Abstract
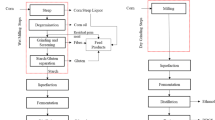
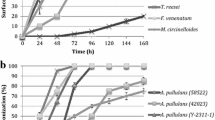
To increase the value of coproducts from corn ethanol fermentation and soybean aqueous processing, distiller’s dried grains with solubles (DDGS) and soybean cotyledon fiber were used as the substrates for solid state fermentation (SSF) to improve feed digestibility. Aspergillus oryzae, Trichoderma reesei, and Phanerochaete chrysosporium were chosen as they produce desirable enzymes and are widely used in SSF for feed. The results showed that the cellulase and xylanase activities were significantly increased after 7 days of fermentation, and cellulose and hemicellulose degradation was also greatly increased. When soybean fiber was used as SSF substrate, the maximum activities of the cellulase and xylanase were 10.3 and 84.2 IU/g substrate (dry weight basis) after SSF treatment, respectively. However, the enzyme activities were relatively low in DDGS, and the growth of the three fungi was poor. The fungi grew better when soybean cotyledon fiber was added to DDGS, and cellulase and xylanase activity increased with the increase of soybean fiber content. Porosity was identified as an important factor for SSF because the addition of inert soybean hull alone improved the fungi growth significantly. These data suggest that the nutritional value of DDGS and soybean cotyledon fiber as monogastric animal feed could be greatly enhanced by SSF treatment.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Denise, S. R., Daniel, P. S., António, A. V., Adilson, R. G., & José, A. T. (2008). Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 147, 85–96.
Nobrega de Moura, J. M. L., de Almeida, N. M., de Almeida, N. M., & Johnson, L. A. (2009). Journal of the American Oil Chemists’ Society, 86, 809–815.
Hema, A., Trivedi, U. B., & Patel, K. C. (2006). Bioresource Technology, 97, 1161–1166.
Graminha, E. B. N., Goncalves, A. Z. L., Pirota, R. D. P. B., Balsalobre, M. A. A., Da Silva, R., & Gomes, E. (2008). Animal Feed Science and Technology, 144, 1–22.
Shankar, S. K., & Mulimani, V. H. (2007). Bioresource Technology, 98, 958–961.
Nizamuddin, S., Sridevi, A., & Narasimha, G. (2008). African Journal of Biotechnology, 7, 1096–1100.
Deshpande, S. K., Bhotmange, M. G., & Chakrabarti, T. (2008). Indian Journal of Chemical Technology, 15, 449–456.
Mekala, N. K., Singhania, R. R., Sukumaran, R. K., & Ashok, P. (2008). Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 151, 122–131.
Dinis, M. J., Bezerra, R. M. F., & Nunes, F. (2009). Bioresource Technology, 100, 4829–4835.
Shrestha, P., Rasmussen, M., & Khanal, S. K. (2008). Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 56, 3918–3924.
Verma, P., & Madamwar, D. (2002). Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 102–103, 109–118.
Hoskins, B., & Lyons, M. (2009). Master Brewers Association of the Americas, 46, 1–7.
Miller, G. L. (1959). Analytical Chemistry, 31, 426–428.
Bailey, M. J., Biely, P., & Poutanen, K. (1992). Journal of Biotechnology, 23, 257–270.
Van Soest, P. J., Robertson, J. B., & Lewis, B. A. (1991). Journal of Dairy Science, 74, 3583–3597.
Van Soest, P. J., & Wine, R. H. (1968). Journal of the Association of Official Analytical Chemists, 51, 780–787.
Thornberry, H. H. (1950). Phytopathology, 40, 419–429.
Jones, A. L., & Ehret, G. R. (1976). Plant Disease Reporter, 60, 765–769.
Alberton, L. R., Luciana, P. S. V., Ricardo, A., Ricardo, C. F., José, R., & Carlos, R. S. (2009). Brazilian Archives of Biology and Technology, 52, 171–180.
Fang, T. J., Liao, B. C., & Lee, S. C. (2010). New Biotechnology, 27, 25–32.
Reeta, R. S. (2006). Indian Journal of Technology, 5, 332–336.
Xin, F. X., & Geng, A. L. (2010). Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 162, 295–306.
Feniksova, R. V., Tikhomirova, A. S., & Rakhleeva, E. E. (1960). Microbiologica, 29, 745–748.
Gibson, M., & Karges, K. (2006). In multi-state poultry feeding and nutrition conference, Indianapolis, IN, May 23–25. West Lafayette: Purdue University.
Spiehs, M. J., Whitney, M. H., & Shurson, G. C. (2002). Journal of Animal Science, 80, 2639–2645.
Cromwell, G. L., Herkelman, K. L., & Stahly, T. S. (1993). Journal of Animal Science, 71, 679–686.
Yu, P., Niu, Z., & Damiran, D. (2010). Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 58, 3460–3464.
Martinez Amezcua, C., Parsons, C. M., & Noll, S. L. (2004). Poultry Science, 83, 971–976.
Lumpkins, B. S., & Batal, A. B. (2005). Poultry Science, 84, 581–586.
Liu, K. (2011). Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 59, 1508–1526.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank for the USDA Special Grant and to Professor Hans van Leeuwen of the Chemical and Biological Engineering Department for sharing the fungi used in this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, S., Lio, J. & Wang, T. Evaluation of Enzyme Activity and Fiber Content of Soybean Cotyledon Fiber and Distiller’s Dried Grains with Solubles by Solid State Fermentation. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 167, 109–121 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-012-9665-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-012-9665-0