Abstract
Background
Hip resurfacing arthroplasty (HRA) could be associated with an increased risk of deep vein thrombosis (DVT) compared to traditional noncemented THA because it involves greater dissection, increased kinking and distortion of the femoral vessels, takes longer to perform, and involves insertion of some cement into the femur.
Questions/purposes
Does HRA lead to greater risk of thromboembolism compared with noncemented THA?
Methods
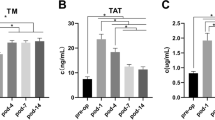
We prospectively studied 20 patients receiving HRA and 20 receiving THA. All patients were younger than 67 years old and were similar in height, weight, American Society of Anesthesiologists status, and gender mix. Patients undergoing HRA were younger (mean, 50 versus 59 years), their surgery was longer (mean, 87 versus 65 minutes), and they required more crystalloid during surgery (mean, 2160 versus 1662 mL). Radial artery blood samples were taken at six events during surgery and assayed for prothrombin fragment F1 + 2 and thrombin-antithrombin III complex (TAT) using enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays.
Results
We observed no differences in the intraoperative increases in F1 + 2 and TAT between the two groups and no differences in surgical events.
Conclusion
Based on these data, HRA and THA should have similar risk of thromboembolism as THA based on the parameters we measured.
Level of Evidence
Level I, diagnostic study. See Guidelines for Authors for a complete description of levels of evidence.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aglietti P, Baldini A, Vena LM, Abbate R, Fedi S, Falciani M. Effect of tourniquet use on activation of coagulation in total knee replacement. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2000;371:169–177.
Andersen BS. Postoperative activation of the haemostatic system—influence of prolonged thromboprophylaxis in patients undergoing total hip arthroplasty. Haemostasis. 1997;27:219–227.
Arnesen H, Dahl OE, Aspelin T, Seljeflot I, Kierulf P, Lyberg T. Sustained prothrombotic profile after hip replacement surgery: the influence of prolonged prophylaxis with dalteparin. J Thromb Haemost. 2003;1:971–975.
Berman AT, Parmet JL, Harding SP, Israelite CL, Chandrasekaran K, Horrow JC, Singer R, Rosenberg H. Emboli observed with use of transesophageal echocardiography immediately after tourniquet release during total knee arthroplasty with cement. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1998;80:389–396.
Cofrancesco E, Cortellaro M, Corradi A, Ravasi F, Bertocchi F. Coagulation activation markers in the prediction of venous thrombosis after elective hip surgery. Thromb Haemost. 1997;77:267–269.
Corradi A, Lazzaro F, Cofrancesco E, Cortellaro M, Ravasi F, Bertocchi F. Preoperative plasma levels of prothrombin fragment 1 + 2 correlate with the risk of venous thrombosis after elective hip replacement. Acta Orthop Belg. 1999;65:39–43.
Cutts S, Carter PB. Hip resurfacing: a technology reborn. Postgrad Med J. 2006;82:802–805.
Dahl OE. The role of the pulmonary circulation in the regulation of coagulation and fibrinolysis in relation to major surgery. J Cardiothorac Vasc Anesth. 1997;11:322–328.
Daniel J, Pradhan A, Pradhan C, Ziaee H, Moss M, Freeman J, McMinn DJ. Multimodal thromboprophylaxis following primary hip arthroplasty: the role of adjuvant intermittent pneumatic calf compression. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2008;90:562–569.
Fedi S, Gori AM, Falciani M, Cellai AP, Aglietti P, Baldini A, Vena LM, Prisco D, Abbate R, Gensini GF. Procedure-dependence and tissue factor-independence of hypercoagulability during orthopaedic surgery. Thromb Haemost. 1999;81:874–878.
Ginsberg JS, Brill-Edwards P, Panju A, Patel A, McGinnis J, Smith F, Dale I, Johnston M, Ofosu F. Pre-operative plasma levels of thrombin-antithrombin III complexes correlate with the development of venous thrombosis after major hip or knee surgery. Thromb Haemost. 1995;74:602–605.
Gonzalez Della Valle A, Serota A, Go G, Sorriaux G, Sculco TP, Sharrock NE, Salvati EA. Venous thromboembolism is rare with a multimodal prophylaxis protocol after total hip arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2006;444:146–153.
Kageyama K, Nakajima Y, Shibasaki M, Hashimoto S, Mizobe T. Increased platelet, leukocyte, and endothelial cell activity are associated with increased coagulability in patients after total knee arthroplasty. J Thromb Haemost. 2007;5:738–745.
