Abstract
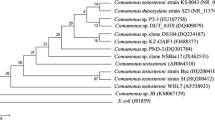
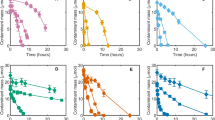
Marinobacter vinifirmus was shown to degrade toluene as sole carbon and energy source under aerobiosis and at NaCl concentrations in the range 30–150 g/L. Maximum toluene consumption rate, total CO2, and biomass productions were measured in the presence of 60 g/L of NaCl. Under these conditions, 90% of the carbon from toluene was recovered as CO2 and biomass. Maximum specific toluene consumption rate was about 0.12 mgC toluene mgC biomass−1 h−1 at NaCl concentrations between 30 and 60 g/L. It decreased to 0.03 mgC toluene mgC biomass−1 h−1 at 150 g/L. Besides toluene, M. vinifirmus degraded benzene, ethylbenzene, and p-xylene. Benzene and toluene were utilized to a lesser extent by another Marinobacter sp., Marinobacter hydrocarbonoclasticus.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lefebvre, O., Habouzit, F., Bru, V., Delgenes, J. P., Godon, J. J., & Moletta, R. (2004). Environmental Technology, 25, 543–553.
Le Borgne, S., Paniagua, D., & Vazquez-Duhalt, R. (2008). Journal of Molecular Microbiology and Biotechnology, 15, 74–92.
Bertrand, J. C., Almallah, M., Acquaviva, M., & Mille, G. (1990). Letters in Applied Microbiology, 11, 260–263.
Emerson, D., Chauhan, S., Oriel, P., & Breznak, J. A. (1994). Archives of Microbiology, 161, 445–452.
Gauthier, M. J., Lafay, B., Christen, R., Fernandez, L., Acquaviva, M., Bonin, P., et al. (1992). International Journal of Systematic Bacteriology, 42, 568–576.
Kuznetsov, V. D., Zaitseva, T. A., Vakulenko, L. V., & Filippova, S. N. (1992). Mikrobiologiya, 61, 84–91.
Oren, A., Gurevich, P., Azachi, M., & Henis, Y. (1992). Biodegradation, 3, 387–398.
Garcia, M. T., Ventosa, A., & Mellado, E. (2005). FEMS Microbiology, Ecology, 54, 97–109.
Cuadros-Orellana, S., Pohlschroder, M., & Durrant, L. R. (2006). International Biodeterioration and Biodegradation, 57, 151–154.
Woolard, C. R., & Irvine, R. L. (1995). Water Research, 29, 1159–1168.
Nicholson, C. A., & Fathepure, B. Z. (2004). Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 70, 1222–1225.
Liebgott, P. P., Casalot, L., Paillard, S., Lorquin, J., & Labat, M. (2006). International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology, 56, 2511–2516.
Widdel, F., & Pfennig, N. (1981). Archives of Microbiology, 129, 395–400.
Prenafeta Boldu, F. X., Vervoort, J., Grotenhuis, J. T. C., & Van Groenestijn, J. W. (2002). Substrate Interactions during the Biodegradation of Benzene, Toluene, Ethylbenzene, and Xylene (BTEX) Hydrocarbons by the Fungus Cladophialophora Sp Strain T1. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 68, 2660–2665.
Dewulf, J., Drijvers, D., & Van Langenhove, H. (1995). Atmospheric Environment, 29, 323–331.
Acunà, M. E., Perez, F., Auria, R., & Revah, S. (1999). Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 63, 175–184.
Arcangeli, J. P., & Arvin, E. (1997). Environmental Science and Technology, 31, 3044–3052.
Nicholson, C. A., & Fathepure, B. Z. (2005). FEMS Microbiology Letters, 245, 257–262.
Diaz, M. P., Boyd, K. G., Grigson, S. J. W., & Burgess, J. G. (2002). Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 79, 145–153.
Shivaji, S., Gupta, P., Chaturvedi, P., Suresh, K., & Delille, D. (2005). International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology, 55, 1453–1456.
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Drs. Pierre Roger and Laurence Casalot from IRD for their suggestions on improving the manuscript, and Ophélie Philipot and Séverine Collin for their technical assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Berlendis, S., Cayol, JL., Verhé, F. et al. First Evidence of Aerobic Biodegradation of BTEX Compounds by Pure Cultures of Marinobacter . Appl Biochem Biotechnol 160, 1992–1999 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-009-8746-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-009-8746-1