Abstract
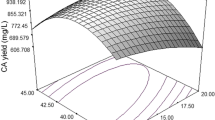
The optimization of nutrient levels for the production of pristinamycins by Streptomyces pristinaespiralis CGMCC 0957 in submerged fermentation was carried out using the statistical methodologies based on the Plackett–Burman design, the steepest ascent method, and the central composite design (CCD). First, the Plackett–Burman design was applied to evaluate the influence of related nutrients in the medium. Soluble starch and MgSO4·7H2O were then identified as the most significant nutrients with a confidence level of 99%. Subsequently, the concentrations of the two nutrients were further optimized using response surface methodology of CCD, together with the steepest ascent method. Accordingly, a second-order polynomial regression model was finally fitted to the experimental data. By solving the regression equation from the model and analyzing the response surface, the optimal levels for soluble starch and MgSO4·7H2O were determined as 20.95 and 5.67g/L, respectively. Under the optimized medium, the yield of pristinamycins in the shake flask and 5-L bioreactor could reach 1.30 and 1.01g/L, respectively, which is the highest yield reported in literature to date.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kumazawa, J., & Yagisawa, M. (2002). Journal of Infection and Chemotherapy, 8, 125–133.
National Academy of Sciences, Institute of Medicine (1998). Forum on emerging infections. Washington, DC: NAS.
Preud’Homme, J., Tarridec, P., & Belloc, A. (1986). Bulletin de la Societe Chimique de France, 2, 586–591.
Ng, J., & Gosbell, I. B. (2005). Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy, 55, 1008–1012.
Paris, J. M., Barrière, J. C., Smith, C., & Bost, P. E. (1990). In recent progress in the synthesis of Antibiotics pp. (pp. 185–245). Heidelberg, Berlin:: Springer.
Qadri, S. M. H., Ueno, Y., Mostafa, F. M. A., & Halim, M. (1997). Chemotherapy, 43, 94–99.
Abdel-Hamid, M. E., & Phillips, O. A. (2003). Journal of Pharmaceutical and Biomedical Analysis, 32, 1167–1174.
Blanc, V., Gil, P., Bamas-Jacques, N., Lorenzon, S., Zagorec, M., & Schleuniger, J., et al. (1997). Molecular Microbiology, 23, 191–202.
Hopwood, D. (1997). Nature Biotechnology, 15, 321.
Bamas-Jacques, N., Lorenzon, S., Lacroix, P., de Swetschin, C., & Crouzet, J. (1999). Journal of Applied Microbiology, 87, 939–948.
Paquet, V., Goma, G., & Soucaille, P. (1992). Biotechnology Letters, 14, 1065–1070.
Corvini, P. F. X., Gautier, H., Rondags, E., Vivier, H., Goergen, J. L., & Germain, P. (2000). Microbiology, 146, 2671–2678.
Francois, V., & Stephane, A. (2001). Microbiology, 147, 2447–2459.
Corvini, P. F. X., Delaunay, S., Maujean, F., Rondags, E., Vivier, H., & Goergen, J. L., et al. (2004). Enzyme and Microbial Technology, 34, 101–107.
Kennedy, M., & Krouse, D. (1999). Journal of Industrial Microbiology & Biotechnology, 23, 456–475.
Jin, Z. H. (2001). PhD thesis, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou, China.
Reddy, P. R. M., Ramesh, B., Mrudula, S., Reddy, G., & Seenayya, G. (2003). Process Biochemistry, 39, 267–277.
Chen, X., Wang, J. H., & Li, D. S. (2007). Biochemical Engineering Journal, 34, 179–184.
Kalil, S. J., Maugeri, F., & Rodrigues, M. I. (2000). Process Biochemistry, 35, 539–550.
Silva, C. J. S. M., Gübitz, G., & Cavaco-Paulo, A. (2006). Journal of Chemical Technology and Biotechnology, 81, 8–16.
Chen, X., Chen, S. W., Sun, M., & Yu, Z. N. (2005). Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 69, 390–396.
Sharma, D. C., & Satyanarayana, T. (2006). Bioresource Technology, 97, 727–733.
Gouda, M. D., Thakur, M. S., & Karanth, N. G. (2001). World Journal of Microbiology & Biotechnology, 17, 595–600.
Bogar, B., Szakacs, G., Pandey, A., Adulhameed, S., Linden, J. C., & Tengerdy, R. P. (2003). Biotechnology Progress, 19, 312–319.
Vaidya, R., Vyas, P., & Chhatpr, H. S. (2003). Enzyme and Microbial Technology, 33, 92–96.
Himabindu, M., Ravichandra, P., Vishalakshi, K., & Jetty, A. (2006). Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 134, 143–154.
Jin, Z. H., Lei, Y. L., Lin, J. P., & Cen, P. L. (2006). World Journal of Microbiology & Biotechnology, 22, 129–134.
Jia, B., Jin, Z. H., Lei, Y. L., Mei, L. H., & Li, N. H. (2006). Biotechnology Letters, 28, 1811–1815.
Plackett, R. L., & Burman, J. P. (1946). Biometals, 33, 305–325.
Reddy, P. R. M., Mrudula, S., Ramesh, B., Reddy, G., & Seenayya, G. (2000). Bioprocess Engineering, 23, 107–112.
Naveena, B. J., Altaf, M., Bhadriah, K., & Reddy, G. (2005). Bioresource Technology, 96, 485–490.
Box, G. E. P., Hunter, W. G., & Hunter, J. S. (1978). Statistics for experimenters.. New York: Wiley.
Chen, Q. H., He, G. Q., & Mokhtar, A. M. A. (2002). Enzyme and Microbial Technology, 30, 667–672.
Xiong, Z. G. (1995). Principles of fermentative techniques. Beijing, China: Medicine Technological.
Paquet, V., Myint, M., & Roque, C. (1994). Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 44, 445–451.
Acknowledgments
This work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (20576122), Department of Science and Technology, Zhejiang Province, China (2004C13007), and the Natural Science Foundation of Zhejiang Province, China (Y404291).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jia, B., Jin, Z.H. & Mei, L.H. Medium Optimization Based on Statistical Methodologies for Pristinamycins Production by Streptomyces pristinaespiralis . Appl Biochem Biotechnol 144, 133–143 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-007-8012-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-007-8012-3