Abstract
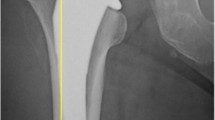
Either excessive or insufficient cement penetration within the femoral head after hip resurfacing influences the risk of femoral failures. However, the factors controlling cement penetration are not yet fully understood. We determined the effect of femoral component design and cementation technique on cement penetration. Six retrieved femoral heads were resurfaced for each implant (BHR®, ASR®, Conserve Plus®, DuROM®, ReCAP®) using the manufacturers’ recommendations for implantation. In addition, the BHR was implanted using the Conserve Plus® high-viscosity cementation technique, “BHR/hvt,” and vice versa for the Conserve, “Conserve/lvt.” The average cement penetration was highest with BHR (65.62% ± 15.16%) compared with ASR® (12.25% ± 5.12%), Conserve Plus® (19.43% ± 5.28%), DuROM® (17.73% ± 3.96%), and ReCAP® (26.09% ± 5.20%). Cement penetration in BHR/hvt remained higher than all other implants equaling 36.7% ± 6.6%. Greater femoral component design clearance correlated with cement mantle thickness. Femoral component design in hip resurfacing plays a major role in cement penetration.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amstutz HC, Beaule PE, Dorey FJ, Campbell PA, Le Duff MJ, Gruen TA. Metal-on-metal hybrid surface arthroplasty: two to six year follow-up. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2004;86:28–39.
Amstutz HC, Dorey F, O’Carroll PF. THARIES resurfacing arthroplasty. Evolution and long-term results. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1986;213:92–114.
Amstutz HC, Le Duff MJ, Campbell PA. Fracture of the neck of the femur after surface arthroplasty of the hip. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2004;86:1874–1877.
Amstutz HC, LeDuff MJ, Campbell PA, Dorey FJ. The effects of technique changes on aseptic loosening of the femoral component in hip resurfacing. Results of 600 Conserve Plus with a 3 to 9 year follow-up. J Arthroplasty. 2007;22:481–489.
Askew MJ, Streege JW, Lewis JL, Ranieri JR, Wixson RL. Effect of cement pressure and bone strength on polymethylmethacrylate fixation. J Orthop Res. 1984;1:412–420.
Beaule PE. Surface arthroplasty of the hip: a review and current indications. Semin Arthroplasty. 2005;16:70–76.
Beaule PE, Antoniades J. Patient selection and surgical technique for surface arthroplasty of the hip. Orthop Clin North Am. 2005;36:177–185.
Beaule PE, Campbell PA, Hoke R, Dorey FJ. Notching of the femoral neck during resurfacing arthroplasty of the hip. A vascular study. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2006;88:35–39.
Beaule PE, Campbell PA, Lu Z, Leunig-Ganz K, Beck M, Leunig M, Ganz R. Vascularity of the arthritic femoral head and hip resurfacing. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2006;88:85–96.
Beaule PE, Dorey FJ, LeDuff MJ, Gruen T, Amstutz HC. Risk factors affecting outcome of metal on metal surface arthroplasty of the hip. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2004;418:87–93.
Beaule PE, Krismer M, Mayrhofer P, Manner M, Le Duff MJ, Mattesich M, Stoeckl B, Amstutz HC, Biedermann R. EBRA-FCA for measurement of migration of the femoral component in surface arthroplasty of the hip. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2005;87:741–744.
Beaule PE, Lee J, LeDuff M, Dorey FJ, Amstutz HC, Ebramzadeh E. Orientation of femoral component in surface arthroplasty of the hip: a biomechanical and clinical analysis. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2004;86:2015–2021.
Benjamin JB, Gie GA, Lee AJC, Ling RSM, Volz RG. Cementing technique and the effects of bleeding. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1987;69:620–624.
Bitsch R, Heisel C, Silva M, Schmalzried TP. Femoral cementing technique for hip resurfacing arthroplasty. J Orthop Res. 2007;25:423–431.
Callaghan JJ. Total hip arthroplasty. Clinical perspective. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1992;276:33–40.
Campbell PA, Beaule PE, Ebramzadeh E, LeDuff MJ, DeSmet KA, Lu Z, Amstutz HC. The John Charnley Award: a study of implant failure in metal-on-metal surface arthroplasties. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2006;453:35–46.
Chandler M, Kowalski RSZ, Watkins ND, Briscoe A, New AMR. Cementing techniques in hip resurfacing. Proc Inst Mech Eng [H]. 2006;220:321–331.
Daniel J, Pynsent PB, McMinn DJW. Metal-on-metal resurfacing of the hip in patients under the age of 55 years with osteoarthritis. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2004;86:177–184.
Ebramzadeh E, Sarmiento A, McKellop HA, Llinas A, Gogan W. The cement mantle in total hip arthroplasty. Analysis of long-term radiographic results. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1994;76:77-87.
Grigoris P, Roberts P, Panousis K, Bosch H. The evolution of hip resurfacing arthroplasty. Orthop Clin North Am. 2005;36:125–134.
Hing CB, Young DA, Dalziel RE, Bailey M, Back DL, Shimmin AJ. Narrowing of the neck in resurfacing arthroplasty of the hip: a radiological study. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2007;89:1019–1024.
Howald R, Kesteris U, Klabunde R. Factors affecting the cement penetration of a hip resurfacing implant: an in-vitro study [Abstract]. Osteologie. 2005;14:10.
