Abstract
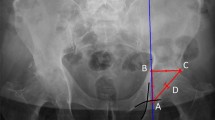
Precise evaluation of acetabular cup version is necessary for patients with recurrent hip dislocation after THA. We retrospectively studied 42 patients, who underwent THAs, with multiple cross-table lateral radiographs and CT scans to determine whether radiographic or CT measurement of acetabular component version is more accurate. One observer measured cup version on all radiographs. CT scans were interpreted by one observer. Twenty radiographs were measured twice each by two observers to determine intraobserver and interobserver reliability. We implanted cups in four model pelvises using navigation and compared measurements of anteversion made with radiographs and CT scans. Intraclass correlation coefficients (ICC) for anteversion measurements of two observers were 0.9990 and 0.9998, respectively, when comparing measurements of identical radiographs (intraobserver). Paired values for two observers measuring the same radiograph had an ICC of 0.9686 (interobserver) compared with 0.7412 for measurements from serial radiographs of the same component. The ICC comparing radiographic versus CT-based measurements was 0.6981. CT measurements had stronger correlations with navigated values than radiographic measurements. Accuracy of anteversion measurements on cross-table radiographs depends on radiographic technique and patient positioning whereas properly performed CT measurements are independent of patient position.
Level of Evidence: Level III, diagnostic study. See the Guidelines for Authors for a complete description of levels of evidence.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ackland MK, Bourne WB, Uhthoff HK. Anteversion of the acetabular cup. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1986;68:409–413.
Ali Khan MA, Brakenbury PH, Reynolds IS. Dislocation following total hip replacement. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1981;63:214–218.
Arai N, Nakamura S, Matsushita T. Difference between 2 measurement methods of version angles of the acetabular component. J Arthroplasty. 2007;22:715–720.
Biedermann R, Tonin A, Krismer M, Rachbauer F, Eibl G, Stockl B. Reducing the risk of dislocation after total hip arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2005;87:762–769.
Calvert GT, Devane PA, Fielden J, Adams K, Horne JG. A double-blind, prospective, randomized controlled trial comparing highly cross-linked and conventional polyethylene in primary total hip arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2008 Jun 9. [Epub ahead of print].
D’Lima DD, Urquhart AG, Buehler KO, Walker RH, Colwell CW Jr. The effect of the orientation of the acetabular and femoral components on the range of motion of the hip at different head-neck ratios. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2000;82:315–332.
Dorr LD, Malik A, Wan Z, Long WT, Harris M. Precision and bias of imageless computer navigation and surgeon estimates for acetabular component position. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2007;465:92–99.
Goergen TG, Resnick D. Evaluation of acetabular anteversion following total hip arthroplasty: necessity of proper centering. Br J Radiol. 1975;48:259–260.
Haaker RG, Tiedjen K, Ottersbach A, Rubenthaler F, Stockheim M, Stiehl JB. Comparison of conventional versus computer-navigated acetabular component insertion. J Arthroplasty. 2007;22:151–159.
Hassan DM, Johnston GH, Dust WN, Watson LG, Cassidy D. Radiographic calculation of anteversion in acetabular prostheses. J Arthroplasty. 1995;10:369–372.
Hassan DM, Johnston GH, Dust WN, Watson G, Dolovich AT. Accuracy of intraoperative assessment of acetabular prosthesis placement. J Arthroplasty. 1998;13:80–84.
Hayakawa K, Minoda Y, Aihara M, Sakawa A, Ohzono K, Tada K. Acetabular component orientation in intra- and postoperative positions in total hip arthroplasty. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2008 Apr 22. [Epub ahead of print].
Hirakawa K, Mitsugi N, Koshino T, Saito T, Hirasawa Y, Kubo T. Effect of acetabular cup position and orientation in cemented total hip arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2001;388:135–142.
Kalteis T, Handel M, Herold T, Perlick L, Paetzel C, Grifka J. Position of the acetabular cup: accuracy of radiographic calculation compared to CT-based measurement. Eur J Radiol. 2006;58:294–300.
