Abstract
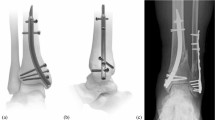
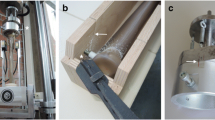
Recently developed inflatable nails avoid reaming and interlocking screws in tibial fractures and reflect a new principle for stabilization of long bone fractures. We asked if the bending stiffness, rotational rigidity, or play (looseness of rotation) differed between an inflatable versus large-diameter reamed interlocked nails, and whether the maximal torque to failure of the two bone-implant constructs differed. In a cadaveric model, we compared the biomechanical properties with those of an interlocked nail in eight pairs of fractured tibial bones. Bending stiffness, rotational rigidity, play (looseness in rotation), and torsional strength within 20° rotation were investigated using a biaxial servohydraulic testing system. For all biomechanical variables, we found a large interindividual variance between the pairs attributable to bone quality (osteoporosis) for both fixation methods. The inflatable nail had a higher bending stiffness, with a mean difference of 58 N/mm, and a lower torsional strength, with a mean difference of 13.5 Nm, compared with the locked nail. During torsional testing we noted slippage between the inflatable nail and bone. We observed no differences in play or rotational rigidity. Given the lower torsional strength we recommend caution with weightbearing until there are signs of fracture consolidation.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alho A, Benterud JG, Høgevold HE, Ekeland A, Stromsøe K. Comparison of functional bracing and locked intramedullary nailing in the treatment of displaced tibial shaft fractures. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1992;277:243–250.
Augat P, Burger J, Schorlemmer S, Henke T, Peraus M, Claes L. Shear movement at the fracture site delays healing in a diaphyseal fracture model. J Orthop Res. 2003;21:1011–1017.
Ben-Galim P, Rosenblatt Y, Parnes N, Dekel S, Steinberg EL. Intramedullary fixation of tibial shaft fractures using an expandable nail. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2007;455:234–240.
Blachut PA, O’Brien PJ, Meek RN, Broekhuyse HM. Interlocking intramedullary nailing with and without reaming for the treatment of closed fractures of the tibial shaft: a prospective, randomized study. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1997;79:640–646.
Blum J, Karagul G, Sternstein W, Rommens PM. Bending and torsional stiffness in cadaver humeri fixed with a self-locking expandable or interlocking nail system: a mechanical study. J Orthop Trauma. 2005;19:535–542.
Capelli RM, Galmarini V, Molinari GP, De Amicis A. The Fixion expansion nail in the surgical treatment of diaphyseal fractures of the humerus and tibia: our experience. Chir Organi Mov. 2003;88:57–64.
Court-Brown CM. Reamed intramedullary tibial nailing: an overview and analysis of 1106 cases. J Orthop Trauma. 2004;18:96–101.
Finkemeier CG, Schmidt AH, Kyle RF, Templeman DC, Varecka TF. A prospective, randomized study of intramedullary nails inserted with and without reaming for the treatment of open and closed fractures of the tibial shaft. J Orthop Trauma. 2000;14:187–193.
Franck WM, Olivieri M, Jannasch O, Hennig FF. An expandable nailing system for the management of pathological humerus fractures. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2002;122:400–405.
Gugala Z, Nana A, Lindsey RW. Tibial intramedullary nail distal interlocking screw placement: comparison of the free-hand versus distally-based targeting device techniques. Injury. 2001;32(suppl 4):SD21–SD25.
Harris I, Lyons M. Reoperation rate in diaphyseal tibia fractures. ANZ J Surg. 2005;75:1041–1044.
Hooper GJ, Keddell RG, Penny ID. Conservative management or closed nailing for tibial shaft fractures: a randomised prospective trial. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1991;73:83–85.
Jovanovic A, Pirpiris M, Semirli H, Doig SG. Fixion nails for humeral fractures. Injury. 2004;35:1140–1142.
Kahn KM, Beals RK. Malrotation after locked intramedullary tibial nailing: three case reports and review of the literature. J Trauma. 2002;53:549–552.
Karladani AH, Granhed H, Edshage B, Jerre R, Styf J. Displaced tibial shaft fractures: a prospective randomized study of closed intramedullary nailing versus cast treatment in 53 patients. Acta Orthop Scand. 2000;71:160–167.
Koval KJ, Clapper MF, Brumback RJ, Ellison PS Jr, Poka A, Bathon GH, Burgess AR. Complications of reamed intramedullary nailing of the tibia. J Orthop Trauma. 1991;5:184–189.
Martens M, van Audekercke R, de Meester P, Mulier JC. The mechanical characteristics of the long bones of the lower extremity in torsional loading. J Biomech. 1980;13:667–676.
Mølster AO. Effects of rotational instability on healing of femoral osteotomies in the rat. Acta Orthop Scand. 1984;55:632–636.
Puloski S, Romano C, Buckley R, Powell J. Rotational malalignment of the tibia following reamed intramedullary nail fixation. J Orthop Trauma. 2004;18:397–402.
Sanders R, Koval KJ, DiPasquale T, Schmelling G, Stenzler S, Ross E. Exposure of the orthopaedic surgeon to radiation. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1993;75:326–330.
Schandelmaier P, Krettek C, Tscherne H. Biomechanical study of nine different tibia locking nails. J Orthop Trauma. 1996;10:37–44.
Seligson D, Byrt W, Hogan M, Pope M. The mechanical basis for the combined use of internal and external fixation by direct measurement of fracture gap motion (abstract). 2nd International Symposium on Internal Fixation of Fractures. Lyon, France: Faculte Medecine Alexis Carrel; 1982:166–167.
Smith MG, Canty SJ, Khan SA. Fixion: an inflatable or deflatable nail? Injury. 2004;35:329–331.
Steinberg EL, Blumberg N, Dekel S. The Fixion proximal femur nailing system: biomechanical properties of the nail and a cadaveric study. J Biomech. 2005;38:63–68.
Steinberg EL, Geller DS, Yacoubian SV, Shasha N, Dekel S, Lorich DG. Intramedullary fixation of tibial shaft fractures using an expandable nail: early results of 54 acute tibial shaft fractures. J Orthop Trauma. 2006;20:303–309.
Acknowledgments
We thank Stein Atle Lie, PhD, Department of Health, University Research Bergen, for assistance in the statistical analysis.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Each author certifies that he or she has no commercial associations (eg, consultancies, stock ownership, equity interest, patent/licensing arrangements, etc) that might pose a conflict of interest in connection with the submitted article.
Each author certifies that his or her institution has approved the human protocol for this investigation and that all investigations were conducted in conformity with ethical principles of research.
About this article
Cite this article
Blomquist, J., Lundberg, O.J., Gjerdet, N.R. et al. Are Inflatable Nails an Alternative to Interlocked Nails in Tibial Fractures?. Clin Orthop Relat Res 466, 1225–1231 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11999-008-0169-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11999-008-0169-8