Abstract
Background
Previous studies show the shape of the femur in developmental dislocation of the hip (DDH) becomes more abnormal with increasing subluxation. Two kinds of high dislocations associated with DDH have been observed in clinical practice, one with (Type C1) and one without (Type C2) a false acetabulum. The presence or absence of a false acetabulum in high dislocated hips is associated with different loading patterns and could influence the development and shape of the proximal femur.
Questions/purposes
We therefore determined whether (1) the proximal femoral shape and dimension in Type C1 and Type C2 hips differ from each other, and (2) the femur dislocated with the same height in Types C1 and C2 hips.
Patients and Methods
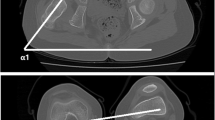
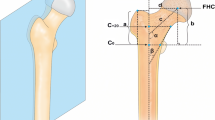
We examined the following variables on 54 proximal femurs from 54 patients with high DDH (28 Type C1 hips and 26 Type C2 hips) on AP and lateral radiographs; the ML widths of the cortical and medullary canals, height of the femoral head, height of dislocation, and height of the greater trochanter. Reproducibility of the measurements was tested by two researchers with high interobserver and intraobserver agreement.
Results
The proximal femur in Type C2 hips was narrower and stovepipe shaped, with a smaller flare index (2.7 ± 0.6), compared with Type C1 hips (3.5 ± 1.2). The proximal femur migrated an average of 18 mm more superiorly in Type C2 than in Type C1 hips.
Conclusions
Our data confirm distinctions in the shape of the proximal femur in the presence and absence of a false acetabulum.
Clinical Relevance
Owing to the abnormal shapes, special implants of different geometries or modular stems may be needed for reconstruction Type C2 high dislocations.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Argenson JN, Ryembault E, Flecher X, Brassart N, Parratte S, Aubaniac JM. Three-dimensional anatomy of the hip in osteoarthritis after developmental dysplasia. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2005;87:1192–1196.
Crowe JF, Mani VJ, Ranawat CS. Total hip replacement in congenital dislocation and dysplasia of the hip. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1979;61:15–23.
Erdemli B, Yilmaz C, Atalar H, Guzel B, Cetin I. Total hip arthroplasty in developmental high dislocation of the hip. J Arthroplasty. 2005;20:1021–1028.
Eskelinen A, Helenius I, Remes V, Ylinen P, Tallroth K, Paavilainen T. Cementless total hip arthroplasty in patients with high congenital hip dislocation. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2006;88:80–91.
Hartofilakidis G, Karachalios T. Total hip arthroplasty for congenital hip disease. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2004;86:242–250.
Hartofilakidis G, Stamos K, Ioannidis TT. Low friction arthroplasty for old untreated congenital dislocation of the hip. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1988;70:182–186.
Hartofilakidis G, Yiannakopoulos CK, Babis GC. The morphologic variations of low and high hip dislocation. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2008;466:820–824.
Khang G, Choi K, Kim CS, Yang JS, Bae TS. A study of Korean femoral geometry. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2003;406:116–122.
Kim YH, Kim JS. Total hip arthroplasty in adult patients who had developmental dysplasia of the hip. J Arthroplasty. 2005;20:1029–1036.
Lai K, Shen WJ, Huang LW, Chen MY. Cementless total hip arthroplasty and limb-length equalization in patients with unilateral Crowe type-IV hip dislocation. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2005;87:339–345.
Makita H, Inaba Y, Hirakawa K, Saito T. Results on total hip arthroplasties with femoral shortening for Crowe’s group IV dislocated hips. J Arthroplasty. 2007;22:32–38.
Nagoya S, Kaya M, Sasaki M, Tateda K, Kosukegawa I, Yamashita T. Cementless total hip replacement with subtrochanteric femoral shortening for severe developmental dysplasia of the hip. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2009;91:1142–1147.
Noble PC, Kamaric E, Sugano N, Matsubara M, Harada Y, Ohzono K, Paravic V. Three-dimensional shape of the dysplastic femur: implications for THR. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2003;417:27–40.
Robertson DD, Essinger JR, Imura S, Kuroki Y, Sakamaki T, Shimizu T, Tanaka S. Femoral deformity in adults with developmental hip dysplasia. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1996;327:196–206.
Sener N, Tozun IR, Asik M. Femoral shortening and cementless arthroplasty in high congenital dislocation of the hip. J Arthroplasty. 2002;17:41–48.
Sugano N, Noble PC, Kamaric E, Salama JK, Ochi T, Tullos HS. The morphology of the femur in developmental dysplasia of the hip. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1998;80:711–719.
Acknowledgments
We thank Dr. X.C. Yang for assistance in doing this study. We also thank Katharine O’ Moore-Klopf, ELS, of East Setauket, NY, for providing editorial assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Each author certifies that he or she has no commercial associations (eg, consultancies, stock ownership, equity interest, patent/licensing arrangements, etc) that might pose a conflict of interest in connection with the submitted article.
Each author certifies that his or her institution approved the human protocol for this investigation, that all investigations were conducted in conformity with ethical principles of research.
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, H., Zhou, Y., Liu, Q. et al. Femoral Morphologic Differences in Subtypes of High Developmental Dislocation of the Hip. Clin Orthop Relat Res 468, 3371–3376 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11999-010-1386-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11999-010-1386-5