Abstract
Background
Cervical spondylotic myelopathy is increasingly prevalent in the elderly and is the leading cause of spinal cord dysfunction in this population. Laminectomy with fusion and laminoplasty halt progression of myelopathy in these patients; however, both procedures have well-documented complications and associated morbidity and it is unclear which might be most advantageous.
Questions/purposes
We therefore compared the pain, function and alignment of patients who underwent laminectomy with fusion to those with laminoplasty for the treatment of multilevel cervical spondylotic myelopathy.
Methods
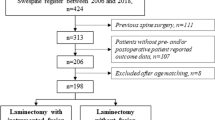
We performed a retrospective matched cohort analysis on all 121 patients from 2002 to 2007 who underwent laminectomy with fusion (82) or laminoplasty (39) for multilevel cervical spondylotic myelopathy. We determined change in preoperative and postoperative sagittal alignment using Cobb measurement, development of junctional stenosis, and subjective improvements in pain and gait. Complications were recorded for both cohorts.
Results
The majority of patients in both cohorts reported improvements in pain and gait postoperatively. There were seven complications in the laminectomy and fusion cohort (9%) with two patients requiring formal revision surgery (2%). There were five complications in the laminoplasty cohort (13%) with two formal revision procedures (5%).
Conclusions
Patients in both the laminectomy with fusion and laminoplasty cohorts reported similar functional improvements after treatment for cervical spondylotic myelopathy. Prospective randomized control trials are needed to determine whether one procedure is truly superior.
Level of Evidence
Level IV, therapeutic study. See Guidelines for Authors for a complete description of levels of evidence.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baba H, Uchida K, Maezawa Y, Furusawa N, Azuchi M, Imura S. Lordotic alignment and posterior migration of the spinal cord following en bloc open-door laminoplasty for cervical myelopathy: a magnetic resonance imaging study. J Neurol. 1996;243:626–632.
Bucciero A, Vizioli L, Carangelo B, Tedeschi G. MR signal enhancement in cervical spondylotic myelopathy: correlation with surgical results in 35 cases. J Neurosurg Sci. 1993;37:217–222.
Butler JC, Whitecloud TS. Postlaminectomy kyphosis: causes and surgical management. Orthop Clin North Am. 1992;23:505–511.
Cherubino P, Benazzo F, Borromeo U, Perle S. Degenerative arthritis of the adjacent spinal joints following anterior cervical spinal fusion: clinicoradiologic and statistical correlations. Ital J Orthop Traumatol. 1990;16:533–543.
Clarke E, Robinson PK. Cervical myelopathy: a complication of cervical spondylosis. Brain. 1956;79:483–510.
Dai L, Ni B, Yuan W, Jia L. Radiculopathy after laminectomy for cervical compression myelopathy. J Bone Joint Surg Br.1998;80:846–849.
Edwards CC, Heller JG, Silcox DH. T-Saw laminoplasty for the management of cervical spondylotic myelopathy: clinical and radiographic outcome. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2000;25:1788–1794.
Fujiwara K, Yonenobu K, Ebara S, Yamashita K, Ono K. The prognosis of surgery for cervical compression myelopathy: an analysis of the factors involved. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1989;71:393–398.
Gok B, McLoughlin GS, Sciubba DM, McGirt MJ, Chaichana KL, Wolinsky JP, Bydon A, Gokaslan ZL, Witham TF. Surgical management of cervical spondylotic myelopathy with laminectomy and instrumented fusion. Neurol Res. 2009;31:1097–1101.
Gonzalez-Feria L, Peraita-Peraita P. Cervical spondylotic myelopathy: a cooperative study. Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 1975;78:19–33.
Guigui P, Benoist M, Deburge A. Spinal deformity and instability after multilevel cervical laminectomy for spondylotic myelopathy. Spine(Phila Pa 1976) 1998;23:440–447.
Heller JG, Edwards CC, Murakami H, Rodts GE. Laminoplasty versus laminectomy and fusion for multilevel cervical myelopathy: an independent matched cohort analysis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2001;26:1330–1336.
Hosono N, Yonenobu K, Ono K. Neck and shoulder pain after laminoplasty: a noticeable complication. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1996;21:1969–1973.
