Abstract
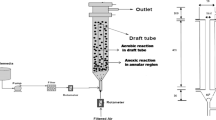
Considering the characteristics of high salinity, high concentration of organic matter, and high biodegradability, a new and efficient anaerobic sequencing batch biofilm reactor (ASBBR) was chosen as an anaerobic pretreatment unit to treat most organic compounds in mustard tuber wastewater. By changing the biofilm density of the reactor, the test was carried out to find out the influence of biofilm density on effluent COD, the content of the sludge dehydrogenase, and gas production rate. Results showed that under the condition of 30 °C, draining ratio of 1/3, and 2 days of hydraulic retention time, COD removal rate increased from 71.5 to 90.5 % when the biofilm density increased from 15 to 50 %; however, COD removal rate increased from 90.5 to 91.3 % when the biofilm density increased from 50 to 70 %. According to the influence of biofilm density on effluent COD, the content of the sludge dehydrogenase, and gas production rate, ASBBR should take 50 % biofilm density in mustard wastewater treatment. At the same time, these design parameters can be used to guide practical engineering.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Pendashteh, A. R., Fakhru’l-Razi, A., Madaeni, S. S., Abdullah, L. C., Abidin, Z. Z., & Biak, D. R. A. (2011). Membrane foulants characterization in a membrane bioreactor (MBR) treating hypersaline oily wastewater. Chemical Engineering Journal, 168, 140–150.
Aminzadeh, B., Torabian, A., Azimi, A. A., Nabi Bidhendi, G. R., & Mehrdadi, N. (2010). Salt inhibition effects on simultaneous heterotrophic/autotrophic denitrification of high nitrate wastewater. International Journal of Environmental Research, 4, 255–262.
Rene, E. R., Kim, S. J., & Park, H. S. (2008). Effect of COD/N ratio and salinity on the performance of sequencing batch reactors. Bioresource Technology, 99, 839–846.
Zhao, X., Wang, Y., Ye, Z., Borthwick, A. G. L., & Ni, J. (2006). Oil field wastewater treatment in biological aerated filter by immobilized microorganisms. Process Biochemistry, 41, 1475–1483.
Peyton, B. M., Wilson, T., & Yonge, D. R. (2002). Kinetics of phenol biodegradation in high salt solutions. Water Research, 36, 4811–4820.
Pendashteh, A. R., Abdullah, L. C., Fakhru’l-Razi, A., Madaeni, S. S., Abidin, Z. Z., & Biak, D. R. A. (2012). Evaluation of membrane bioreactor for hypersaline oily wastewater treatment. Process Safety and Environmental Protection, 90, 45–55.
Yang, J. C., Zhang, L., Hira, D., Fukuzaki, Y., & Furukawa, K. (2011). Anammox treatment of high-salinity wastewater at ambient temperature. Bioresource Technology, 102, 2367–2372.
Liu, C., Yamamoto, T., Nishiyama, T., Fujii, T., & Furukawa, K. (2009). Effect of salt concentration in anammox treatment using non woven biomass carrier. Journal of Bioscience and Bioengineering, 107, 519–523.
Osaka, T., Shirotani, K., Yoshie, S., & Tsuneda, S. (2008). Effects of carbon source on denitrification efficiency and microbial community structure in a saline wastewater treatment process. Water Research, 42, 3709–3718.
Lefebvre, O., & Moletta, R. (2006). Treatment of organic pollution in industrial saline wastewater: a literature review. Water Research, 40, 3671–3682.
Aloui, F., Khoufi, S., Loukil, S., & Sayadi, S. (2009). Performances of an activated sludge process for the treatment of fish processing saline wastewater. Desalination, 246, 389–396.
Ozalp, G., Gomec, C. Y., Ozturk, I., Gonuldinc, S., & Altinbas, M. (2003). Effect of high salinity on anaerobic treatment of low strength effluents. Water Science and Technology, 48, 207–212.
