Abstract
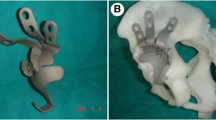
Combined segmental and cavitary deficiencies of the acetabulum (American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons Type III) are a difficult problem that revision arthroplasty surgeons must tackle with increasing frequency. Porous-coated bilobed acetabular components are a reconstruction option that allows for increased host bone-prosthesis contact with restoration of the anatomic hip center without the use of a structural bone graft. Eleven consecutive Type III acetabular defects in 11 patients were revised with a porous-coated bilobed cup without a structural bone graft between January 1999 and January 2001 and prospectively followed. Average Harris hip scores improved from 36 preoperatively to 85 postoperatively. Radiographic analysis showed improvement in the average vertical displacement of the hip center. Average leg length discrepancies decreased from 34 mm preoperatively to 7 mm postoperatively. There have been no revisions performed or planned. Porous-coated bilobed acetabular components can provide good clinical and radiographic results at intermediate followup for treatment of Type III acetabular deficiencies. Bilobed components offer a viable option for reconstruction of Type III defects without the use of a structural bone graft or cement while maximizing the host bone-implant contact and restoring the native hip center.
Level of Evidence: Level IV, therapeutic study. See the Guidelines for Authors for a complete description of levels of evidence.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Berry DJ, Müller ME. Revision arthroplasty using an anti-protrusio cage for massive acetabular deficiency. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1992;74:711–715.
Berry DJ, Sutherland CJ, Trousdale RT, Colwell CW Jr, Chandler HP, Ayres D, Yashar AA. Bilobed oblong porous coated acetabular components in revision total hip arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2000;371:154–160.
Bolder SB, Melenhorst J, Gardeniers JWM, Slooff TJ, Veth RPH, Schreurs BW. Cemented total hip arthroplasty with impacted morcellized bone-grafts to restore acetabular bone defects in congenital hip dysplasia. J Arthroplasty. 2001;16(8 suppl 1):164–169.
Callaghan JJ, Salvati EA, Pellicci PM, Wilson PD Jr, Ranawat CS. Results of revision for mechanical failure after cemented total hip replacement, 1972–1982: a two to five-year follow-up. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1985;67:1074–1085.
Chen WM, Engh CA Jr, Hopper RH Jr, McAuley JP, Engh CA. Acetabular revision with use of a bilobed component inserted without cement in patients who have acetabular bone stock deficiency. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2000;82:197–206.
D’Antonio JA, Capello WN, Borden LS, Bargar WL, Bierbaum BF, Boettcher WG, Steinberg ME, Stulberg SD, Wedge JH. Classification and management of acetabular abnormalities in total hip arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1989;243:126–137.
Dearborn JT, Harris WH. Acetabular revision arthroplasty using so-called jumbo cementless components: an average 7-year follow-up study. J Arthroplasty. 2000;15:8–15.
DeBoer DK, Christie MJ. Reconstruction of the deficient acetabulum with an oblong prosthesis: three to seven-year results. J Arthroplasty. 1998;13:674–680.
DeLee JG, Charnley J. Radiological demarcation of cemented sockets in total hip replacement. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1976;121:20–32.
Dorr LD, Wan Z. Ten years of experience with porous acetabular components for revision surgery. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1995;319:191–200.
Garbuz D, Morsi E, Gross AE. Revision of the acetabular component of a total hip arthroplasty with a structural allograft: study with a minimum five-year follow-up. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1996;78:693–697.
Gerber SD, Harris WH. Femoral head autografting to augment acetabular deficiency in patients requiring hip replacement: a minimum five-year and an average seven-year follow-up study. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1986;68:1241–1248.
Gie GA, Linder L, Ling LS, Simon JP, Slooff TJ, Timperley AJ. Impacted cancellous allografts and cement for revision total hip arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1993;75:14–21.
Glassman AH, Engh CA, Bobyn JD. A technique of extensile exposure for total hip arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 1987;2:11–21.
Hooten JP Jr, Engh CA Jr, Engh CA. Failure of structural acetabular allografts in cementless revision hip arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1994;76:419–422.
Jasty M, Harris WH. Salvage total hip reconstruction in patients with major acetabular bone deficiency using structural femoral head allografts. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1990;72:63–67.
Kwong LM, Jasty M, Harris WH. High failure rate of bulk femoral head allografts in total hip acetabular reconstructions at 10 years. J Arthroplasty. 1993;8:341–346.
Linde F, Jensen J. Socket loosening in arthroplasty for congenital dislocation of the hip. Acta Orthop Scand. 1988;59:254–257.
Moskal JT, Danisa OA, Shaffrey CI. Isolated revision acetabuloplasty using a porous-coated cementless acetabular component without removal of a well-fixed femoral component: a 3- to 9-year follow-up study. J Arthroplasty. 1997;12:719–727.
Moskal JT, Shen FH. The use of bilobed-porous coated acetabular components without structural bone graft for type III acetabular defects in revision total hip arthroplasty: a prospective study with a minimum 2-year follow-up. J Arthroplasty. 2004;19:867–873.
Moskal JT, Shen FH, Brown TE. The fate of stable femoral components retained during isolated acetabular revision: a six- to twelve-year follow-up study. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2002;84:250–255.
Nehme A, Lewallen DG, Hanssen AD. Modular porous metal augments for treatment of severe acetabular bone loss during revision total hip arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2004;429:201–208.
Paprosky WG, Magnus RE. Principals of bone grafting in revision total hip arthroplasty: acetabular technique. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1994;298:147–155.
Pollock FH, Whiteside LA. The fate of massive allografts in total hip revision acetabular surgery. J Arthroplasty. 1992;7:271–276.
Russotti GM, Harris WH. Proximal placement of the acetabular component in total hip arthroplasty: a long term follow-up study. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1991;73:587–592.
Schreurs BW, Thien TM, de Waal Malefijt MC, Buma P, Veth RP, Slooff TJ. Acetabular revision with impacted morselized cancellous bone graft and a cemented cup in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: three to fourteen-year follow-up. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2003;85:647–652.
Schutzer SF, Harris WH. High placement of porous-coated acetabular components in complex total hip arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 1994;9:359–367.
Stulberg SD. Impaction grafting: doing it right. J Arthroplasty. 2002;17(4 suppl 1):147–152.
Sutherland CJ. Treatment of type III acetabular deficiencies in revision total hip arthroplasty without structural bone graft. J Arthroplasty. 1996;11:91–98.
Unger AS, Lewis RJ, Greun T. Evaluation of a porous tantalum uncemented acetabular cup in revision total hip arthroplasty: clinical and radiological results of 60 hips. J Arthroplasty. 2005;20:1002–1009.
Whaley AL, Berry DJ, Harmsen WS. Extra-large uncemented hemispherical acetabular components for revision total hip arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2001;83:1352–1357.
Acknowledgments
We thank Linda L. Franklin, RN, ONC, for help in collecting Harris hip scores.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Each author certifies that he or she has no commercial associations (eg, consultancies, stock ownership, equity interest, patent/licensing arrangements, etc) that might pose a conflict of interest in connection with the submitted article.
Each author certifies that his or her institution has either waived or does not require approval for the human study protocol for this investigation and that all investigations were conducted in conformity with ethical principles of research.
An erratum to this article can be found at http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s11999-008-0215-6.
About this article
Cite this article
Moskal, J.T., Higgins, M.E. & Shen, J. Type III Acetabular Defect Revision With Bilobed Components. Clin Orthop Relat Res 466, 691–695 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11999-007-0079-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11999-007-0079-1