Abstract
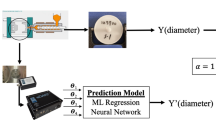
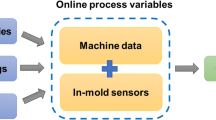
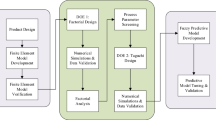
Using different raw material in injection molding could happen in situations where the original material becomes unavailable, material cost rises, or in response to customer demands. However, applying different materials on the same mold often leads to excessive dimensional deviation, causing quality degradation. To reduce defect rate and circumvent high cost expenditure on new molds, this paper presents an experimental framework aiming to implement process optimization efficiently and attain a predictable level for the quality characteristics. The methodology starts from a Taguchi experimental design where process parameters including both controllable factors and uncontrollable factors were arranged into an orthogonal array. Driven by its efficiency, Taguchi method was able to produce optimal process parameter levels that significantly improved the process capability. Subsequently, data collected by an in-mold sensing system was analyzed to extract the contribution from in-mold process variables that are not externally accessible. In order to quantitatively rank the impacts from in-mold process variables, a multiple linear regression (MLR) were performed with top influential factors identified. The selected influential variables allowed for the quality characteristic to be predicted through a fuzzy logic based predictive model. In conclusion, the methodology presented in this paper has the potential of reducing or eliminating defect rate caused by material variation, and at the same time allows dimension prediction of injection molded parts with real time sensed in-mold conditions.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kalpakjian, S., Schmid, S.: Manufacturing engineering and technology, 8th Edition, Pearson, (2020)
Kazmer D. O.: Injection mold design engineering, 2nd Edition, Hanser Fachbuchverlag (2016)
He, X., Wu, W.: A practical numerical approach to characterizing non-linear shrinkage and optimizing dimensional deviation of injection-molded small module plastic gears. Polymers 13(13), 2092 (2021)
Song, Z., Liu, S., Wang, X., Hu, Z.: Optimization and prediction of volume shrinkage and warpage of injection-molded thin-walled parts based on neural network. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 109(3–4), 755–769 (2020)
Chang, R.-Y., Yang, W.-H.: Numerical simulation of mold filling in injection molding using a three-dimensional finite volume approach. Int. J. Numer. Meth. Fluids 37, 125–148 (2001)
Hétu, J.-F., Gao, D.M., Garcia-Rejon, A., Salloum, G.: 3D finite element method for the simulation of the filling stage in injection molding. Polym. Eng. Sci. 38, 223–236 (1998)
Ilinca, F., Hétu, J.-F.: Finite element solution of three-dimensional turbulent flows applied to mold-filling problems. Int. J. Numer. Meth. Fluids 34, 729–750 (2000)
Mavridis, H., Hrymak, A.N., Vlachopoulos, J.: Finite element simulation of fountain flow in injection molding. Polym Eng Sci 26, 449–454 (1986)
Zhou, J., Turng, L.-S.: Three-dimensional numerical simulation of injection mold filling with a finite-volume method and parallel computing. Adv. Polym. Technol. 25, 247–258 (2006)
Johnston, S.P., Kazmer, D.O., Gao, R.X.: Online simulation-based process control for injection molding. Polym. Eng. Sci. 49(12), 2482–2491 (2009)
Guo, G., Li, Y., Zhao, X., Rizvi, R.: Tensile and longitudinal shrinkage behaviors of polylactide/wood-fiber composites via direct injection molding. Polym. Compos. 41, 4663–4677 (2020)
Mukras, S.M.S.: Experimental-based optimization of injection molding process parameters for short product cycle time. Adv. Polym. Technol. 2020, 1–15 (2020)