Kubo, M., Hiroe, J., Murakami, M., Fukami, H., & Tachiki, T. (2001). Treatment of hypersaline-containing wastewater with salt-tolerant microorganisms. Journal of Bioscience and Bioengineering, 91, 222–224.
Lu, M., Zhang, Z., Yu, W., & Zhu, W. (2009). Biological treatment of oilfield-produced water: a field pilot study. International Biodeterioration & Biodegradation, 63, 316–321.
Rovirosa, N., Sanchez, E., Cruz, M., Veiga, M. C., & Borja, R. (2004). Coliform concentration reduction and related performance evaluation of a down-flow anaerobic fixed bed reactor treating low-strength saline wastewater. Bioresource Technology, 94, 119–127.
Tong, Y. (2010). Study on the photosynthetic bacteria with UASB process treatment of high salinity organic wastewater. Journal of Qingdao Technological University, 31, 69–73 (in Chinese).
Gomec, C. Y., Gonuldinc, S., Eldem, N., & Ozturk, I. (2005). Behavior of an up-flow anaerobic sludge bed (UASB) reactor at extreme salinity. Water Science and Technology, 51, 115–120.
Li, J., Yu, D. S., Wang, Q., Li, Y., & Ren, X. J. (2009). Experimental study on treatment of wastewater containing 50 % seawater by MBR process. Chinese Journal of Environment Engineering, 3, 1947–1950 (in Chinese).
Pendashteh, A. R., Fakhru’l-Razi, A., Chaibakhsh, N., Abdullah, L. C., Madaeni, S. S., & Abidin, Z. Z. (2011). Modeling of membrane bioreactor treating hypersaline oily wastewater by artificial neural network. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 192, 568–575.
Vyrides, I., & Stuckey, D. C. (2009). Saline sewage treatment using a submerged anaerobic membrane reactor (SAMBR): effects of activated carbon addition and biogas-sparging time. Water Research, 43, 933–942.
Chai, H. X., Li, X. P., Zhou, J., Chen, Y., & Long, T. R. (2010). Treatment of mustard tuber wastewater by anaerobic sequencing batch biofilm reactor-two-stage sequencing batch biofilm reactor-chemical-dephosphorization process. Chinese Journal of Environmental Engineering, 4, 785–788 (in Chinese).
Wang, X. M., Zhou, J., Long, T. R., & Liu, J. (2008). Efficiency of phosphorus removal from high-salinity mustard tuber wastewater by combined biological/chemical process. China Water and Wastewater, 24, 29–33 (in Chinese).
Yang, H. W., Jiang, Z. P., Shi, S. Q., & Tang, W. Z. (2002). INT–dehydrogenase activity test for assessing anaerobic biodegradability of organic compounds. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 53, 416–421.
APHA. (2005). Standard methods for water and wastewater examination (21st ed.). Washington: American Public Health Association.
Dun, M. N., Hu, W. R., Pei, H. Y., & Xie, J. (2008). Determination of dehydrogenase activity and its application. Industrial Water Treatment, 28, 1–4 (in Chinese).
Ghaly, A. E., & Mahmoud, N. S. (2007). Effects of tetrazolium chloride concentration, O2, and cell age on dehydrogenase activity of Aspergillus niger. Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 136, 207–222.
Zhou, P., He, J. H., & Qian, Y. (2003). Biofilm airlift suspension reactor treatment of domestic wastewater. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 144, 81–100.
Park, J. J., Byun, I. G., Park, S. R., & Park, T. J. (2008). Nitrifying bacterial communities and its activities in aerobic biofilm reactors under different temperature conditions. Korean Journal of Chemical Engineering, 25, 1448–1455.
Li, R. P., Chen, S. L., & Li, X. J. (2010). Biogas production from anaerobic co-digestion of food waste with dairy manure in a two-phase digestion system. Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 160, 643–654.
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant no. 51008318).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chai, H., Kang, W. Influence of Biofilm Density on Anaerobic Sequencing Batch Biofilm Reactor Treating Mustard Tuber Wastewater. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 168, 1664–1671 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-012-9887-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-012-9887-1