Abstract
Background
First-generation bioabsorbable implants have been associated with a high complication rate attributable to weak mechanical properties and rapid degradation. This has led to the development of stronger devices with improved durability. However, the modern implants have raised concerns about potential late-occurring adverse reactions.
Questions/purposes
This retrospective study addressed the following questions: Can absorbable implants consisting of trimethylene carbonate, L-lactide, and D,L-lactide provide adequate fixation for healing of a metacarpal fracture? Will these implants obviate a second removal operation? What complications can occur in the reaction to implant breakdown?
Patients and Methods
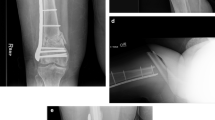
Twelve unstable, displaced, metacarpal fractures were studied in 10 consecutive patients (seven men, three women; mean age, 36.4 years; range, 18–75 years). The fractures were treated with absorbable plates and screws consisting of the aforementioned copolymers and designed to resorb in 2 to 4 years. Nine patients (10 fractures) were available for clinical and radiographic followups (mean, 45.7 months; range, 34–61 months).
Results
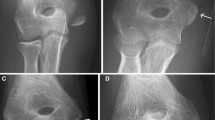
Fracture healing was uneventful in all cases. Four patients experienced a foreign-body reaction during the second postoperative year and required surgical débridement to remove implant remnants. Histologic examination confirmed the diagnosis of a foreign-body reaction. Two other patients reported a transient local swelling that subsided without treatment.
Conclusions
Our results indicate these absorbable implants for metacarpal fractures achieved adequate bone healing but simply postponed the problem of foreign-body reactions. Patients treated with bioabsorbable implants should be advised of potential late complications and should be followed for at least 2 years, possibly longer.
Level of Evidence
Level IV, therapeutic study. See Guidelines for Authors for a complete description of levels of evidence.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bostman OM. Osteolytic changes accompanying degradation of absorbable fracture fixation implants. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1991;73:679–682.
Bostman OM. Intense granulomatous inflammatory lesions associated with absorbable internal fixation devices made of polyglycolide in ankle fractures. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1992;278:193–199.
Bostman OM, Hirvensalo E, Makinen J, Rokkanen P. Foreign-body reactions to fracture fixation implants of biodegradable synthetic polymers. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1990;72:592–596.
Bostman OM, Hirvensalo E, Vainionpaa S, Makela A, Vihtonen K, Tormala P, Rokkanen P. Ankle fractures treated using biodegradable internal fixation. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1989;238:195–203.
Bostman OM, Pihlajamaki H. Clinical biocompatibility of biodegradable orthopaedic implants for internal fixation: a review. Biomaterials. 2000;21:2615–2621.
Bostman OM, Pihlajamaki HK. Adverse tissue reactions to bioabsorbable fixation devices. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2000;371:216–227.
Bozic KJ, Perez LE, Wilson DR, Fitzgibbons PG, Jupiter JB. Mechanical testing of bioresorbable implants for use in metacarpal fracture fixation. J Hand Surg Am. 2001;26:755–761.
Casteleyn PP, Handelberg F, Haentjens P. Biodegradable rods versus Kirschner wire fixation of wrist fractures: a randomised trial. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1992;74:858–861.
Choung EW, Tan V. Foreign-body reaction to the Artelon CMC joint spacer: case report. J Hand Surg Am. 2008;33:1617–1620.
Dumont C, Fuchs M, Burchhardt H, Appelt D, Bohr S, Sturmer KM. Clinical results of absorbable plates for displaced metacarpal fractures. J Hand Surg Am. 2007;32:491–496.
Feehan LM, Sheps SB. Incidence and demographics of hand fractures in British Columbia, Canada: a population-based study. J Hand Surg Am. 2006;31:1068–1074.
Fraser RK, Cole WG. Osteolysis after biodegradable pin fixation of fractures in children. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1992;74:929–930.
Freeland AE, Geissler WB, Weiss AP. Surgical treatment of common displaced and unstable fractures of the hand. Instr Course Lect. 2002;51:185–201.
Frokjaer J, Moller BN. Biodegradable fixation of ankle fractures: complications in a prospective study of 25 cases. Acta Orthop Scand. 1992;63:434–436.
Giuffrida AY, Gyuricza C, Perino G, Weiland AJ. Foreign body reaction to artelon spacer: case report. J Hand Surg Am. 2009;34:1388–1392.
Givissis PK, Symeonidis PD, Ditsios KT, Dionellis PS, Christodoulou AG. Late results of absorbable pin fixation in the treatment of radial head fractures. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2008;466:1217–1224.