Azdast, Taher; Hasanzadeh, Rezgar, Experimental assessment and optimization of shrinkage behavior of injection molded polycarbonate parts, Materials Research Express, 2019, Vol.6(11), p.115334
Lin, C.-M., Chen, W.-C.: Optimization of injection-molding processing conditions for plastic double-convex Fresnel lens using grey-based Taguchi method. Microsyst. Technol. 26(8), 2575–2588 (2020)
Usman, J.Q.M., Habib, T., Noor, S., Abas, M., Azim, S., Yaseen, Q.M., Pham, D.: Multi response optimization of injection moulding process parameters of polystyrene and polypropylene to minimize surface roughness and shrinkage’s using integrated approach of S/N ratio and composite desirability function. Cogent Eng 7(1), 1781424 (2020)
Chen, J.C., Guo, G., Wang, W.N.: Artificial neural network based online defect detection system with in mold temperature and pressure sensors for high precision injection molding. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 110, 2023–2033 (2020)
Abdul, R., Guo, G., Chen, J.C., Yoo, J.J.-W.: Shrinkage prediction of injection molded high density polyethylene parts with taguchi/artificial neural network hybrid experimental design. Int. J. Interact. Design Manuf. (IJIDeM) 14(2), 345–357 (2020)
Liao, S.J., Hsieh, W.H., Wang, J.T., Su, Y.C.: Shrinkage and warpage prediction of injection-molded thin-wall parts using artificial neural networks. Polym. Eng. Sci. 44(11), 2029–2040 (2004)
Wang, R., Zeng, J., Feng, X., Xia, Y.: Evaluation of effect of plastic injection molding process parameters on shrinkage based on neural network simulation. J. Macromol. Sci. 52(1), 206–221 (2013)
Lee, S.C., Youn, J.R.: Shrinkage analysis of molded parts using neural network. J. Reinf. Plastic. Compos. 18(2), 186–195 (1999)
Lotti, C., Ueki, M.M., Bretas, R.E.S.: Prediction of the shrinkage of injection molded iPP plaques using artificial neural networks. J. Inject. Mold. Technol. 6(3), 157–176 (2002)
Xu, G., Yang, Z.-T., Long, G.-D.: Multi-objective optimization of MIMO plastic injection molding process conditions based on particle swarm optimization. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 58(5–8), 521–531 (2012)
Cao, Y., Fan, X., Guo, Y., Li, S., Huang, H.: Multi-objective optimization of injection-molded plastic parts using entropy weight, random forest, and genetic algorithm methods. J. Polym. Eng. 40(4), 360–371 (2020)
Farahani, S., Brown, N., Loftis, J., Krick, C., Pichl, F., Vaculik, R., Pilla, S.: Evaluation of in-mold sensors and machine data towards enhancing product quality and process monitoring via Industry 4. 0. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 105(1–4), 1371–1389 (2019)
Ageyeva, T., Horváth, S., Kovács, J.G.: In-mold sensors for injection molding: on the way to industry 4. 0. Sensors 9(16), 3551 (2019)
Chen, J.-Y., Yang, K.-J., Huang, M.-S.: Online quality monitoring of molten resin in injection molding. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 122, 681–693 (2018)
Hopmann, C., Heinisch, J.: Process control strategies for injection molding processes with changing raw material viscosity. J. Polym. Eng. 38(5), 483–492 (2018)
Nam, J.S., Na, C.R., Jo, H.H., Song, J.Y., Ha, T.H., Lee, S.W.: Injection-moulded lens form error prediction using cavity pressure and temperature signals based on k-fold cross validation. Proceed. Inst. Mech. Eng., Part B: J. Eng. Manuf. 232(5), 928–934 (2018)
Zhang, J.Z., Chen, J.C., Kirby, D.E.: Surface roughness optimization in an end-milling operation using the Taguchi design method. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 184(1–3), 233–239 (2007)
