Abstract
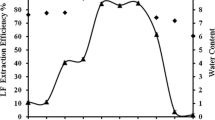
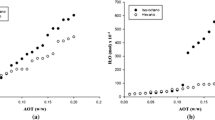
The extraction of bovine serum albumin (BSA) has been investigated using reverse micelles of hexadecyl trimethyl ammonium chloride/n-octanol/isooctane. Forward extraction process parameters such as the surfactant concentration, co-solvent concentration, pH, ionic strength, and species of the initial aqueous phase were important factors affecting the extraction performance. These parameters were varied to optimize the extraction efficiency. Under the optimized conditions, forward extraction efficiencies of BSA can reach practically 99.55%. The thermodynamic study revealed that the extraction of BSA is controlled by entropy changes. Maximum back-extraction efficiency of 85.16% can be obtained at low pH values and high salt concentrations. The structures of BSA during reverse micelle extraction did not change by comparing the circular dichroism spectra of BSA back-extracted to the aqueous phase with that of feed BSA.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Luisi, P. L. (1985). Enzymes hosted in reverse micelles in hydrocarbon solution. Angewandte Chemie International Edition in English, 24, 439–450.
Goklen, K. E., & Hatton, T. A. (1987). Liquid–liquid extraction of low molecular weight proteins by selective solubilization in reverse micelles. Separation Science and Technology, 22, 831–842.
Jolivalt, C., Miner, M., & Renon, H. (1990). Extraction of α-chymotrypsin using reversed micelles. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 135, 85–96.
Marcozz, G., Correa, N., Luisi, P. L., & Caselli, M. (1991). Protein extraction by reverse micelles: a study of the factors affecting the forward and backward transfer of α-chymotrypsin and its activity. Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 38, 1239–1246.
Hebbar, H. U., Sumana, B., & Raghavarao, K. S. M. S. (2008). Use of reverse micellar systems for the extraction and purification of bromelain from pineapple wastes. Bioresource Technology, 99, 4896–4902.
Dungan, S. R., Bausch, T. E., Hatton, T. A., Plucinski, P. K., & Nitch, W. (1991). Interfacial transport process in the reverse micellar extraction of proteins. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 145, 30–45.
Kinuguasa, T., Tanahshi, S., & Takeuchi, H. (1991). Extraction of lysozyme using reversed micellar solution: distribution equilibrium and extraction rates. Industrial and Engineering Chemistry Research, 30, 2470–2476.
Rho, S. G., & Kang, C. H. (2003). The factors affecting the backward-transfer of bovine serum albumin (BSA) from sodium bis (2-ethylhexyl) sulfosuccinate reverse micellar solutions. Korean Journal of Chemical Engineering, 20, 519–521.
Kadam, K. L. (1986). Reverse micelles as a bioseparation tool. Enzyme and Microbial Technology, 8, 266–273.
Wolbert, R. B. G., Hilhorst, R., Voskuilen, G., Nachtegaal, H., Dekker, M. R. V. K., & Bijsterbosch, B. H. (1989). Protein transfer from an aqueous phase into reversed micelles. European Journal of Biochemistry, 184, 627–633.
Lu, Q., Chen, H. Y., Li, K. H., & Shi, Y. J. (1998). Transport between an aqueous phase and a CTAB/hexanol-octane reversed micellar phase. Biochemical Engineering Journal, 45, 45–52.
Ayala, G. A., Kamat, S., Beckman, E. J., & Rassell, A. J. (1992). Protein extraction and activity in reverse micelles of a nonionic detergent. Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 39, 806–814.
Hebbar, H. U., & Raghavarao, K. S. M. S. (2007). Extraction of bovine serum albumin using nanoparticulate reverse micelles. Process Biochemistry, 42, 1602–1608.
Sun, Y., Ichikawa, S., Sugiura, S., & Furusaki, S. (1998). Affinity extraction of proteins with a reversed micellar system composed of unbound cibacron bluemodified lecithin. Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 58, 58–64.
Zhang, W., Liu, H., & Chen, J. (2002). Forward and backward extraction of BSA using mixed reverse micellar system of CTAB and alkyl halides. Biochemical Engineering Journal, 12, 1–5.
Zhang, T., Liu, H., & Chen, J. (1999). Affinity extraction of BSAwith reversed micellar system composed of unbound cibacron blue. Biotechnology Progress, 15, 1078–1082.
Hong, D. P., Lee, S. S., & Kuboi, R. (2000). Conformational transition and mass transfer inextraction of proteins by AOT–alcohol–isooctane revere micellar systems. Journal of Chromatography B, 743, 203–213.
Bradford, M. M. (1972). A rapid and sensitive method for quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Analytical Biochemistry, 72, 248–254.
Lazarova, Z., & Tonova, K. (1999). Integrated reversed micellar extraction and stripping of α-amylase. Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 63, 583–592.
Krei, G. A., & Hustedt, H. (1992). Extraction of enzymes by reverse micelles. Chemical Engineering Science, 47, 90–111.
Pessoa, A., Jr., & Vitolo, M. (1998). Recovery of insulinase using BDBAC reversed micelles. Process Biochemistry, 33, 291–297.
Regalado, C., Asenjo, J. A., & Pyle, D. L. (1996). Studies on the purification of peroxidase from horseradish roots using reverse micelles. Enzyme and Microbial Technology, 18, 332–339.
Gaikar, V. G., & Kulkarni, M. S. (2001). Selective reverse micellar extraction of penicillin acylase from E coli. Journal of Chemical Technology and Biotechnology, 76, 729–736.
Harikrishna, S., Srinivas, N. D., Raghavarao, K. S. M. S., & Karanth, N. G. (2002). Reverse micellar extraction for downstream processing of proteins/enzymes. Advances in Biochemical Engineering/Biotechnology, 75, 119–183.
Dungan, S. R., Bausch, T., Hatton, T. A., Plucinski, P., & Nitsch, W. (1991). Interfacial transport processes in the reversed micellar extraction of proteins. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 145, 30–50.
Spelzini, D., Farruggia, B., & Pico, G. (2005). Features of the acid protease partition in aqueous two-phase systems of polyethylene glycol–phosphate: chymosin and pepsin. Journal of Chromatography B, 821, 60–66.
Bianco-Peled, H., & Gryc, S. (2004). Binding of amino acid to “smart” sorbents:where does hydrophobicity come into play. Langmuir, 20, 169–174.
Dekker, M., Hilhorst, R., & Laane, C. (1989). Isolating enzyme by reversed micelles. Analytical Biochemistry, 178, 217–226.
Ono, T., Goto, M., Nakashio, F., & Hatton, T. A. (1996). Extraction behavior of hemoglobin using reversed micelles by dioleyl phosphoric acid. Biotechnology Progress, 12, 793–800.
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge the financial support for this work from The National Natural Science Foundation of China (no. 20876089), the Key Technologies R&D Programme of China (no. 2007BAD87B05), and the Natural Science Foundation of Shandong Province (no. Y2007B05).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sun, Q., Yang, Y., Lu, Y. et al. Extraction of Bovine Serum Albumin Using Reverse Micelles Formed by Hexadecyl Trimethyl Ammonium Chloride. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 163, 744–755 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-010-9079-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-010-9079-9