Hirvensalo E. Fracture fixation with biodegradable rods: forty-one cases of severe ankle fractures. Acta Orthop Scand. 1989;60:601–606.
Hoffmann R, Krettek C, Hetkamper A, Haas N, Tscherne H. [Osteosynthesis of distal radius fractures with biodegradable fracture rods: results of two years follow-up][in German]. Unfallchirurg. 1992;95:99–105.
Hughes TB. Bioabsorbable implants in the treatment of hand fractures: an update. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2006;445:169–174.
Laughlin RM, Block MS, Wilk R, Malloy RB, Kent JN. Resorbable plates for the fixation of mandibular fractures: a prospective study. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2007;65:89–96.
Leonhardt H, Demmrich A, Mueller A, Mai R, Loukota R, Eckelt U. INION compared with titanium osteosynthesis: a prospective investigation of the treatment of mandibular fractures. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2008;46:631–634.
Losken HW, van Aalst JA, Mooney MP, Godfrey VL, Burt T, Teotia S, Dean SB, Moss JR, Rahbar R. Biodegradation of Inion fast-absorbing biodegradable plates and screws. J Craniofac Surg. 2008;19:748–756.
Mavrogenis AF, Kanellopoulos AD, Nomikos GN, Papagelopoulos PJ, Soucacos PN. Early experience with biodegradable implants in pediatric patients. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2009;467:1591–1598.
Middleton JC, Tipton AJ. Synthetic biodegradable polymers as orthopedic devices. Biomaterials. 2000;21:2335–2346.
Nieminen T, Rantala I, Hiidenheimo I, Keranen J, Kainulainen H, Wuolijoki E, Kallela I. Degradative and mechanical properties of a novel resorbable plating system during a 3-year follow-up in vivo and in vitro. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2008;19:1155–1163.
Omokawa S, Fujitani R, Dohi Y, Okawa T, Yajima H. Prospective outcomes of comminuted periarticular metacarpal and phalangeal fractures treated using a titanium plate system. J Hand Surg Am. 2008;33:857–863.
Page SM, Stern PJ. Complications and range of motion following plate fixation of metacarpal and phalangeal fractures. J Hand Surg Am. 1998;23:827–832.
Rokkanen PU, Bostman O, Hirvensalo E, Makela EA, Partio EK, Patiala H, Vainionpaa SI, Vihtonen K, Tormala P. Bioabsorbable fixation in orthopaedic surgery and traumatology. Biomaterials. 2000;21:2607–2613.
Souer JS, Mudgal CS. Plate fixation in closed ipsilateral multiple metacarpal fractures. J Hand Surg Eur Vol. 2008;33:740–744.
Waris E, Ashammakhi N, Happonen H, Raatikainen T, Kaarela O, Tormala P, Santavirta S, Konttinen YT. Bioabsorbable miniplating versus metallic fixation for metacarpal fractures. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2003;410:310–319.
Waris E, Ashammakhi N, Raatikainen T, Tormala P, Santavirta S, Konttinen YT. Self-reinforced bioabsorbable versus metallic fixation systems for metacarpal and phalangeal fractures: a biomechanical study. J Hand Surg Am. 2002;27:902–909.
Weiler A, Helling HJ, Kirch U, Zirbes TK, Rehm KE. Foreign-body reaction and the course of osteolysis after polyglycolide implants for fracture fixation: experimental study in sheep. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1996;78:369–376.
Wood GD. Inion biodegradable plates: the first century. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2006;44:38–41.
Acknowledgments
We thank Dr Styliani Papaemmanuel, senior pathologist in the Department of Pathology of G. Papanikolaou General Hospital, for conducting the histologic analyses of all tissue samples.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Each author certifies that he or she has no commercial associations (eg, consultancies, stock ownership, equity interest, patent/licensing arrangements, etc) that might pose a conflict of interest in connection with the submitted article.
Each author certifies that his or her institution approved the human protocol for this investigation that all investigations were conducted in conformity with ethical principles of research, and that informed consent for participation in the study was obtained.
This work was performed at the 1st Department of Orthopaedics, Aristotle University of Thessaloniki.
About this article
Cite this article
Givissis, P.K., Stavridis, S.I., Papagelopoulos, P.J. et al. Delayed Foreign-body Reaction to Absorbable Implants in Metacarpal Fracture Treatment. Clin Orthop Relat Res 468, 3377–3383 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11999-010-1388-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11999-010-1388-3