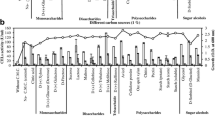
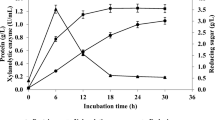
Abstract
Either the natural biodegradation process or the industrial hydrolytic process requires synergistic interactions between various cellulases. However, it is sometimes impeded by low hydrolytic rate of existing cellulases and the lack of accessory enzymes. Herein, the ability of a commercial cellulase (Spezyme CP, from Genencor) to degrade steam explosion-pretreated corn stover was significantly improved. Firstly, a fungal cellulase producer, Aspergillus fumigatus ECU0811, was isolated from hundreds of soil samples. A 96-deep-well microscale-based platform was developed here to reduce the labor-intensive screening work and proved to be consistent with macroscale screening work. After optimization of fermentation, 3% corn cob could induce A. fumigatus ECU0811 to yield the highest cellulase production. Based on the high activities of β-glucosidase and xylanase by A. fumigatus ECU0811, 0.91 and 125 U/mg protein, respectively, an enzyme cocktail was composed with a fixed dosage of Spezyme CP (CPCel) at 14.2 filter paper units (FPU)/g glucan and varied dosages of A. fumigatus cellulase (AFCel). Consequently, the glucan-to-glucose conversion of corn stover was increased from 25.6% in the presence of CPCel at a dosage of 14.2 FPU/g glucan to 99.5% in the presence of the enzyme cocktail (14.2 FPU CPCel plus 1.21 FPU AFCel per gram of glucan). On the other side, it reduced the total protein amount of CPCel by as much as tenfold, which extremely improved the hydrolytic rate of Spezyme CP and reduced its dosage.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Himmel, M. E., Ding, S. Y., Johnson, D. K., Adney, W. S., Nimlos, M. R., Brady, J. W., et al. (2007). Science, 315, 804–807.
Percival Zhang, Y. H., Himmel, M. E., & Mielenz, J. R. (2006). Biotechnology Advances, 24, 452–481.
Perez, J., Munoz-Dorado, J., de la Rubia, T., & Martinez, J. (2002). International Microbiology, 5, 53–63.
Service, R. F. (2007). Science, 315, 1488–1491.
Lynd, L. R., Weimer, P. J., van Zyl, W. H., & Pretorius, I. S. (2002). Microbiology and Molecular Biology Reviews, 66, 506–577.
Sanchez, O. J., & Cardona, C. A. (2008). Bioresource Technology, 99, 5270–5295.
Baker, J. O., Ehrman, C. I., Adney, W. S., Thomas, S. R., & Himmel, M. E. (1998). Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 70–72, 395–403.
Berlin, A., Maximenko, V., Gilkes, N., & Saddler, J. (2007). Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 97, 287–296.
Meyer, A. S., Rosgaard, L., & Sorensen, H. R. (2009). Journal of Cereal Science, 50, 337–344.
Tu, M. B., Chandra, R. P., & Saddler, J. N. (2007). Biotechnology Progress, 23, 1130–1137.
Wu, Z., & Lee, Y. Y. (1998). Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 70–72, 479–492.
Yang, B., Willies, D. M., & Wyman, C. E. (2006). Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 94, 1122–1128.
Reczey, K., Brumbauer, A., Bollok, M., Szengyel, Z., & Zacchi, G. (1998). Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 70–72, 225–235.
Chen, H. Z., Hayn, M., & Esterbauer, H. (1992). Biochimica et Biophysica Acta, 1121, 54–60.
Golias, H., Dumsday, G. J., Stanley, G. A., & Pamment, N. B. (2000). Biotechnology Letters, 22, 617–621.
Nieves, R. A., Ehrman, C. I., Adney, W. S., Elander, R. T., & Himmel, M. E. (1998). World Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology, 14, 301–304.
Sternberg, D., Vijayakumar, P., & Reese, E. T. (1977). Canadian Journal of Microbiology, 23, 139–147.
Chandrasekaran, A., Bharadwaj, R., Park, J. I., Sapra, R., Adams, P. D., & Singh, A. K. (2010). Journal of Proteome Research, 9, 5677–5683.
Chundawat, S. P., Balan, V., & Dale, B. E. (2008). Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 99, 1281–1294.
King, B. C., Donnelly, M. K., Bergstrom, G. C., Walker, L. P., & Gibson, D. M. (2009). Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 102, 1033–1044.
Bharadwaj, R., Wong, A., Knierim, B., Singh, S., Holmes, B. M., Auer, M., et al. (2011). Bioresource Technology, 102, 1329–1337.
Cianchetta, S., Galletti, S., Burzi, P. L., & Cerato, C. (2010). Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 107, 461–468.
Kim, Y. S., Jung, H. C., & Pan, J. G. (2000). Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 66, 788–793.
Mandels, M., & Weber, J. (1969). Journal of the American Chemical Society, 95, 391–414.
Xiao, Z., Storms, R., & Tsang, A. (2004). Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 88, 832–837.
Anderson, I. C., Campbell, C. D., & Prosser, J. I. (2003). Environmental Microbiology, 5, 36–47.
Smith, P. K., Krohn, R. I., Hermanson, G. T., Mallia, A. K., Gartner, F. H., Provenzano, M. D., et al. (1985). Analytical Biochemistry, 150, 76–85.
Miller, G. L. (1959). Analytical Chemistry, 31, 426–428.
Yu, H. L., Xu, J. H., Lu, W. Y., & Lin, G. Q. (2007). Enzyme and Microbial Technology, 40, 354–361.
Shi, Q. Q., Sun, J., Yu, H. L., Li, C. X., Bao, J., & Xu, J. H. (2011). Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 164, 819–830.
Juhász, T., Szengyel, Z., Réczey, K., Siika-Aho, M., & Viikari, L. (2005). Process Biochemistry, 40, 3519–3525.
Olsson, L., Christensen, T. M. I. E., Hansen, K. P., & Palmqvist, E. A. (2003). Enzyme and Microbial Technology, 33, 612–619.
Wang, C. H., Hseu, T. H., & Huang, C. M. (1988). Journal of Biotechnology, 9, 47–59.
Reese, E. T., & Maguire, A. (1969). Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 17, 242–245.
Sherief, A. A., El-Tanash, A. B., & Atia, N. (2010). Research Journal of Microbiology, 5, 199–211.
Wase, D. A. J., Raymahasay, S., & Wang, C. W. (1985). Enzyme and Microbial Technology, 7, 225–229.
Gusakov, A. V., Salanovich, T. N., Antonov, A. I., Ustinov, B. B., Okunev, O. N., Burlingame, R., et al. (2007). Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 97, 1028–1038.
Zhang, M., Su, R., Qi, W., & He, Z. (2010). Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 160, 1407–1414.
Acknowledgments
This work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 20902023 & 31071604), Ministry of Science and Technology, P.R. China (Nos. 2009CB724706), and China National Special Fund for State Key Laboratory of Bioreactor Engineering (No. 2060204).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Dan Wang and Jie Sun contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, D., Sun, J., Yu, HL. et al. Maximum Saccharification of Cellulose Complex by an Enzyme Cocktail Supplemented with Cellulase from Newly Isolated Aspergillus fumigatus ECU0811. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 166, 176–186 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-011-9414-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-011-9414-9