Abstract
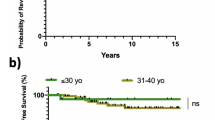
Revision total knee arthroplasty in patients with rheumatoid arthritis can be challenging. We asked whether we could confirm previously reported high failure rates following revision total knee arthroplasty in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. We therefore determined the Knee Society knee score and function scores, radiographic evidence of failure, and overall survival of the revision procedure in these patients. We retrospectively reviewed 39 patients with rheumatoid arthritis who underwent 45 TKA revisions from 1994 to 2006. Twenty-seven of the 45 TKA revisions were for mechanical failure of the prosthetic components and 18 for infection. Five of the 27 knees (19%) revised for mechanical failure subsequently failed a second time. Five of the 18 patients who underwent revision for infection died within 6 months and three of the remaining knees failed secondary to reinfection. Excluding the knees that failed, the average Knee Society knee score and function score improved in both subgroups. Two knees had radiographic evidence of nonprogressive tibial radiolucencies. The probability of survival for all knees (revision as the end point) was 76% ± 9% at 5 years. We confirmed the previously reported high mortality and subsequent failure rates following revision total knee arthroplasty for both mechanical issues and infection in patients with rheumatoid arthritis and emphasize the potential difficulties in treating these patients.
Level of Evidence: Level IV, therapeutic study. See Guidelines for Authors for a complete description of levels of evidence.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Berbari EF, Osmon DR, Duffy MC, Harmssen RN, Mandrekar JN, Hanssen AD, Steckelberg JM. Outcome of prosthetic joint infection in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: the impact of medical and surgical therapy in 200 episodes. Clin Infect Dis. 2006;42:216–223.
Bohm P, Holy T, Pietsch-Breitfeld B, Meisner C. Mortality after total knee arthroplasty in patients with osteoarthrosis and rheumatoid arthritis. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2000;120:75–78.
Bongartz T, Halligan CS, Osmon DR, Reinalda MS, Bamlet WR, Crowson CS, Hanssen AD, Matteson EL. Incidence and risk factors of prosthetic joint infection after total hip or knee replacement in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2008;59:1713–1720.
Caplan L, Wolfe F, Russell AS, Michaud K. Corticosteroid use in rheumatoid arthritis: prevalence, predictors, correlates, and outcomes. J Rheumatol. 2007;34:696–705.
Ewald FC. The Knee Society total knee arthroplasty roentgenographic evaluation and scoring system. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1989; 248:9–12.
Fink B, Berger I, Siegmuller C, Fassbender HG, Meyer-Scholten C, Tillmann K, Ruther W. Recurring synovitis as a possible reason for aseptic loosening of knee endoprostheses in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2001;83:604–608.
Font-Rodriguez DE, Scuderi GR, Insall JN. Survivorship of cemented total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1997;345:79–86.
Friedman RJ, Hirst P, Poss R, Kelley K, Sledge CB. Results of revision total knee arthroplasty performed for aseptic loosening. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1990;255:235–241.
Gill GS, Joshi AB. Long-term results of cemented, posterior cruciate ligament-retaining total knee arthroplasty in osteoarthritis. Am J Knee Surg. 2001;14:209–214.
Gofton WT, Tsigaras H, Butler RA, Patterson JJ, Barrack RL, Rorabeck CH. Revision total knee arthroplasty: fixation with modular stems. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2002;404:158–168.
Goldberg VM, Figgie MP, Figgie HE 3rd, Heiple KG, Sobel M. Use of a total condylar knee prosthesis for treatment of osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis. Long-term results. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1988;70:802–811.
Hanssen AD, Rand JA. A comparison of primary and revision total knee arthroplasty using the kinematic stabilizer prosthesis. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1988;70:491–499.
Hanyu T, Murasawa A, Tojo T. Survivorship analysis of total knee arthroplasty with the kinematic prosthesis in patients who have rheumatoid arthritis. J Arthroplasty. 1997;12:913–919.
Himanen AK, Belt E, Nevalainen J, Hamalainen M, Lehto MU. Survival of the AGC total knee arthroplasty is similar for arthrosis and rheumatoid arthritis. Finnish Arthroplasty Register report on 8,467 operations carried out between 1985 and 1999. Acta Orthop. 2005;76:85–88.
Insall JN, Dorr LD, Scott RD, Scott WN. Rationale of the Knee Society clinical rating system. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1989;248:13–14.
