Abstract
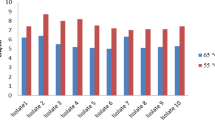
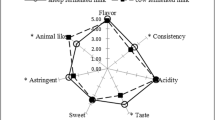
The objective of this study was to evaluate the suitability of two strains of probiotic bacteria (Bifidobacterium animalis subsp. lactis and Lactobacillus rhamnosus) incorporated individually into Boursin-type goat cheese and their in vitro resistance through the passage of the gastrointestinal tract in the cheese. The viability of B. lactis and Lb. rhamnosus cultures was unaffected throughout 35 days of storage at 4 °C, with a final count of > 7 log CFU/g. No significant difference (p > 0.05) was observed between probiotic treatments and control in relation to pH and titratable acidity. B. animalis presented greater resistance to the artificial gastric and enteric juices than Lb. rhamnosus, with mean decreases in the initial populations of 0.2 and 4.0 log CFU/g within 35 days of storage, respectively. The addition of probiotic cultures did not affect the consumer acceptance of the goat cheeses. Three segments of consumers with different liking were identified. The results demonstrated that “Boursin” goat cheese is a promising matrix for the incorporation and protection of B. animalis subsp. lactis.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abadía-García, L., Cardador, A., Martín del Campo, S. T., Arvízu, S. M., Castaño-Tostado, E., Regalado-González, C., et al. (2013). Influence of probiotic strains added to cottage cheese on generation of potentially antioxidant peptides, anti-listerial activity, and survival of probiotic microorganisms in simulated gastrointestinal conditions. International Dairy Journal, 33(2), 191–197. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.idairyj.2013.04.005
Aljewicz, M., & Cichosz, G. (2015). The effect of probiotic Lactobacillus rhamnosus HN001 on the in vitro availability of minerals from cheeses and cheese-like products. LWT - Food Science and Technology, 60(2, part 1), 841–847. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lwt.2014.09.052
AOAC. (1996). Official methods of analysis. Arlington: EUA: Association of Official Analytical Chemists.
AOAC (2002). Official methods of analysis—991.14. EUA: Association of Official Analytical Chemist.
AOAC. (2005). Official methods of analysis. Washington: Association of Official Analytical Chemists.
AOAC. (2010). Official methods of analysis. EUA: Association of Official Analytical Chemist.
Bedani, R., Rossi, E. A., & Saad, S. M. I. (2013). Impact of inulin and okara on Lactobacillus acidophilus La-5 and Bifidobacterium animalis Bb-12 viability in a fermented soy product and probiotic survival under in vitro simulated gastrointestinal conditions. Food Microbiology, 34(2), 382–389. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fm.2013.01.012
Bezerra, T. K. A., de Araujo, A. R. R., do Nascimento, E. S., de Matos Paz, J. E., Gadelha, C. A., Gadelha, T. S., et al. (2016). Proteolysis in goat “coalho” cheese supplemented with probiotic lactic acid bacteria. Food Chemistry, 196, 359–366. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2015.09.066
Brasil (1996). Regulamentos Técnicos de Identidade e Qualidade dos Produtos Lácteos. In P. e. A. Ministro de Estado da Agricultura (Ed.), Portaria n° 146 de 07 de março de 1996 Brasília: Ministério da Agricultura Secretaria de Defesa Agropecuária.
BRASIL (2003). Resolução RDC n° 359, de 23 de dezembro de 2003. Aprova Regulamento Técnico de Porções de Alimentos Embalados para Fins de Rotulagem Nutricional. In ANVISA (Ed.). Brasília: D.O.U.—Diário Oficial da União.
Brasil (2017). Alimentos com alegações de propriedades funcionais e ou de saúde, novos alimentos/ingredientes, substâncias bioativas e probióticos. In ANVISA (Ed.). Brasília,.
Brodziak, A., Król, J., Barłowska, J., & Litwińczuk, Z. (2014). Effect of production season on protein fraction content in milk of various breeds of goats in Poland. International Journal of Dairy Technology, 67(3), 410–419. https://doi.org/10.1111/1471-0307.12130
Cárdenas, N., Calzada, J., Peirotén, Á., Jiménez, E., Escudero, R., Rodríguez, J. M., Medina, M., & Fernández, L. (2014). Development of a potential probiotic fresh cheese using two Lactobacillus salivarius strains isolated from human milk. BioMed Research International, 2014, 1–12. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/801918
Champagne, C. P., Ross, R. P., Saarela, M., Hansen, K. F., & Charalampopoulos, D. (2011). Recommendations for the viability assessment of probiotics as concentrated cultures and in food matrices. International Journal of Food Microbiology, 149(3), 185–193. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2011.07.005
Chaves, K. S., & Gigante, M. L. (2016). Prato cheese as suitable carrier for Lactobacillus acidophilus La5 and Bifidobacterium Bb12. International Dairy Journal, 52, 10–18. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.idairyj.2015.08.009
Collado, M. C., & Sanz, Y. (2007). Induction of acid resistance in Bifidobacterium: a mechanism for improving desirable traits of potentially probiotic strains. Journal of Applied Microbiology, 103(4), 1147–1157. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2672.2007.03342.x
Correia, R. T. P., & Borges, K. C. (2009). Posicionamento do consumidor frente ao consumo de leite de cabra e seus derivados na cidade de Natal-RN. Revista do Instituto de Laticínios Cândido Tostes, 64(366), 36–43.
