Abstract
Background
Long-term survival of uncemented total joint replacements relies on osseointegration. With reduced bone stock impacted morselized allograft enhances early implant fixation but is subject to resorption.
Purpose
We therefore asked whether soaking morselized allograft in different concentrations of bisphosphonate before impaction would enhance fixation.
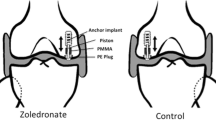
Methods
In each of 10 dogs, we implanted four unloaded titanium implants surrounded by a 2.5-mm gap into the proximal humerus, two implants in each humerus. The gap was filled with impacted morselized allograft soaked in saline or a low-, middle-, or high-dose bisphosphonate solution (0.005, 0.05, or 0.5 mg zoledronate/mL). At 4 weeks, the implants were evaluated by histomorphometric analysis and mechanical pushout test.
Results
The low dose of zoledronate increased new bone formation in the allograft but the high dose decreased new bone formation. The high dose of zoledronate resulted in the greatest inhibition of allograft resorption, whereas the low dose of zoledronate resulted in the lowest inhibition of allograft resorption. Implants surrounded allograft soaked in the low dose of zoledronate or saline had better fixation for all three mechanical parameters compared with implants surrounded by allograft soaked in the middle or high dose of zoledronate.
Conclusions
These data suggest bisphosphonate may enhance osseointegration of allografted implants and emphasize the need for preclinical testing of antiresorptive therapies.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aerssens J, Boonen S, Lowet G, Dequeker J. Interspecies differences in bone composition, density, and quality: potential implications for in vivo bone research. Endocrinology. 1998;139:663–670.
Aspenberg P, Astrand J. Bone allografts pretreated with a bisphosphonate are not resorbed. Acta Orthop Scand. 2002;73:20–23.
Astrand J, Aspenberg P. Systemic alendronate prevents resorption of necrotic bone during revascularization: a bone chamber study in rats. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2002;3:19–23.
Astrand J, Harding AK, Aspenberg P, Tagil M. Systemic zoledronate treatment both prevents resorption of allograft bone and increases the retention of new formed bone during revascularization and remodelling: a bone chamber study in rats. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2006;7:63–69.
Baas J. Adjuvant therapies of bone graft around non-cemented experimental orthopedic implants stereological methods and experiments in dogs. Acta Orthop Suppl. 2008;79:1–43.
Baas J, Elmengaard B, Jensen TB, Jakobsen T, Andersen NT, Soballe K. The effect of pretreating morselized allograft bone with rhBMP-2 and/or pamidronate on the fixation of porous Ti and HA-coated implants. Biomaterials. 2008;29:2915–2922.
Baas J, Lamberg A, Jensen TB, Elmengaard B, Soballe K. The bovine bone protein lyophilisate Colloss improves fixation of allografted implants: an experimental study in dogs. Acta Orthop. 2006;77:791–798.
Baddeley AJ, Gundersen HJ, Cruz-Orive LM. Estimation of surface area from vertical sections. J Microsc. 1986;142:259–276.
Dhert WJ, Verheyen CC, Braak LH, de Wijn JR, Klein CP, de Groot K, Rozing PM. A finite element analysis of the push-out test: influence of test conditions. J Biomed Mater Res. 1992;26:119–130.
Fleisch H. Development of bisphosphonates. Breast Cancer Res. 2002;4:30–34.
Gie GA, Linder L, Ling RS, Simon JP, Slooff TJ, Timperley AJ. Impacted cancellous allografts and cement for revision total hip arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1993;75:14–21.
Idris AI, Rojas J, Greig IR, Van’t Hof RJ, Ralston SH. Aminobisphosphonates cause osteoblast apoptosis and inhibit bone nodule formation in vitro. Calcif Tissue Int. 2008;82:191–201.
Im GI, Qureshi SA, Kenney J, Rubash HE, Shanbhag AS. Osteoblast proliferation and maturation by bisphosphonates. Biomaterials. 2004;25:4105–4115.
