Abstract
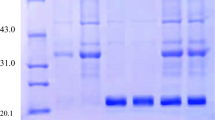
The 7S and 11S globulins from soybean proteins using reverse micelle and aqueous buffer extraction methods were characterized by using sodium dodecyl sulfate polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE) and scanning electron microscope (SEM), and their amino acid compositions were also evaluated. SDS-PAGE did not show electrophoretic differences between 7S and 11S globulin subunits with two extraction methods. SEM analysis showed that the AOT reverse micelle processing of 7S and 11S globulins induced a reduction of droplet size. Some individual amino acid contents of 7S and 11S globulins using two extraction methods were different, some were similar. In all the samples, the glutamic acid, aspartic acid, and leucine were the dominant amino acids while the cystine and methionine were the first-limiting amino acids. The proportion of essential amino acids to the total amino acids (E/T) of the 7S globulin from aqueous buffer and reverse micelles was similar. While significant differences were obtained in the proportion of E/T of the 11S globulin.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fulushima, D. (1991). Recent progress of soybean protein foods: chemistry, technology, and nutrition. Food Reviews International, 7, 323–351.
Adachi, M., Takenaka, Y., Gidamis, A. B., Mikami, B., & Utsumi, S. (2001). Crystal structure of soybean proglycinin A1aB1b homotrimer. Journal of Molecular Biology, 305, 291–305.
Maruyama, M., Fukuda, T., Saka, S., Inui, N., Kotoh, J., Miyagawa, M., et al. (2003). Molecular and structural analysis of electrophoretic variants of soybean seed storage proteins. Phytochemistry, 64, 701–708.
Ashida, K., Iida, S., & Yasui, T. (2006). Lack of 26 kDa globulin accompanies increased free amino acid content in rice (Oryza sativa L.) grains. Journal of Cereal Science, 43, 387–392.
Netto, F. M., & Galeazzi, M. A. M. (1998). Production and characterization of enzymatic hydrolysate from soy protein isolate. Lebensm Wiss U Technology, 31, 624–631.
Skjærvik, O. F., Refstie, S., Aslaksen, M. A., & Skrede, A. (2006). Digestibility of diets containing different soybean meals in Atlantic cod (Gadus morhua); comparison of collection methods and mapping of digestibility in different sections of the gastrointestinal tract. Aquaculture, 261, 241–258.
Rodriguez, C., Frias, J., Valverde, C. V., & Hernandez, A. (2008). Correlations between some nitrogen fractions, lysine, histidine, trrosine, and ornithine contents during the germination of peas, beans, and lentils. Food Chemistry, 108, 245–252.
Fathi Nasri, M. H., France, J., Danesh Mesgaran, M., & Kebreab, E. (2008). Effect of heat processing on ruminal degradability and intestinal disappearance of nitrogen and amino acids in Iranian whole soybean. Livestock Science, 113, 43–51.
Matzke, S. F., Creagh, A. L., Haynes, L. C., Prausnitz, J. M., & Blanch, H. W. (1992). Mechanisms of protein solubilization in reverse micelles. Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 40, 91–102.
Rashid, O. A., Svetlana, N. K., Alexandra, L. Z. I., Nadejda, R., & Olyga, I. L. (2005). DNA polymerase activity in water-structured and confined environment of reverse micelles. Journal of Molecular Catalysis B: Enzymatic, 33, 29–34.
Stephanie, R. D., Thorsten, B., Alan, H. T., Pawel, P., & Walter, N. (1991). Interfacial transport processes in the reverse micellar extraction of proteins. Journal of Colloid and Interference Science, 145, 33–50.
Leser, M. E., & Luisi, P. L. (1989). The use of reverse micelles for the simultaneous extraction of oil and proteins from vegetable meal. Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 34, 1140–1146.
Correa, N. M., Durantini, E. N., & Silber, J. J. (1998). Binding of nitrodiphenylamines to reverse micelles of AOT in n-hexane and carbon tetrachloride: solvent and substituent effects. Journal of Colloid and Interference Science, 208, 96–103.
Zhao, X. Y., Chen, F. S., Xue, W. T., & Lee, L. T. (2008). FTIR spectra studies on the secondary structures of 7S and 11S globulins from soybean proteins using AOT reverse micellar extraction. Food Hydrocolloids, 22, 568–575.
Zhao, X. Y., Chen, F. S., Chen, J. Q., Gai, G. S., Xue, W. T., & Li, L. T. (2008). Effects of AOT reverse micelle on properties of soy globulins. Food Chemistry, 111, 599–605.
Utsumi, S., Matsumura, Y., & Mori, T. (1997). Structure function relationships of soy proteins. In S. Damodaran & A. Paraf (Eds.), Food proteins and their applications (pp. 257–291). New York: Marcel Dekker.