Katsumata S, Nagashima M, Kato K, Tachihara A, Wauke K, Saito S, Jin E, Kawanami O, Ogawa R, Yoshino S. Changes in coagulation-fibrinolysis marker and neutrophil elastase following the use of tourniquet during total knee arthroplasty and the influence of neutrophil elastase on thromboembolism. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. 2005;49:510–516.
Lieberman JR, Huo MH, Hanway J, Salvati EA, Sculco TP, Sharrock NE. The prevalence of deep venous thrombosis after total hip arthroplasty with hypotensive epidural anesthesia. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1994;76:341–348.
Lowe GD, Haverkate F, Thompson SG, Turner RM, Bertina RM, Turpie AG, Mannucci PM. Prediction of deep vein thrombosis after elective hip replacement surgery by preoperative clinical and haemostatic variables: the ECAT DVT Study. European Concerted Action on Thrombosis. Thromb Haemost. 1999;81:879–886.
Peternel P, Terbizan M, Tratar G, Bozic M, Horvat D, Salobir B, Stegnar M. Markers of hemostatic system activation during treatment of deep vein thrombosis with subcutaneous unfractionated or low-molecular weight heparin. Thromb Res. 2002;105:241–246.
Pitto RP, Blunk J, Kossler M. Transesophageal echocardiography and clinical features of fat embolism during cemented total hip arthroplasty. A randomized study in patients with a femoral neck fracture. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2000;120:53–58.
Pitto RP, Hamer H, Heiss-Dunlop W, Kuehle J. Mechanical prophylaxis of deep-vein thrombosis after total hip replacement a randomised clinical trial. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2004;86:639–642.
Planes A, Vochelle N, Fagola M. Total hip replacement and deep vein thrombosis. A venographic and necropsy study. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1990;72:9–13.
Ranawat CS, Beaver WB, Sharrock NE, Maynard MJ, Urquhart B, Schneider R. Effect of hypotensive epidural anaesthesia on acetabular cement-bone fixation in total hip arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1991;73:779–782.
Salvati EA, Pellegrini VD, Jr., Sharrock NE, Lotke PA, Murray DW, Potter H, Westrich GH. Recent advances in venous thromboembolic prophylaxis during and after total hip replacement. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2000;82:252–270.
Sharrock NE, Go G, Harpel PC, Ranawat CS, Sculco TP, Salvati EA. Thrombogenesis during total hip replacement. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1995;319:16–27.
Sharrock NE, Go G, Sculco TP, Salvati EA, Westrich GH, Harpel PC. Dose response of intravenous heparin on markers of thrombosis during primary total hip replacement. Anesthesiology. 1999;90:981–987.
Sharrock NE, Go G, Williams-Russo P, Haas SB, Harpel PC. Comparison of extradural and general anaesthesia on the fibrinolytic response to total knee arthroplasty. Br J Anaesth. 1997;79:29–34.
Sharrock NE, Gonzalez Della Valle A, Go G, Lyman S, Salvati EA. Potent anticoagulants are associated with a higher all-cause mortality rate after hip and knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2008;466:714–721.
Sharrock NE, Salvati EA. Hypotensive epidural anesthesia for total hip arthroplasty. Acta Orthop Scand. 1996;67:91–107.
Turpie AG, Lassen MR, Davidson BL, Bauer KA, Gent M, Kwong LM, Cushner FD, Lotke PA, Berkowitz SD, Bandel TJ, Benson A, Misselwitz F, Fisher WD. Rivaroxaban versus enoxaparin for thromboprophylaxis after total knee arthroplasty (RECORD4): a randomised trial. Lancet. 2009;373:1673–1680.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Each author certifies that he or she has no commercial associations (eg, consultancies, stock ownership, equity interest, patent/licensing arrangements, etc) that might pose a conflict of interest in connection with the submitted article.
Each author certifies that his or her institution approved the human protocol for this investigation, that all investigations were conducted in conformity with ethical principles of research, and that informed consent for participation in the study was obtained.
This work was performed at the Hospital for Special Surgery, New York, NY, USA.
About this article
Cite this article
Su, E.P., Chatzoudis, N., Sioros, V. et al. Markers of Thrombin Generation During Resurfacing and Noncemented Total Hip Arthroplasty: A Pilot Study. Clin Orthop Relat Res 469, 535–540 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11999-010-1659-z
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11999-010-1659-z