Abstract
Background
Osteoid osteoma has a nidus surrounded by sclerotic bone with a size usually less than 20 mm. Its diagnosis is made on typical presentation of nocturnal pain and imaging findings. Excision of the niduses, which are often small and difficult to precisely identify, sometimes may result in resection of surrounding normal bone. Minimally invasive percutaneous treatments have been used to try to minimize resection of normal bone. Although minimally invasive radiofrequency ablation generally relieves pain, its ability to relieve pain is less well known in locations other than lower extremity long bones.
Questions/purposes
We determined the pain relief and complication rates after radiofrequency ablation of osteoid osteomas presenting in atypical locations and followed patients to assess possible recurrence or late complications.
Patients and Methods
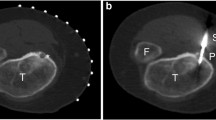
We retrospectively reviewed 21 patients with osteoid osteomas in unusual locations (eg, hip, radioulnar joint, and proximal phalanx) in whom we used radiofrequency ablation. Postoperative activities were not restricted for any of the patients. We assessed the time for patients to become symptom free, their activity status, and possible recurrence or complications. The minimum clinical followup was 12 months (mean, 27.8 months; range, 12–37 months).
Results
All patients became symptom free within 24 hours to 1 week. During followup, none of the patients experienced recurrence or any major complications.
Conclusions
Radiofrequency ablation for osteoid osteomas in unusual locations reliably relieves pain with few complications and recurrences at short-term followup.
Level of Evidence
Level IV, case series. See Guidelines for Authors for a complete description of level of evidence.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akhlaghpoor S, Tomasian A, Arjmand Shabestari A, Ebrahimi M, Alinaghizadeh MR. Percutaneous osteoid osteoma treatment with combination of radiofrequency and alcohol ablation. Clin Radiol. 2007;62:268–273.
Albisinni U, Chiatante M, Rinaldi R. Efficacy of percutaneous radiofrequency ablation of osteoid osteoma in children. Pediatr Radiol. 2008;38:1356.
Assoun J, Railhac JJ, Bonnevialle P, Poey C, Salles de Gauzy J, Baunin C, Cahuzac JP, Clement JL, Coustets B, Railhac N. Osteoid osteoma: percutaneous resection with CT guidance. Radiology. 1993;188:541–547.
Assoun J, Richardi G, Railhac JJ, Baunin C, Fajadet P, Giron J, Maquin P, Haddad J, Bonnevialle P. Osteoid osteoma: MR imaging versus CT. Radiology. 1994;191:217–223.
Barei DP, Moreau G, Scarborough MT, Neel MD. Percutaneous radiofrequency ablation of osteoid osteoma. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2000;373:115–124.
Boriani S, Capanna R. [Osteoid osteoma of the hand. Review of literature and case report] [in Italian]. Chir Organi Mov. 1979;65:555–560.
Campanacci M, Ruggieri P, Gasbarrini A, Ferraro A, Campanacci L. Osteoid osteoma: direct visual identification and intralesional excision of the nidus with minimal removal of bone. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1999;81:814–820.
Cantwell CP, Obyrne J, Eustace S. Current trends in treatment of osteoid osteoma with an emphasis on radiofrequency ablation. Eur Radiol. 2004;14:607–617.
Carter TR. Osteoid osteoma of the hip: an alternate method of excision. Orthop Rev. 1990;19:903–905.
Cioni R, Armillotta N, Bargellini I, Zampa V, Cappelli C, Vagli P, Boni G, Marchetti S, Consoli V, Bartolozzi C. CT-guided radiofrequency ablation of osteoid osteoma: long-term results. Eur Radiol. 2004;14:1203–1208.
de Berg JC, Pattynama PM, Obermann WR, Bode PJ, Vielvoye GJ, Taminiau AH. Percutaneous computed-tomography-guided thermocoagulation for osteoid osteomas. Lancet. 1995;346:350–351.
Di Gennaro GL, Lampasi M, Bosco A, Donzelli O. Osteoid osteoma of the distal thumb phalanx: a case report. Chir Organi Mov. 2008;92:179–182.
Finstein JL, Hosalkar HS, Ogilvie CM, Lackman RD. Case reports: an unusual complication of radiofrequency ablation treatment of osteoid osteoma. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2006;448:248–251.
Gebauer B, Tunn PU, Gaffke G, Melcher I, Felix R, Stroszczynski C. Osteoid osteoma: experience with laser- and radiofrequency-induced ablation. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 2006;29:210–215.
Helms CA, Hattner RS, Vogler JB III. Osteoid osteoma: radionuclide diagnosis. Radiology. 1984;151:779–784.
Hoffmann RT, Jakobs TF, Kubisch CH, Trumm CG, Weber C, Duerr HR, Helmberger TK, Reiser MF. Radiofrequency ablation in the treatment of osteoid osteoma: 5-year experience. Eur J Radiol. 2009 Jan 12. [Epub ahead of print]
Ilyas I, Younge DA. Medical management of osteoid osteoma. Can J Surg. 2002;45:435–437.
Kneisl JS, Simon MA. Medical management compared with operative treatment for osteoid-osteoma. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1992;74:179–185.
Kohler R, Rubini J, Postec F, Canterino I, Archimbaud F. [Treatment of osteoid osteoma by CT-controlled percutaneous drill resection: apropos of 27 cases] [in French]. Rev Chir Orthop Reparatrice Appar Mot. 1995;81:317–325.
Lee EH, Shafi M, Hui JH. Osteoid osteoma: a current review. J Pediatr Orthop. 2006;26:695–700.
