Abstract
Background
Prosthetic replacement is the most commonly used option for reconstruction of osteoarticular bone loss resulting from bone neoplasm resection or prosthetic failure. Starting in late 2001, we began exclusively using a single system for large-segment osteoarticular reconstruction after tumor resection; to our knowledge, there are no published series from one center evaluating the use of this implant.
Questions/purposes
We investigated the following issues: (1) What is the overall survival, excluding local tumor recurrence, for these endoprostheses used for tumor reconstructions of the lower extremities (knee and hip)? (2) What types of failure were observed in these reconstructions? (3) Do the survival and complications vary according to site of implant?
Methods
Between September 2001 and March 2012, we exclusively used this implant for tumor reconstructions. During that time, 278 patients underwent tumor reconstructions of the hip or knee, of whom 200 (72%) were available at a minimum 2 years followup. Seventy-eight patients were excluded from the study for insufficient followup as a result of early death (42) or loss at followup (36). The reconstruction types were the following: proximal femur (69 cases), distal femur (87), proximal tibia (32), and total knee (12). Failures were classified according to the Henderson classification. Nine patients among those with followup shorter than 2 years had presented one or more failures and they were included in our analysis but separately evaluated.
Results
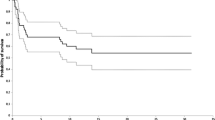
Overall survival (no further surgical procedures of any type after primary surgery), excluding Type 5 failure (tumor recurrence), was 75.9% at 5 years and 66.2% at 10 years. Seventy-one failures occurred in 58 implants (29%). Mechanical failures accounted for 59.2% and nonmechanical failures for 40.8%. The first causes of failure of the implants were the result of soft tissue failure in 6%, aseptic loosening in 3%, structural failure in 7%, infection in 8.5%, and tumor recurrence in 4.5% of the whole series. Nine implants sustained two or more failures. Overall incidence of infection was 9.5%. No statistically significant differences were observed according to anatomical site.
Conclusions
Like in the case with many such complex oncologic reconstructions, the failure rate at short- to midterm in this group was over 20%. Comparative trials are called for to ascertain whether one implant is superior to another. Infection and structural failure were the most frequent modes of failure in our experience.
Level of Evidence
Level IV, therapeutic study. See Instructions for Authors for a complete description of levels of evidence.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahlmann ER, Menendez LR, Kermani C, Gotha H. Survivorship and clinical outcome of modular endoprosthetic reconstruction for neoplastic disease of the lower limb. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2006;88:790–795.
Benedetti MG, Bonatti E, Malfitano C, Donati D. Comparison of allograft-prosthetic composite reconstruction and modular prosthetic replacement in proximal femur bone tumors: functional assessment by gait analysis in 20 patients. Acta Orthop. 2013;84:218–223.
Berry DJ, Harmsen WS, Cabanela ME, Morrey BF. Twenty-five-year survivorship of two thousand consecutive primary Charnley total hip replacements: factors affecting survivorship of acetabular and femoral components. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2002;84:171–177.
Biau D, Faure F, Katsahian S, Jeanrot C, Tomeno B, Anract P. Survival of total knee replacement with a megaprosthesis after bone tumor resection. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2006;88:1285–1293.
Capanna R, Scoccianti G, Campanacci DA, Beltrami G, De Biase P. Surgical technique: extraarticular knee resection with prosthesis-proximal tibia-extensor apparatus allograft for tumors invading the knee. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2011;469:2905–2914.
Dean BJ, Matthews JJ, Price A, Stubbs D, Whitwell D, Gibbons CM. Modular endoprosthetic replacement for failed internal fixation of the proximal femur following trauma. Int Orthop. 2012;36:731–734.
Donati D, Colangeli M, Colangeli S, Di Bella C, Mercuri M. Allograft-prosthetic composite in the proximal tibia after bone tumor resection. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2008;466:459–465.
Donati D, Giacomini S, Gozzi E, Mercuri M. Proximal femur reconstruction by an allograft prosthesis composite. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2002;394:192–200.
Donati D, Zavatta M, Gozzi E, Giacomini S, Campanacci L, Mercuri M. Modular prosthetic replacement of the proximal femur after resection of a bone tumour: a long-term follow-up. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2001;83:1156–1160.
Flint MN, Griffin AM, Bell RS, Ferguson PC, Wunder JS. Aseptic loosening is uncommon with uncemented proximal tibia tumor prostheses. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2006;450:52–59.
Font-Rodriguez DE, Scuderi GR, Insall JN. Survivorship of cemented total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1997;345:79–86.
Frink SJ, Rutledge J, Lewis VO, Lin PP, Yasko AW. Favorable long-term results of prosthetic arthroplasty of the knee for distal femur neoplasms. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2005;438:65–70.
Funovics P, Hipfl C, Hofstaetter J, Puchner S, Kotz R, Dominkus M. Management of septic complications following modular endoprosthetic reconstruction of the proximal femur. Int Orthop. 2011;35:1437–1444.
Gebert C, Wessling M, Götze C, Gosheger G, Hardes J. The Modular Universal Tumour and Revision System (MUTARS) in endoprosthetic revision surgery. Int Orthop. 2010;34:1261–1265.
Gilbert NF, Yasko AW, Oates SD, Lewis VO, Cannon CP, Lin PP. Allograft-prosthetic composite reconstruction of the proximal part of the tibia. An analysis of the early results. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2009;91:1646–1656.
Gosheger G, Gebert C, Ahrens H, Streitbuerger A, Winkelmann W, Hardes J. Endoprosthetic reconstruction in 250 patients with sarcoma. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2006;450:164–171.
Griffin AM, Parsons JA, Davis AM, Bell RS, Wunder JS. Uncemented tumor endoprostheses at the knee: root causes of failure. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2005;438:71–79.