Kuram, E., Ozcelik, B.: Optimization of machining parameters during micro-milling of Ti6Al4V titanium alloy and Inconel 718 materials using Taguchi method. Proceed. Inst. Mech. Eng., Part B: J. Eng. Manuf. 231(2), 228–242 (2015)
Kim, N.P., Cho, D., Zielewski, M.: Optimization of 3D printing parameters of Screw Type Extrusion (STE) for ceramics using the Taguchi method. Ceramics Int 45, 2351–2360 (2019)
Dong, G., Wijaya, G., Tang, Y., Zhao, Y.F.: Optimizing process parameters of fused deposition modeling by Taguchi method for the fabrication of lattice structures. Addit. Manuf. 19, 62–72 (2018)
Jiang, H.-Z., et al.: Factor analysis of selective laser melting process parameters with normalised quantities and Taguchi method. Opt. Laser Technol. 119, 105592 (2019)
Fotovvati, B., Balasubramanian, M., Asadi, E.: Modeling and Optimization approaches of laser-based powder-bed fusion process for Ti-6Al-4V alloy. Coatings 10(11), 1104–1129 (2020)
Aravind, S.S., Razmi, J., Mian, M.J., Ladani, L.: Mechanical anisotropy and surface roughness in additively manufactured parts fabricated by stereolithography (SLA) using statistical analysis. Materials 13(11), 2496 (2020)
Guerra, A.J., et al.: Optimization of photocrosslinkable resin components and 3D printing process parameters. Acta Biomater. 97, 154–161 (2019)
Jelokhani, N.R., Fazli, A., Soltanpour, M.: Electromagnetically activated high-speed hydroforming process: a novel process to overcome the limitations of the electromagnetic forming process. CIRP J. Manuf. Sci. Technol. 27, 21–30 (2019)
Ye, Li., Travis, R.: Capability study of 2D Heat-assisted Mill-bend process. Int. J. Interact. Design Manuf. 14, 759–772 (2020)
Chen, J.C., Li, Ye., Cox, R.A.: Taguchi-based six sigma approach to optimize plasma cutting process: an industrial case study. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 41, 760–769 (2009)
Gani, A., Ion, W., Yang, E.: Experimental investigation of plasma cutting two separate thin steel sheets simultaneously and parameters optimisation using taguchi approach. J. Manuf. Process. 64, 1013–1023 (2021)
Fischer, J. M., Handbook of Molded Part Shrinkage and Warpage, William Andrew Publishing, (2013)
Kirby, E.D., Chen, J.C.: Development of a fuzzy-nets-based surface roughness prediction system in turning operations. Comput Ind Eng 53, 30–42 (2007)
Chen, J.C., Black, J.T.: A fuzzy-nets in-process (FNIP) system for tool-breakage monitoring in end-milling operations. Int J Mach Tools Manuf 37(6), 783–880 (1997)
Yang, L.D., Chen, J., Chow, H.M.: Fuzzy-nets-based in-process surface roughness adaptive control system in end-milling operations. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 28, 236–248 (2006)
Hua, Y., Choi, J.: Adaptive direct metal/material deposition process using a fuzzy logic-based controller. J. Laser Appl. 17, 200 (2005)
Yongzhe, Li., Xinlei, Li., Guangjun, Z., Imre, H., Qinglin, H.: Interlayer closed-loop control of forming geometries for wire and arc additive manufacturing based on fuzzy-logic inference. J. Manuf. Process. 63, 35–47 (2021)
Hoi-Pang, T., Furong, G.: Control of injection velocity using a fuzzy logic rule-based controller for thermoplastics injection molding. Polym. Eng. Sci. 39(1), 3–17 (1999)
Huang, S.-J., Lee, T.-H.: Fuzzy logic controller for a retrofitted closed-loop injection moulding machine. Proceed. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part I J. Syst. Control Eng. 214(1), 9–22 (2000)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Y., Chen, J.C. & Ali, W.M. Process optimization and in-mold sensing enabled dimensional prediction for high precision injection molding. Int J Interact Des Manuf 16, 997–1013 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12008-021-00800-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12008-021-00800-1