Howie DW, Campbell D, McGee M, Cornish BL. Wagner resurfacing hip arthroplasty. The results of one hundred consecutive arthroplasties after eight to ten years. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1990;72:708–714.
Huiskes R, Heck J, Slooff TJJH. Interface stresses in the resurfaced hip. Finite element analysis of load transmission in the femoral head. Acta Orthop Scand. 1985;56:474–478.
Jansson V, Kheimkes B, Zimmer M. Stress transfer at the femoral bone/bone cement interface as a function of the cement thickness. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 1993;112:65–68.
Jolley MN, Salvati EA, Brown GC. Early results and complications of surface replacement of the hip. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1982;64:366–377.
Juliusson R, Flivik G, Nilsson J, Ryd L, Onnerfalt R. Circulating blood diminishes cement penetration into cancellous bone. In vitro studies of 21 arthrotic femoral heads. Acta Orthop Scand. 1995;66:234–238.
Juliusson R, Ryd L, Arve J. Cementation pressure in arthroplasty. In vitro study of cement penetration into femoral heads. Acta Orthop Scand. 1994;65:131–134.
Kilgus DJ, Dorey FJ, Finerman GA, Amstutz HC. Patient activity, sports participation, and impact loading on the durability of cemented total hip replacements. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1991;269:25–31.
Krause WR, Krug W, Miller J. Strength of the cement-bone interface. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1982;163:290–299.
Little CP, Ruiz AL, Harding IJ, McLardy-Smith P, Gundle R, Murray DW, Athanasou NA. Osteonecrosis in retrieved femoral heads after failed resurfacing arthroplasty of the hip. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2005;87:320–323.
Markolf KL, Amstutz HC. In vitro measurement of bone-acrylic interface pressure during femoral component insertion. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1976;121:60–66.
Markolf KL, Kabo JM, Stoller DW, Zager SA, Amstutz HC. Flow characteristics of acrylic bone cements. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1984;183:246–254.
Mjoberg B, Pettersson H, Rosenqvist R, Rydholm A. Bone cement, thermal injury and the radiolucent zone. Acta Orthop Scand. 1984;55:597–600.
Mont MA, Seyler TM, Ulrich SD, Beaule PE, Boyrd HS, Grecula MJ, Goldberg VM, Kennedy WR, Marker DR, Schmalzried TP, Sparling EA, Vail TP, Amstutz HC. Effect of changing indications and techniques on total hip resurfacing. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2007;465:63–70.
Morlock MM, Bishop N, Ruther W, Delling G, Hahn M. Biomechanical, morphological, and histological analysis of early failures in hip resurfacing. Proc Inst Mech Eng [H]. 2006;220:333–344.
Noble PC, Swarts E. Penetration of acrylic bone cements into cancellous bone. Acta Orthop Scand. 1983;54:566–573.
Pollard TCB, Baker RP, Eastaugh-Waring SJ, Bannister GC. Treatment of the young active patient with osteoarthritis of the hip. Two to seven year comparison of hybrid total hip arthroplasty and metal-on-metal resurfacing. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2006;88:592–600.
Radcliffe IA, Taylor M. Investigation into the affect of cementing techniques on load transfer in the resurfaced femoral head: a multi-femur finite element analysis. Clin Biomech (Bristol, Avon). 2007;22:422–430.
Shimmin A, Back D. Femoral neck fractures following Birmingham hip resurfacing. A national review of 50 cases. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2005;87:463–464.
Treacy R, Pynsent P. Birmingham Hip Resurfacing arthroplasty. A minimum follow-up of five years. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2005;87:167–170.
Trudel G, Koike Y, Dinh L, Uhthoff HK. Thawing of frozen calcaneus bone specimens has no effect on the bone mineral density using dual energy x-ray absorptiometry: a study in rabbits and humans. Physiol Meas. 2005;26:769–777.
Valdivia GG, Dunbar MJ, Parker DA, Woolfrey MR, MacDonald SJ, McCalden RW, Rorabeck CH, Bourne RB. The John Charnley Award: three-dimensional analysis of the cement mantle in total hip arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2001;393:38–51.
Watanabe Y, Shiba N, Matsuo S, Higuchi F, Tagawa Y, Inoue A. Biomechanical study of the resurfacing hip arthroplasty. Finite element analysis of the femoral component. J Arthroplasty. 2000;15:505–511.
Acknowledgments
We thank Patricia Campbell, PhD, and Christina Esposito from Los Angeles Orthopaedic Hospital for their assistance in cutting the DuROM® resurfaced femoral heads; Diane Robertson for her assistance in collecting the femoral heads; Philippe St-Laurent for his assistance with the DEXA scans; Maryam Shahrokni for her assistance in cutting the femoral heads; and Steve Doucette, PhD, for statistical support. Finally, this study would not have been possible without the manufacturers of implants and bone cement providing the materials free of charge.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
One or more of the authors (PEB) have received funding from Wright Medical Technologies.
Each author certifies that his or her institution has approved the human protocol for this investigation and that all investigations were conducted in conformity with ethical principles of research.
About this article
Cite this article
Beaulé, P.E., Matar, W.Y., Poitras, P. et al. 2008 Otto Aufranc Award: Component Design and Technique Affect Cement Penetration in Hip Resurfacing. Clin Orthop Relat Res 467, 84–93 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11999-008-0541-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11999-008-0541-8