Houten JK, Cooper PR. Laminectomy and posterior cervical plating for multilevel cervical spondylotic myelopathy and ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligament: effects on cervical alignment, spinal cord compression, and neurological outcome. Neurosurgery. 2003;52:1081–1087; discussion 1087–1088.
Huang RC, Girardi FP, Poynton AR, Cammisa FP Jr. Treatment of multilevel cervical spondylotic myeloradiculopathy with posterior decompression and fusion with lateral mass plate fixation and local bone graft. J Spinal Disord Tech. 2003;16:123–129.
Kato Y, Iwasaki M, Fuji T, Yonenobu K, Ochi T. Long-term follow-up results of laminectomy for cervical myelopathy caused by ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligament. J Neurosurg. 1998;89:217–223.
Kawakami M, Tamaki T, Iwasaki H, Yoshida M, Ando M, Yamada H. A comparative study of surgical approaches for cervical compressive myelopathy. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2000:381;129–136.
Kumar VG, Rea GL, Mervis LJ, McGregor JM. Cervical spondylotic myelopathy: functional and radiographic long-term outcome after laminectomy and posterior fusion. Neurosurgery. 1999;44:771–777; discussion 777–778.
Lee JY, Hanks SE, Oxner W, Tannoury C, Donaldson WF, Kang JD. Use of small suture anchors in cervical laminoplasty to maintain canal expansion: a technical note. J Spinal Disord Tech. 2007;20:33–35.
Lonstein JE. Post-laminectomy kyphosis. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1977;128:93–100.
Maurer PK, Ellenbogen RG, Ecklund J, Simonds GR, Van Dam B, Ondra SL. Cervical spondylotic myelopathy: treatment with posterior decompression and Luque rectangle bone fusion. Neurosurgery. 1991;28:680–683; discussion 683–684.
Rao RD, Gourab K, David KS. Operative treatment of cervical spondylotic myelopathy. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2006;88:1619–1640.
Ratliff JK, Cooper PR. Cervical laminoplasty: a critical review. J Neurosurg 2003;98:230–238.
Satomi K, Nishu Y, Kohno T, Hirabavashi K. Long-term follow-up studies of open-door expansive laminoplasty for cervical stenotic myelopathy. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1994;19:507–510.
Sodeyama T, Goto S, Mochizuki M, Takahashi J, Moriya H. Effect of decompression enlargement laminoplasty for posterior shifting of the spinal cord. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1999;24:1527–1531; discussion 1531-1532.
Suri A, Chabbra RP, Mehta VS, Gaikwad S, Pandey RM. Effect of intramedullary signal changes on the surgical outcome of patients with cervical spondylotic myelopathy. Spine J. 2003;3:33–45.
Tomita K, Kawahara N, Toribatake Y, Heller JG. Expansive midline T-saw laminoplasty (modified spinous process-splitting) for the management of cervical myelopathy. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1998;23:32–37.
Wang MY, Shah S, Green BA. Clinical outcomes following cervical laminoplasty for 204 patients with cervical spondylotic myelopathy. Surg Neurol. 2004;62:487–492; discussion 492–493.
Yonenobu K, Fuji T, Ono K, Okada K, Yamamoto T, Harada N. Choice of surgical treatment for multisegmental cervical spondylotic myelopathy. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1985;10:710–716.
Yonenobu K, Hosono N, Iwasaki M, Asano M, Ono K. Laminoplasty versus subtotal corpectomy: a comparative study of results in multisegmental cervical spondylotic myelopathy. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1992;17:1281–1284.
Acknowledgments
We thank Cara Davies and Robert Hartman for their vital contributions with data collection and statistical analysis, which aided in the completion of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Each author certifies that he or she has no commercial associations (eg, consultancies, stock ownership, equity interest, patent/licensing arrangements, etc) that might pose a conflict of interest in connection with the submitted article.
Each author certifies that his or her institution approved or waived approval for the human protocol for this investigation and that all investigations were conducted in conformity with ethical principles of research.
This work was performed at The Ferguson Lab for Orthopaedic and Spine Research, University of Pittsburgh Medical Center.
About this article
Cite this article
Woods, B.I., Hohl, J., Lee, J. et al. Laminoplasty versus Laminectomy and Fusion for Multilevel Cervical Spondylotic Myelopathy. Clin Orthop Relat Res 469, 688–695 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11999-010-1653-5
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11999-010-1653-5