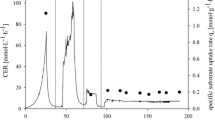
Abstract
The enzyme manganese peroxidase (MnP) is produced by numerous white-rot fungi to overcome biomass recalcitrance caused by lignin. MnP acts directly on lignin and increases access of the woody structure to synergistic wood-degrading enzymes such as cellulases and xylanases. Recombinant MnP (rMnP) can be produced in the yeast Pichia pastoris αMnP1-1 in fed-batch fermentations. The effects of pH and temperature on recombinant manganese peroxidase (rMnP) production by P. pastoris αMnP1-1 were investigated in shake flask and fed-batch fermentations. The optimum pH and temperature for a standardized fed-batch fermentation process for rMnP production in P. pastoris αMnP1-1 were determined to be pH 6 and 30 °C, respectively. P. pastoris αMnP1-1 constitutively expresses the manganese peroxidase (mnp1) complementary DNA from Phanerochaete chrysosporium, and the rMnP has similar kinetic characteristics and pH activity and stability ranges as the wild-type MnP (wtMnP). Cultivation of P. chrysosporium mycelia in stationary flasks for production of heme peroxidases is commonly conducted at low pH (pH 4.2). However, shake flask and fed-batch fermentation experiments with P. pastoris αMnP1-1 demonstrated that rMnP production is highest at pH 6, with rMnP concentrations in the medium declining rapidly at pH less than 5.5, although cell growth rates were similar from pH 4–7. Investigations of the cause of low rMnP production at low pH were consistent with the hypothesis that intracellular proteases are released from dead and lysed yeast cells during the fermentation that are active against rMnP at pH less than 5.5.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kirk, T. K., & Cullen, D. (1998). In R. A. Young & M. Akhtar (Eds.), Environmentally friendly technologies for the pulp and paper industry (pp. 273–307). New York, NY: Wiley.
Harazono, K., Kondo, R., & Sakai, K. (1996). Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 62(3), 913–917.
Gu, L., Lajoie, C. A., & Kelly, C. J. (2003). Biotechnology Progress, 19(5), 1403–1409.
Jiang, F., Kongsaeree, P., Charron, R., Lajoie, C., Xu, H., Scott, G., & Kelly, C. (2007). Biotechnology and Bioengineering (in press).
Sutherland, G. R. J., & Aust, S. D. (1996). Archives of Biochemistry and Biophysics, 332(1), 128–134.
Mielgo, I., Palma, C., Guisan, J. M., Fernandez-Lafuente, R., Moreira, M. T., Feijoo, G., et al. (2003). Enzyme and Microbial Technology, 32, 769–775.
Urek, R. O., & Pazarlioglu, N. K. (2004). Process Biochemistry, 39, 2061–2068.
Shin, K. S., Kim, Y. H., & Lim, J. S. (2005). Journal of Microbiology, 43(6), 503–509.
Baborova, P., Moder, M., Baldrian, P., Cajthamlova, K., & Cajthaml, T. (2006). Research in Microbiology, 157(3), 248–253.
Banci, L., Bartalesi, I., Ciofi-baffoni, S., Tien, M. (2003). Biopolymers, 72, 38–47.
Sreekrishna, K., Barr, K. A., Hoard, S. A., Prevatt, W. D., Torregrosa, R. E., Levingston, R. E., et al. (1990). Topic 09-37B. In S. G. Oliver & R. Wickner (Eds.), 15th International Congress on Yeast Genetics and Molecular Biology, 1990, Hague, The Netherlands. Yeast, 6(Special Issue), S447.
Jahic, M., Gustavsson, M., Jansen, A. K., Martinelle, M., & Enfors, S. O. (2003). Journal of Biotechnology, 102, 45–53.
Cassland, P., & Josson, L. J. (1999). Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 52, 393–400.
Clare, J. J., Romanos, M. A., Rayment, F. B., Rowedder, J. E., Smith, M. A., Payne, M. M., et al. (1991). Gene, 105, 205–212.
Cregg, J. M., Vedvick, T. S., & Raschke, W. C. (1993). Bio/Technology, 11, 905–910.
Jönsson, L. J., Saloheimo, M., & Penttila, M. (1997). Current Genetics, 32, 425–430.
Shi, X., Karkut, T., Chamankhah, M., Alting-Mees, M., Hemmingsen, S. M., & Hegedus, D. (2003). Protein Expression and Purification, 28(2), 321–330.
Sinha, J., Plantz, B. A., Zhang, W., Gouthro, M., Schlegel, V., Liu, C. P., et al. (2003). Biotechnology Progress, 19, 794–802.
Sinha, J., Plantz, B. A., Inan, M., & Meagher, M. M. (2004). Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 89(1),102–112.
Damasceno, L. M., Pla, I., Chang, H. J., Cohen, L., Ritter, G., Old, L. J., et al. (2004). Protein Expression and Purification, 37(1), 18–26.
Werten, M. W. T., Bosch, T. J. V. D., Wind, R. D., Mooibroek, H., & Wolf, F. A. D. (1999). Yeast, 15, 1087–1096.
Zhu, A., Monahan, C., Zhang, Z., Hurst, R., Leng, L., & Goldstein, J. (1995). Archives of Biochemistry and Biophysics, 324(1), 65–70.
Clare, J., Scorer, C., Buckholz, R., & Romanos, M. (1998). Methods in Molecular Biology, 103, 209–225.
Bencurova, M., Rendic, D., Fabini, G., Kopecky, E. M., Altmann, F., & Wilson, I. B. H. (2003). Biochimie, 85, 413–422.
Li, Z., Xiong, F., Lin, Q., d’Anjou, M., Daugulis, A. J., Yang, D. S. C., et al. (2001). Protein Expression and Purification, 21(3), 438–445.
Whittaker, M. M., & Whittaker, J. W. (2000). Protein Expression and Purification, 20(1), 105–111.
Pritchett, J., & Baldwin, S. A. (2004). Journal of Industrial Microbiology and Biotechnology, 31, 553–558.
Inan, M., Chiruvolu, V., Eskridge, K. M., Vlasuk, G. P., Dickerson, K., Brown, S., et al. (1999). Enzyme and Microbial Technology, 24, 438–445.
Ohya, T., Morita, M., Masami, M., Shinobu, K., & Kaoru, K. (2002). Journal of Bioscience and Bioengineering, 94(5), 467–473.
Saelens, X., Vanlandschoot, P., Martinet, W., Maras, M., Neirynck, S., Contreras, R., et al. (1999). European Journal of Biochemistry, 260, 166–175.
Hong, F., Meinander, N. Q., & Jönsson, L. J. (2002). Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 79, 438–449.
Sarramegna, V., Demange, P., Milon, A., & Talmont, F. (2002). Protein Expression and Purification, 24, 212–220.
Wariishi, H., Valli, K., & Gold, M. H. (1992). Journal of Biological Chemistry, 267, 23688–23695.
Tien, M., & Kirk, T. K. (1983). Science, 221(4611), 661–663.
Vasudevan, P., Padmavathy, V., & Dhingra, S. C. (2002). Bioresource Technology, 82(3), 285–289.
Wang, J., & Chen, C. (2006). Biotechnology Advances, 24(2), 427–451.
Acknowledgment
This work was supported by the National Science Foundation grants BES-0536128 and BES-0328031.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jiang, F., Kongsaeree, P., Schilke, K. et al. Effects of pH and Temperature on Recombinant Manganese Peroxidase Production and Stability. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 146, 15–27 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-007-8039-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-007-8039-5