Abstract
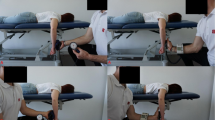
Reports using the Constant-Murley score often lack details regarding how strength measurement was performed, which may have an important impact on the results obtained. A description of the measurement is especially important when patients are unable to adopt the prescribed position of 90° shoulder abduction, leading to invalid or highly discrepant scores. We investigated the influence of shoulder abduction and torso position on strength measurement with special emphasis on intraobserver reliability. Thirty-three healthy volunteers were examined using a handheld dynamometer (Isobex®) in 30°, 60°, and 90° abduction with or without stabilization of the torso. A linear correlation between strength measurements in different degrees of abduction was observed, with values at 90° abduction on average 15% lower than at 60° and 45% lower than at 30°. In multivariate analysis, gender and weight had a substantial impact on the strength of individual measurement positions. Intraobserver reliability was related to arm and torso position (intraclass correlation coefficients, 0.71–0.93) and was highest for 90° abduction without torso stabilization. These findings emphasize the importance of standardized torso and arm positions ensuring high reliability when performing the strength measurement of the Constant-Murley score.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bankes MJ, Crossman JE, Emery RJ. A standard method of shoulder strength measurement for the Constant score with a spring balance. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 1998;7:116–121.
Beaton D, Richards RR. Assessing the reliability and responsiveness of 5 shoulder questionnaires. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 1998;7:565–572.
Boehm D, Wollmerstedt N, Doesch M, Handwerker M, Mehling E, Gohlke F. [Development of a questionnaire based on the Constant-Murley Score for self-evaluation of shoulder function by patients] [in German]. Unfallchirurg. 2004;107:397–402.
Brinker MR, Cuomo JS, Popham GJ, O’Connor DP, Barrack RL. An examination of bias in shoulder scoring instruments among healthy collegiate and recreational athletes. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2002;11:463–469.
Conboy VB, Morris RW, Kiss J, Carr AJ. An evaluation of the Constant-Murley shoulder assessment. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1996;78:229–232.
Constant CR. Age Related Recovery of Shoulder Function After Injury [master thesis, Mch]. Cork, Ireland: University College; 1986.
Constant CR. [Assessment of shoulder function] [in German]. Orthopade. 1991;20:289–294.
Constant CR. An evaluation of the Constant-Murley shoulder assessment. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1997;79:695–696.
Constant CR, Gerber C, Emery RJ, Søjbjerg JO, Gohlke F, Boileau P. A review of the Constant score: modifications and guidelines for its use. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2008;17:355–361.
Constant CR, Murley AH. A clinical method of functional assessment of the shoulder. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1987;214:160–164.
Dimakopoulos P, Kasimatis G, Panagopoulos A. Transosseous suture fixation of proximal humeral fractures. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2007;89:1700–1709.
Gerber C, Arneberg O. Measurement of abductor strength using an electronic device (Isobex). J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 1993;2:56.
Gerber C, Hersche O, Farron A. Isolated rupture of the subscapularis tendon. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1996;78:1015–1023.
Gore DR, Murray MP, Sepic SB, Gardner GM. Shoulder-muscle strength and range of motion following surgical repair of full-thickness rotator-cuff tears. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1986;68:266–272.
Hintermann B, Trouillier HH, Schäfer D. Rigid internal fixation of fractures of the proximal humerus in older patients. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2000;82:1107–1112.
Hirschmann M, Quarz V, Audige L, Ludin D, Messmer P, Regazzoni P, Gross T. Internal fixation of unstable proximal humerus fractures with an anatomically preshaped interlocking plate: a clinical and radiologic evaluation. J Trauma. 2007;63:1314–1323.
Johansson KM, Adolfsson LE. Intraobserver and interobserver reliability for the strength test in the Constant-Murley shoulder assessment. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2005;14:273–278.
Katolik LI, Romeo AA, Cole BJ, Verma NN, Hayden JK, Bach BR. Normalization of the Constant score. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2005;14:279–285.
Leggin BG, Neuman RM, Iannotti JP, Williams GR, Thompson EC. Intrarater and interrater reliability of three isometric dynamometers in assessing shoulder strength. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 1996;5:18–24.
Lillkrona U. How should we use the Constant Score? A commentary. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2008;17:362–363.
Meier R, Messmer P, Regazzoni P, Rothfischer W, Gross T. Unexpected high complication rate following internal fixation of unstable proximal humerus fractures with an angled blade plate. J Orthop Trauma. 2006;20:253–260.
Michiels I, Grevenstein J. Kinematics of shoulder abduction in the scapular plane: on the influence of abduction velocity and external load. Clin Biomech Bristol Avon. 1995;10:137–143.
Moonot P, Ashwood N, Hamlet M. Early results for treatment of three- and four-part fractures of the proximal humerus using the PHILOS plate system. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2007;89:1206–1209.
Moseley H. Examination of the Shoulder. New York, NY: Paul B. Hober; 1972.
Othman A, Taylor G. Is the Constant score reliable in assessing patients with frozen shoulder? 60 shoulders scored 3 years after manipulation under anaesthesia. Acta Orthop Scand. 2004;75:114–116.
Patel VR, Singh D, Calvert PT, Bayley JI. Arthroscopic subacromial decompression: results and factors affecting outcome. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 1999;8:231–237.
Robinson CM, Page RS. Severely impacted valgus proximal humeral fractures: results of operative treatment. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2003;85:1647–1655.
Rocourt MH, Radlinger L, Kalberer F, Sanavi S, Schmid NS, Leunig M, Hertel R. Evaluation of intratester and intertester reliability of the Constant-Murley shoulder assessment. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2008;17:364–369.
Sharkey NA, Marder RA, Hanson PB. The entire rotator cuff contributes to elevation of the arm. J Orthop Res. 1994;12:699–708.
Thomas M, Dieball O, Busse M. [Normal values of the shoulder strength in dependency on age and gender-comparison with the Constant, UCLA, ASES scores and SF36 health survey] [in German]. Z Orthop Ihre Grenzgeb. 2003;141:160–170.
Walton MJ, Walton JC, Honorez LA, Harding VF, Wallace WA. A comparison of methods for shoulder strength assessment and analysis of Constant score change in patients aged over fifty years in the United Kingdom. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2007;16:285–289.
Wijgman AJ, Roolker W, Patt TW, Raaymakers EL, Marti RK. Open reduction and internal fixation of three and four-part fractures of the proximal part of the humerus. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2002;84:1919–1925.
Yian EH, Ramappa AJ, Arneberg O, Gerber C. The Constant score in normal shoulders. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2005;14:128–133.
Acknowledgments
We thank J. Buchanan for editorial assistance with the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Each author certifies that he or she has no commercial associations (eg, consultancies, stock ownership, equity interest, patent/licensing arrangements, etc) that might pose a conflict of interest in connection with the submitted article.
Each author certifies that his or her institution has approved the human protocol for this investigation, that all investigations were conducted in conformity with ethical principles of research, and that informed consent for participation in the study was obtained.
This work was performed at Department of Orthopaedic Surgery and Traumatology, Kantonsspital Bruderholz.
About this article
Cite this article
Hirschmann, M.T., Wind, B., Amsler, F. et al. Reliability of Shoulder Abduction Strength Measure for the Constant-Murley Score. Clin Orthop Relat Res 468, 1565–1571 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11999-009-1007-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11999-009-1007-3