Lindner NJ, Ozaki T, Roedl R, Gosheger G, Winkelmann W, Wortler K. Percutaneous radiofrequency ablation in osteoid osteoma. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2001;83:391–396.
Mahnken AH, Tacke JA, Wildberger JE, Gunther RW. Radiofrequency ablation of osteoid osteoma: initial results with a bipolar ablation device. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2006;17:1465–1470.
Martel J, Bueno A, Ortiz E. Percutaneous radiofrequency treatment of osteoid osteoma using cool-tip electrodes. Eur J Radiol. 2005;56:403–408.
Osti OL, Sebben R. High-frequency radio-wave ablation of osteoid osteoma in the lumbar spine. Eur Spine J. 1998;7:422–425.
Parlier-Cuau C, Champsaur P, Nizard R, Hamze B, Laredo JD. Percutaneous removal of osteoid osteoma. Radiol Clin North Am. 1998;36:559–566.
Parlier-Cuau C, Nizard R, Champsaur P, Hamze B, Laredo JD. Percutaneous resection of osteoid osteomas. Semin Musculoskelet Radiol. 1997;1:257–264.
Pfeiffer M, Sluga M, Windhager R, Dominkus M, Kotz R. [Surgical treatment of osteoid osteoma of the extremities] [in German]. Z Orthop Ihre Grenzgeb. 2003;141:345–348.
Pratali R, Zuiani G, Inada M, Hanasilo C, Reganin L, Etchebehere E, Etchebehere M. Open resection of osteoid osteoma guided by a gamma-probe. Int Orthop. 2009;33:219–223.
Ramos L, Santos JA, Santos G, Guiral J. Radiofrequency ablation in osteoid osteoma of the finger. J Hand Surg Am. 2005;30:798–802.
Rosenthal DI. Percutaneous radiofrequency treatment of osteoid osteomas. Semin Musculoskelet Radiol. 1997;1:265–272.
Rosenthal DI, Alexander A, Rosenberg AE, Springfield D. Ablation of osteoid osteomas with a percutaneously placed electrode: a new procedure. Radiology. 1992;183:29–33.
Rosenthal DI, Hornicek FJ, Wolfe MW, Jennings LC, Gebhardt MC, Mankin HJ. Percutaneous radiofrequency coagulation of osteoid osteoma compared with operative treatment. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1998;80:815–821.
Saccomanni B. Osteoid osteoma and osteoblastoma of the spine: a review of the literature. Curr Rev Musculoskelet Med. 2009;2:65–67.
Sans N, Galy-Fourcade D, Assoun J, Jarlaud T, Chiavassa H, Bonnevialle P, Railhac N, Giron J, Morera-Maupome H, Railhac JJ. Osteoid osteoma: CT-guided percutaneous resection and follow-up in 38 patients. Radiology. 1999;212:687–692.
Shinozaki T, Sato J, Watanabe H, Takagishi K, Aoki J, Koyama Y, Takahashi A. Osteoid osteoma treated with computed tomography-guided percutaneous radiofrequency ablation: a case series. J Orthop Surg (Hong Kong). 2005;13:317–322.
Sluga M, Windhager R, Pfeiffer M, Dominkus M, Kotz R. Peripheral osteoid osteoma: is there still a place for traditional surgery? J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2002;84:249–251.
Soong M, Jupiter J, Rosenthal D. Radiofrequency ablation of osteoid osteoma in the upper extremity. J Hand Surg Am. 2006;31:279–283.
Sung KS, Seo JG, Shim JS, Lee YS. Computed-tomography-guided percutaneous radiofrequency thermoablation for the treatment of osteoid osteoma: 2 to 5 years follow-up. Int Orthop. 2009;33:215–218.
Towbin R, Kaye R, Meza MP, Pollock AN, Yaw K, Moreland M. Osteoid osteoma: percutaneous excision using a CT-guided coaxial technique. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1995;164:945–949.
Vanderschueren GM, Taminiau AH, Obermann WR, Bloem JL. Osteoid osteoma: clinical results with thermocoagulation. Radiology. 2002;224:82–86.
Ward WG, Eckardt JJ, Shayestehfar S, Mirra J, Grogan T, Oppenheim W. Osteoid osteoma diagnosis and management with low morbidity. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1993;291:229–235.
Weber KL. What’s new in musculoskeletal oncology. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2004;86:1104–1109.
Woertler K, Vestring T, Boettner F, Winkelmann W, Heindel W, Lindner N. Osteoid osteoma: CT-guided percutaneous radiofrequency ablation and follow-up in 47 patients. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2001;12:717–722.
Yildiz Y, Bayrakci K, Altay M, Saglik Y. Osteoid osteoma: the results of surgical treatment. Int Orthop. 2001;25:119–122.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Each author certifies that he or she has no commercial associations (eg, consultancies, stock ownership, equity interest, patent/licensing arrangements, etc) that might pose a conflict of interest in connection with the submitted article.
Each author certifies that his or her institution approved the human protocol for this investigation, that all investigations were conducted in conformity with ethical principles of research, and that informed consent for participation in the study was obtained.
The work was performed at Noor Medical Imaging Center.
About this article
Cite this article
Akhlaghpoor, S., Aziz Ahari, A., Arjmand Shabestari, A. et al. Radiofrequency Ablation of Osteoid Osteoma in Atypical Locations: A Case Series. Clin Orthop Relat Res 468, 1963–1970 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11999-010-1265-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11999-010-1265-0