AOCS. (1973). Official tentative methods of the American Oil Chemists’ Society. In W. E. LinK (Ed.), Method Ac 4–41 (3rd ed.). Chicago: AOCS.
Vassiliki, P., Aristotelis, X., & Athanasios, E. E. (1993). Proteolytic activity in various water-in-oil microemulsionsf as related to the polarity of the reaction medium. Colloid Surfaces B, 1, 295–303.
Smith, P. K., Krohn, R. I., Hermanson, G. T., Mallia, A. K., Gartener, F. H., Provenzano, M. D., et al. (1985). Measurement of protein using bichinchoninic acid. Analytical Biochemistry, 150, 76–85.
Nagano, T., Hirotsuka, M., Mori, H., Kohyama, K., & Nishinari, K. (1992). Dynamic viscoelastic study on the gelation of 7S globulin from soybeans. Journal of Agriculture and Food Chemistry, 40, 941–944.
Laemmli, U. K. (1970). Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature, 227, 680–686.
Spackann, D. H., Stein, W. H., & Moore, S. (1958). Automatic recording apparatus for use in the chromatography of amino acid. Analytical Biochemistry, 30, 1190–1206.
Zarkadas, C. G., Voldeng, H. D., Yu, Z. R., & Choi, V. (1999). Assessment of the protein quality of nine northern adapted yellow and brown seed coated soybean cultivars by amino acid analysis. Journal of Agriculture and Food Chemistry, 47, 5009–5018.
Zarkadas, C. G., Gagnon, C., Gleddie, S., Khanizadeh, S., Cober, E. R., & Guillemette, R. J. D. (2007). Assessment of the protein quality of fourteen soybean [Glycine max (L.) Merr.] cultivars using amino acid analysis and two-dimensional electrophoresis. Food Research International, 40, 129–146.
Oser, B. L. (1959). An integrated essential amino acid index for predicting the biological value of proteins. In A. A. Albanese (Ed.), Protein and amino acid nutrition (pp. 295–311). New York: Academic.
Hidvegi, M., & Bekes, F. (1984). Mathematical modeling of protein quality from amino acid composition. In R. Lasztity & M. Hidvegi (Eds.), Processing of the international association of the cereal chemistry symposium (pp. 205–286). Budapest: Akademiai Kiado.
FAO/WHO. (1991). Protein quality evaluation. Report of the joint FAO/WHO expert consultation (p. 51). Rome: FAO Food and Nutrition.
Koshiyama, I. (1972). Purification and physico-chemical properties of 11S globulin in soy bean seeds. International Journal of Peptide and Protein Research, 4, 167–176.
Miller, R., Fainerman, V. B., Makievski, A. V., Krägel, J., Grigoriev, D. O., Kazakov, V. N., et al. (2000). Dynamics of protein and mixed proteinrsurfactant adsorption layers at the waterrfluid interface. Advances in Colloid and Interface Science, 86, 39–82.
Zhao, X. Y., Chen, F. S., Xue, W. T., & Li, L. T. (2008). FTIR spectra studies on the secondary structures of soybean 7S and 11S globulins using AOT reverse micellar extraction. Food Hydrocolloids, 22(4), 568–575.
Gochman-Hecht, H., & Bianco-Peled, H. (2006). Structure modifications of AOT reverse micelles due to protein incorporation. Journal of Colloid and Interference Science, 297, 276–283.
Gayler, K. R., & Sykes, G. E. (1985). Effects of nutritional stress on the storage proteins of soybeans. Plant Physiology, 78, 582–585.
Christopher, D. J., Yarwood, J., Belton, P. S., & Hills, B. P. (1992). A Fourier transform infrared study of water-head group interactions in reversed micelles containing sodium bis(2-ethylhexyl) sulfosuccinate (AOT). Journal of Colloid and Interference Science, 152, 465–471.
Grieshop, C. M., Kadzere, C. T., Clapper, G. M., Flickinger, E. A., Bauer, L. L., Frazier, R. L., et al. (2003). Chemical and nutritional characteristics of United States soybeans and soybean meals. Journal of Agriculture and Food Chemistry, 51, 7684–7691.
Karr-Lilienthal, L. K., Grieshop, C. M., Spears, J. K., & Fahey, G. C. (2005). Amino acid, carbohydrate, and fat composition of soybean meals prepared at 55 commercial U.S. soybean processing plants. Journal of Agriculture and Food Chemistry, 53, 2146–2150.
Acknowledgments
Financial support of this work came from the Promotive Research Fund for Excellent Young and Middle-Aged Scientists of Shandong Province of China (grant no. BS2010NY027) and Project of Agriculture Scientific and Technological Achievement Transfer of China (grant no. 2009GB2C600198).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, X., Chen, J., Lu, Z. et al. Analysis of the Amino Acids of Soy Globulins by AOT Reverse Micelles and Aqueous Buffer. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 165, 802–813 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-011-9298-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-011-9298-8