Jakobsen T, Baas J, Bechtold JE, Elmengaard B, Soballe K. Soaking morsellized allograft in bisphosphonate can impair implant fixation. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2007;463:195–201.
Jakobsen T, Baas J, Kold S, Bechtold JE, Elmengaard B, Soballe K. Local bisphosphonate treatment increases fixation of hydroxyapatite-coated implants inserted with bone compaction. J Orthop Res. 2009;27:189–194.
Jakobsen T, Kold S, Bechtold JE, Elmengaard B, Soballe K. Local alendronate increases fixation of implants inserted with bone compaction: 12-week canine study. J Orthop Res. 2007;25:432–441.
Jensen TB, Overgaard S, Lind M, Rahbek O, Bunger C, Soballe K. Osteogenic protein 1 device increases bone formation and bone graft resorption around cementless implants. Acta Orthop Scand. 2002;73:31–39.
Karrholm J, Borssen B, Lowenhielm G, Snorrason F. Does early micromotion of femoral stem prostheses matter? 4–7-year stereoradiographic follow-up of 84 cemented prostheses. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1994;76:912–917.
Kesteris U, Aspenberg P. Rinsing morcellised bone grafts with bisphosphonate solution prevents their resorption: a prospective randomised double-blinded study. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2006;88:993–996.
Overgaard S, Soballe K, Jorgen H, Gundersen H. Efficiency of systematic sampling in histomorphometric bone research illustrated by hydroxyapatite-coated implants: optimizing the stereological vertical-section design. J Orthop Res. 2000;18:313–321.
Reinholz GG, Getz B, Pederson L, Sanders ES, Subramaniam M, Ingle JN, Spelsberg TC. Bisphosphonates directly regulate cell proliferation, differentiation, and gene expression in human osteoblasts. Cancer Res. 2000;60:6001–6007.
Ryd L, Albrektsson BE, Carlsson L, Dansgard F, Herberts P, Lindstrand A, Regner L, Toksvig-Larsen S. Roentgen stereophotogrammetric analysis as a predictor of mechanical loosening of knee prostheses. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1995;77:377–383.
Slooff TJ, Huiskes R, van Horn J, Lemmens AJ. Bone grafting in total hip replacement for acetabular protrusion. Acta Orthop Scand. 1984;55:593–596.
Tagil M, Aspenberg P. Impaction of cancellous bone grafts impairs osteoconduction in titanium chambers. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1998;352:231–238.
Toms AD, Barker RL, Jones RS, Kuiper JH. Impaction bone-grafting in revision joint replacement surgery. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2004;86:2050–2060.
Venesmaa PK, Kroger HP, Miettinen HJ, Jurvelin JS, Suomalainen OT, Alhav EM. Alendronate reduces periprosthetic bone loss after uncemented primary total hip arthroplasty: a prospective randomized study. J Bone Miner Res. 2001;16:2126–2131.
Wilkinson JM, Stockley I, Peel NF, Hamer AJ, Elson RA, Barrington NA, Eastell R. Effect of pamidronate in preventing local bone loss after total hip arthroplasty: a randomized, double-blind, controlled trial. J Bone Miner Res. 2001;16:556–564.
Acknowledgments
We thank Jane Pauli and Anette Milton, Orthopaedic Research Laboratory, Aarhus University Hospital, for technical expertise.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
One or more of the authors (TJ) have received funding from The Danish Rheumatism Association, Denmark. Biomet Inc coated the implants.
Each author certifies that his or her institution has approved the animal protocol for this investigation and that all investigations were conducted in conformity with ethical principles of research.
This work was performed at the Orthopaedic Research Laboratory, Aarhus University Hospital, Aarhus, Denmark (specimen preparation, testing, and analysis), and Orthopaedic Biomechanics Laboratory, Midwest Research Foundation, Minneapolis, MN, USA (surgery).
About this article
Cite this article
Jakobsen, T., Baas, J., Bechtold, J.E. et al. The Effect of Soaking Allograft in Bisphosphonate: A Pilot Dose-response Study. Clin Orthop Relat Res 468, 867–874 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11999-009-1099-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11999-009-1099-9