Ito J, Koshino T, Okamoto R, Saito T. 15-year follow-up study of total knee arthroplasty in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. J Arthroplasty. 2003;18:984–992.
Kristensen O, Nafei A, Kjaersgaard-Andersen P, Hvid I, Jensen J. Long-term results of total condylar knee arthroplasty in rheumatoid arthritis. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1992;74:803–806.
Kurtz S, Mowat F, Ong K, Chan N, Lau E, Halpern M. Prevalence of primary and revision total hip and knee arthroplasty in the United States from 1990 through 2002. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2005;87:1487–1497.
Kurtz S, Ong K, Lau E, Mowat F, Halpern M. Projections of primary and revision hip and knee arthroplasty in the United States from 2005 to 2030. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2007;89:780–785.
Kurtz SM, Ong KL, Schmier J, Mowat F, Saleh K, Dybvik E, Karrholm J, Garellick G, Havelin LI, Furnes O, Malchau H, Lau E. Future clinical and economic impact of revision total hip and knee arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2007;89 Suppl 3:144–151.
Laskin RS. Total condylar knee replacement in patients who have rheumatoid arthritis. A ten-year follow-up study. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1990;72:529–535.
Laskin RS, O’Flynn HM. The Insall Award. Total knee replacement with posterior cruciate ligament retention in rheumatoid arthritis. Problems and complications. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1997;345:24–28.
Peters CL, Hennessey R, Barden RM, Galante JO, Rosenberg AG. Revision total knee arthroplasty with a cemented posterior-stabilized or constrained condylar prosthesis: a minimum 3-year and average 5-year follow-up study. J Arthroplasty. 1997;12:896–903.
Rinonapoli E, Mancini GB, Azzara A, Aglietti P. Long-term results and survivorship analysis of 89 total condylar knee prostheses. J Arthroplasty. 1992;7:241–246.
Rodriguez JA, Saddler S, Edelman S, Ranawat CS. Long-term results of total knee arthroplasty in class 3 and 4 rheumatoid arthritis. J Arthroplasty. 1996;11:141–145.
Rööser B, Boegard T, Knutson K, Rydholm U, Lidgren L. Revision knee arthroplasty in rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1987;219:169–173.
Scuderi GR, Insall JN, Windsor RE, Moran MC. Survivorship of cemented knee replacements. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1989;71:798–803.
Sheng PY, Jamsen E, Lehto M, Pajamaki J, Halonen P, Konttinen YT. Revision total knee arthroplasty with the total condylar III system: a comparative analysis of 71 consecutive cases of osteoarthritis or inflammatory arthritis. Acta Orthop. 2006;77:512–518.
Sheng PY, Jamsen E, Lehto MU, Konttinen YT, Pajamaki J, Halonen P. Revision total knee arthroplasty with the Total Condylar III system in inflammatory arthritis. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2005;87:1222–1224.
Sheng PY, Konttinen L, Lehto M, Ogino D, Jamsen E, Nevalainen J, Pajamaki J, Halonen P, Konttinen YT. Revision total knee arthroplasty: 1990 through 2002. A review of the Finnish arthroplasty registry. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2006;88:1425–1430.
Sihvonen S, Korpela M, Mustonen J, Huhtala H, Karstila K, Pasternack A. Mortality in patients with rheumatoid arthritis treated with low-dose oral glucocorticoids. A population-based cohort study. J Rheumatol. 2006;33:1740–1746.
Westhovens R, Dequeker J. Rheumatoid arthritis and osteoporosis. Z Rheumatol. 2000;59 Suppl 1:33–38.
Whaley AL, Trousdale RT, Rand JA, Hanssen AD. Cemented long-stem revision total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2003;18:592–599.
Acknowledgments
We thank Rebecca Moore and Patricia Conroy-Smith for their help in maintaining the total joint registry and database at our institution.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
One or more of the authors (VMG) have received funding and royalties from Zimmer, Inc, Warsaw, Ind.
Each author certifies that his or her institution has approved the human protocol for this investigation and that all investigations were conducted in conformity with ethical principles of research, and that informed consent for participation in the study was obtained.
About this article
Cite this article
Garcia, R.M., Hardy, B.T., Kraay, M.J. et al. Revision Total Knee Arthroplasty for Aseptic and Septic Causes in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis. Clin Orthop Relat Res 468, 82–89 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11999-009-1061-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11999-009-1061-x