylation, de novo methylation, and maintenance methylation. The enzyme responsible for maintenance of methylation status is DNA methyltransferase 1 (DNMT1), the continuous activity of which is required to maintain the pattern of epimutation; thus, its inhibition is a promising strategy for the treatment of cancer. To the best of our knowledge, this study is the first to focus on the recently developed crystal structure of the catalytic site of DNMT1. Here in this study, we have used the crystal structure for the development of non-nucleoside DNMT1 inhibitors using virtual screening (VS), absorption, distribution, metabolism, elimination/toxicology analysis, and molecular docking studies. In this study, VS was carried out on 48,531 natural products to create a subset of lead-like natural products. Three of them were found to form hydrogen bonds with the catalytic site of the DNMT1 (Cys 1226). Thus, this study adumbrates potential lead compounds for treatment of epimutation.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC), Globacon 2002 in World Health Organization (WHO) and International Union Against Cancer (UICC) Report (2005) Global action against cancer. pp.1.
Jones, P. A., & Baylin, S. B. (2007). Cell, 128, 683–692.
Banno, K., Kisu, I., Yanokura, M., Tsuji, K., Masuda, K., Ueki, A., et al. (2012). International Journal of Oncology, 41, 793–797.
Brueckner, B., & Lyko, F. (2004). Trends in Pharmacological Sciences, 25(11), 551–554.
Esteller, M., Corn, P. G., Baylin, S. B., & Herman, J. G. (2001). Cancer Research, 61(8), 3225–3229.
Das, P. M., & Singal, R. J. (2004). Journal of Clinical Oncology, 15(22), 4632–4642.
Sippl, W., & Jung, M. (2009). Epigenetic targets in drug discovery. London: Wiley-VCH.
Bestor, T., Laudano, A., Mattaliano, R., & Ingram, V. (1988). Journal of Molecular Biology, 203, 971–983.
Robertson, K. D. (2001). Oncogene, 20(24), 3139–3155.
Baylin, S. B., & Herman, J. G. (2000). Trends in Genetics, 16, 168–174.
Huang, Y. W., Kuo, C. T., Stoner, K., Huang, T. H., & Wang, L. S. (2011). FEBS Letters, 585, 2129–2136.
Lyko, F., & Brown, R. (2005). Journal of the National Cancer Institute, 97(20), 1498–1506.
Medina-Franco, J. L., & Caulfield, T. (2011). Drug Discovery Today, 9–10, 418–425.
Fang, M. Z. W., Ai, Y., Hou, N., Sun, Z., Lu, Y., Welsh, H., et al. (2003). Cancer Research, 63, 7563–7570.
Singh, N., Dueñas-González, A., Lyko, F., & Medina-Franco, J. L. (2009). ChemMedChem, 4, 792–799.
Liu, Z. F., Xie, Z. L., Jones, W., Pavlovicz, R. E., Liu, S. J., Yu, J. H., et al. (2009). Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry Letters, 19, 706–709.
Lee, W. J., & Zhu, B. T. (2006). Carcinogenesis, 27, 269–277.
Kirchmair, J., Distinto, S., Schuster, D., Spitzer, G., Langer, T., & Wolber, G. (2008). Current Medicinal Chemistry, 15, 2040–2053.
Siedlecki, P. G., Boy, R., Musch, T., Brueckner, B., Suhai, S., Lyko, F., et al. (2006). Journal of Medicinal Chemistry, 49, 678–683.
Kuck, D., Singh, N., Lyko, F., & Medina-Franco, J. L. (2010). Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry, 18, 822–829.
Suzuki, T., Tanaka, R., Hamada, S., Nakagawa, H., & Miyata, N. (2010). Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry Letters, 2011, 1124–1127.
Yu, N., & Wang, M. (2008). Current Medicinal Chemistry, 15, 1350–1375.
Fandy, T. E. (2009). Current Medicinal Chemistry, 16, 2075–2085.
Siedlecki, P., Boy, R. G., Comagic, S., Schirrmacher, R., Wiessler, M., Zielenkiewicz, P., et al. (2003). Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications, 306, 558–563.
Hashimoto, H. & Cheng, X. (2012). Structure of human DNMT1 (residues 600–1600) in complex with Sinefungin. http://www.rcsb.org/pdb/explore/explore.do?structureId=3SWR. Accessed 2012
Hodgson, J. (2001). Nature Biotechnology, 19(8), 722–726.
Davis, A. M., & Riley, R. J. (2004). Current Opinion in Chemical Biology, 8(4), 378–386.
Lee, S. K., Chang, G. S., Lee, I. H., Chung, J. E., Sung, K. Y., & No, K. T. (2004). EuroQSAR 2004. 9, 5–10, Istanbul, Turkey.
Lee, S. K., Lee, I. H., Kim, H. J., Chang, G. S., Chung, J. E., & No, K. T. (2003). Designing drugs and crop protectants: processes, problems and solutions. In M. G. Ford, D. Livingstone, J. Dearden, & H. V. de Waterbeemd (Eds.), Web-based program for rapid prediction of physic-chemical, drug absorption and drug-like properties (1st ed., pp. 418–420). Boston: Blackwell Publishing.
Van de Waterbeemd, H., & Gifford, E. (2003). Nature Reviews Drug Discovery, 2(3), 192–204.
Trott, O., & Olson, A. J. (2010). Journal of Computational Chemistry, 31(2), 455–461.
Morris, G. M., Huey, R., Lindstrom, W., Sanner, M. F., Belew, R. K., Goodsell, D. S., et al. (2009). Journal of Computational Chemistry, 30(16), 2785–2791.
Accelrys Software Inc. (2012). Discovery studio modeling environment, Release 3.5. San Diego: Accelrys Software Inc.
Medina-Franco, J. L., Lopez-Vallejo, F., Kuck, D., & Lyko, F. (2011). Molecular Diversity, 15, 293–304.
Lipinski, C. A., Lombardo, F., Dominy, B. W., & Feeney, P. J. (2001). Advanced Drug Delivery Reviews, 46(1-3), 3–26.
Zhoa, Y. H., Le, J., Abraham, M. H., Hersey, A., Eddershah, P. J., Luscombe, C. N., et al. (2001). Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences, 90, 749–784.
Van de Waterbeemed, H., Camenisch, G., Folkers, G., Chretien, J. R., & Raevsky, O. A. (1998). Journal of Drug Targeting, 6, 151–165.
Lipinski, C. A. (2004). Drug Discovery Today: Technologies, 4, 337–341.
Yamashita, S., Furubayashi, T., Kataoka, M., Sakane, T., Sezaki, H., & Tokuda, H. (2000). European Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences, 10, 195–204.
Yazdanian, M., Glynn, S. L., Wright, J. L., & Hawi, A. (1998). Pharmaceutical Research, 15(9), 1490–1494.
Irvine, J. D., Takahashi, L., Lockhart, K., Cheong, J., Tolan, J. W., Selick, H. E., et al. (1999). Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences, 88, 28–33.
Yee, S. (1997). Pharmaceutical Research, 14, 763–766.
Ajay, A., Bemis, G. W., & Murcko, M. A. (1999). Journal of Medicinal Chemistry, 42, 4942–4951.
Acknowledgments
We would like to sincerely thank VIT University for providing the facilities for this research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chikan, N.A., Bhavaniprasad, V., Anbarasu, K. et al. From Natural Products to Drugs for Epimutation Computer-Aided Drug Design. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 170, 164–175 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-013-0158-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-013-0158-6