Grimer RJ, Carter SR, Tillman RM, Sneath RS, Walker PS, Unwin PS, Shewell PC. Endoprosthetic replacement of the proximal tibia. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1999;81:488–494.
Guo W, Ji T, Yang R, Tang X, Yang Y. Endoprosthetic replacement for primary tumours around the knee: experience from Peking University. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2008;90:1084–1089.
Hardes J, Henrichs MP, Gosheger G, Gebert C, Höll S, Dieckmann R, Hauschild G, Streitbürger A. Endoprosthetic replacement after extra-articular resection of bone and soft-tissue tumours around the knee. Bone Joint J. 2013;95:1425–1431.
Healey JH, Morris CD, Athanasian EA, Boland PJ. Compress knee arthroplasty has 80% 10-year survivorship and novel forms of bone failure. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2013;471:774–783.
Henderson ER, Groundland JS, Pala E, Dennis JA, Wooten R, Cheong D, Windhager R, Kotz RI, Mercuri M, Funovics PT, Hornicek FJ, Temple HT, Ruggieri P, Letson GD. Failure mode classification for tumor endoprostheses: retrospective review of five institutions and a literature review. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2011;93:418–429.
Hwang JS, Mehta AD, Yoon RS, Beebe KS. From amputation to limb salvage reconstruction: evolution and role of the endoprosthesis in musculoskeletal oncology. J Orthop Traumatol. 2013 Sep 22 [Epub ahead of print].
Jeys LM, Grimer RJ, Carter SR, Tillman RM. Periprosthetic infection in patients treated for an orthopaedic oncological condition. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2005;87:842–849.
Jeys LM, Kulkarni A, Grimer RJ, Carter SR, Tillman RM, Abudu A. Endoprosthetic reconstruction for the treatment of musculoskeletal tumors of the appendicular skeleton and pelvis. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2008;90:1265–1271.
Mittermayer F, Windhager R, Dominkus M, Krepler P, Schwameis E, Sluga M, Kotz R, Strasser G. Revision of the Kotz type of tumour endoprosthesis for the lower limb. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2002;84:401–406.
Morii T, Morioka H, Ueda T, Araki N, Hashimoto N, Kawai A, Mochizuki K, Ichimura S. Deep infection in tumor endoprosthesis around the knee: a multi-institutional study by the Japanese musculoskeletal oncology group. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2013;14:51.
Morgan HD, Cizik AM, Leopold SS, Hawkins DS, Conrad EU 3rd. Survival of tumor megaprostheses replacements about the knee. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2006;450:39–45.
Myers GJ, Abudu AT, Carter SR, Tillman RM, Grimer RJ. The long-term results of endoprosthetic replacement of the proximal tibia for bone tumours. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2007;89:1632–1637.
Ogilvie CM, Wunder JS, Ferguson PC, Griffin AM, Bell RS. Functional outcome of endoprosthetic proximal femoral replacement. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2004;426:44–48.
Pala E, Henderson ER, Calabrò T, Angelini A, Abati CN, Trovarelli G, Ruggieri P. Survival of current production tumor endoprostheses: complications, functional results, and a comparative statistical analysis. J Surg Oncol. 2013;108:403–408.
Parvizi J, Tarity TD, Slenker N, Wade F, Trappler R, Hozack WJ, Sim FH. Proximal femoral replacement in patients with non-neoplastic conditions. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2007;89:1036–1043.
Schwartz AJ, Kabo JM, Eilber FC, Eilber FR, Eckardt JJ. Cemented distal femoral endoprostheses for musculoskeletal tumor. Improved survival of modular versus custom implants. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2010;468:2198–2210.
Shehadeh A, Noveau J, Malawer M, Henshaw R. Late complications and survival of endoprosthetic reconstruction after resection of bone tumors. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2010;468:2885–2895.
Soderman P, Malchau H, Herberts P. Outcome after total hip arthroplasty: part I. General health evaluation in relation to definition of failure in the Swedish National Total Hip Arthroplasty register. Acta Orthop Scand. 2000;71:354–359.
Walenkamp MM, Roes KC, Bhandari M, Goslings JC, Schep NW. Multiple testing in orthopedic literature: a common problem? BMC Research Notes. 2013;6:374–378.
Zeegen EN, Aponte-Tinao LA, Hornicek FJ, Gebhardt MC, Mankin HJ. Survivorship analysis of 141 modular metallic endoprostheses at early followup. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2004;420:239–250.
Zehr RJ, Enneking WF, Scarborough MT. Allograft-prosthesis composite versus megaprosthesis in proximal femoral reconstruction. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1996;322:207–223.
Acknowledgments
We thank M. J. Ceglia MD, for his kind contribution in revising the English version of the paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
One or more of the authors (RC, DAC) certify that they have or may receive payments or benefits, during the study period, an amount of USD 10,000 to USD 100.000 from Waldemar Link (Hamburg, Germany).
All ICMJE Conflict of Interest Forms for authors and Clinical Orthopaedics and Related Research ® editors and board members are on file with the publication and can be viewed on request.
Clinical Orthopaedics and Related Research ® neither advocates nor endorses the use of any treatment, drug, or device. Readers are encouraged to always seek additional information, including FDA-approval status, of any drug or device prior to clinical use.
Each author certifies that his or her institution approved the human protocol for this investigation, that all investigations were conducted in conformity with ethical principles of research, and that informed consent for participation in the study was obtained.
About this article
Cite this article
Capanna, R., Scoccianti, G., Frenos, F. et al. What Was the Survival of Megaprostheses in Lower Limb Reconstructions After Tumor Resections?. Clin Orthop Relat Res 473, 820–830 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11999-014-3736-1
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11999-014-3736-1