Kennedy JG, Rogers WB, Soffe KE, Sullivan RJ, Griffen DG, Sheehan LJ. Effect of acetabular component orientation on recurrent dislocation, pelvic osteolysis, polyethylene wear and component migration. J Arthroplasty. 1998;13:530–534.
Lembeck B, Mueller O, Reize P, Wuelker N. Pelvic tilt makes acetabular cup navigation inaccurate. Acta Orthop. 2005;76:517–523.
Lewinnek GE, Lewis JL, Tarr R, Compere CL, Zimmermann JR. Dislocation after total hip-replacement arthroplasties. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1978;60:217–220.
Liaw CK, Hou SM, Yang RS, Wu TY, Fuh CS. A new tool for measuring cup orientation in total hip arthroplasties from plain radiographs. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2006;451:134–139.
Liaw CK, Yang RS, Hou SM, Wu TY, Fuh CS. Measurement of the acetabular cup anteversion on the simulated radiographs. J Arthroplasty. 2008 Apr 2. [Epub ahead of print].
Marx A, von Knoch M, Pfortner J, Wiese M, Saxler G. Misinterpretation of cup anteversion in total hip arthroplasty using planar radiography. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2006;126:487–492.
McCollum DE, Gray WJ. Dislocation after total hip arthroplasty: causes and prevention. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1990;261:159–170.
Mian SW, Truchly G, Pflum FA. Computer tomography measurement of acetabular cup anteversion and retroversion in total hip arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1992;276:206–209.
Munro BH. Correlation. In: Munro BH, ed. Statistical Methods for Healthcare Research. 3rd ed. Philadelphia, PA: Lippincott-Raven; 1997:224–245.
Murray DW. The definition and measurement of acetabular orientation. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1993;75:228–232.
Najarian BC, Kilgore JE, Markel DC. Evaluation of component positioning in primary total hip arthroplasty using an imageless navigation device compared with traditional methods. J Arthroplasty. 2008;24:15–21.
Nogler M, Kessler O, Prassl A, Donnelly B, Streicher R, Sledge JB, Krismer M. Reduced variability of acetabular cup positioning with use of an imageless navigation system. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2004;426:159–163.
Olivecrona H, Weidenhielm L, Olivecrona L, Beckman MO, Stark A, Noz ME, Maguire GQ, Zeleznik MP, Svensson L, Jonson T. A new CT method for measuring cup orientation after total hip arthroplasty. Acta Orthop Scand. 2004;75:252–260.
Ritter MA. Dislocation and subluxation of the total hip replacement. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1976;121:92–94.
Sah AP, Estok DM 2nd. Dislocation rate after conversion from hip hemiarthroplasty to total hip arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2008;90:506–516.
Schmalzried TP, Guttmann D, Grecula M, Amstutz H. The relationship between the design, position, and articular wear of acetabular components inserted without cement and the development of pelvic osteolysis. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1994;76:677–688.
Seradge H, Nagle KR, Miller RJ. Analysis of version in the acetabular cup. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1982;166:152–157.
Wines AP, McNicol D. Computer tomography measurement of the accuracy of component version in total hip arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2006;21:696–701.
Yao L, Yao J, Gold RH. Measurement of acetabular version on the axiolateral radiograph. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1995;316:106–111.
Acknowledgments
We thank Dr. Thomas P. Sculco for allowing use of his patients in this study, Clara Hilario for assistance in the computer navigation laboratory, and Gregory Schack of Smith and Nephew for donating the computer navigation system and acetabular components used in the study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Each author certifies that he or she has no commercial associations (eg, consultancies, stock ownership, equity interest, patent/licensing arrangements, etc) that might pose a conflict of interest in connection with the submitted article.
Each author certifies that his or her institution has approved the human protocol for this investigation and that all investigations were conducted in conformity with ethical principles of research.
About this article
Cite this article
Ghelman, B., Kepler, C.K., Lyman, S. et al. CT Outperforms Radiography for Determination of Acetabular Cup Version after THA. Clin Orthop Relat Res 467, 2362–2370 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11999-009-0774-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11999-009-0774-1