Costa, M. P., Balthazar, C. F., Franco, R. M., Mársico, E. T., Cruz, A. G., & Conte Junior, C. A. (2014). Changes on expected taste perception of probiotic and conventional yogurts made from goat milk after rapidly repeated exposure. Journal of Dairy Science, 97(5), 2610–2618. https://doi.org/10.3168/jds.2013-7617
Cruz, A. G. d., Buriti, F. C. A., Souza, C. H. B. d., Faria, J. A. F., & Saad, S. M. I. (2009). Probiotic cheese: health benefits, technological and stability aspects. Trends in Food Science & Technology, 20(8), 344–354. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tifs.2009.05.001
Cruz, A. G., Cadena, R. S., Walter, E. H. M., Mortazavian, A. M., Granato, D., Faria, J. A. F., & Bolini, H. M. A. (2010). Sensory analysis: relevance for prebiotic, probiotic, and synbiotic product development. Comprehensive Reviews in Food Science and Food Safety, 9(4), 358–373. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1541-4337.2010.00115.x
da Silva, P. D. L., de Bezerra, M. F., dos Santos, K. M. O., & Correia, R. T. P. (2015). Potentially probiotic ice cream from goat’s milk: characterization and cell viability during processing, storage and simulated gastrointestinal conditions. LWT - Food Science and Technology, 62(1, Part 2), 452–457. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lwt.2014.02.055
da Silveira, E. O., Lopes Neto, J. H., da Silva, L. A., Raposo, A. E. S., Magnani, M., & Cardarelli, H. R. (2015). The effects of inulin combined with oligofructose and goat cheese whey on the physicochemical properties and sensory acceptance of a probiotic chocolate goat dairy beverage. LWT - Food Science and Technology, 62(1, Part 2), 445–451. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lwt.2014.09.056
Daddaoua, A., Puerta, V., Requena, P., Martínez-Férez, A., Guadix, E., Sánchez de Medina, F., et al. (2006). Goat milk oligosaccharides are anti-inflammatory in rats with Hapten-induced colitis. The Journal of Nutrition, 136(3), 672–676.
de Azambuja Ribeiro, E. L., & de Souza Ribeiro, H. J. S. (2001). Uso nutricional e terapêutico do leite de cabra. Semina: Ciências Agrárias, 22(2), 229–235. https://doi.org/10.5433/1679-0359.2001v22n2p229
de Azambuja Ribeiro, E. L., & de Souza Ribeiro, H. J. S. (2010). Specialty products made from goat milk. Small Ruminant Research, 89(2–3), 225–233. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.smallrumres.2009.12.048
de Cássia Ramos do Egito Queiroga, R., Santos, B. M., Gomes, A. M. P., Monteiro, M. J., Teixeira, S. M., de Souza, E. L., et al. (2013). Nutritional, textural and sensory properties of Coalho cheese made of goats’, cows’ milk and their mixture. LWT - Food Science and Technology, 50(2), 538–544. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lwt.2012.08.011
de Oliveira, G. M. E., Garcia, E. F., de Cássia Ramos do Egito Queiroga, R., & Souza, E. L. d. (2012). Technological, physicochemical and sensory characteristics of a Brazilian semi-hard goat cheese (coalho) with added probiotic lactic acid bacteria. Scientia Agricola, 69(6), 370–379. https://doi.org/10.1590/S0103-90162012000600005
de Oliveira, G. M. E., Fernandes Garcia, E., Vasconcelos de Oliveira, C. E., Pereira Gomes, A. M., Esteves Pintado, M. M., Ferreira Madureira, A. R. M., et al. (2014). Addition of probiotic bacteria in a semi-hard goat cheese (coalho): survival to simulated gastrointestinal conditions and inhibitory effect against pathogenic bacteria. Food Research International, 64, 241–247. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodres.2014.06.032
dos Santos, K. M. O., do Egito, A. S., da Vieira, A. D. S., Buriti, F. C. A., Benevides, S. D., & Laguna, L. E. (2010). Processamento de queijo caprino cremoso probiótico adicionado de Bifidobacterium animalis e Lactobacillus acidophilus. Embrapa Caprinos e Ovinos. Comunicado Técnico, 118, 5p.
dos Santos, K. M. O., Vieira, A. D. S., Buriti, F. C. A., do Nascimento, J. C. F., de Melo, M. E. S., Bruno, L. M., de Fátima Borges, M., Rocha, C. R. C., de Souza Lopes, A. C., de Melo Franco, B. D. G., & Todorov, S. D. (2015). Artisanal Coalho cheeses as source of beneficial Lactobacillus plantarum and Lactobacillus rhamnosus strains. Dairy Science & Technology, 95(2), 209–230. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13594-014-0201-6
Dubeuf, J. P., Morand-Fehr, P., & Rubino, R. (2004). Situation, changes and future of goat industry around the world. Small Ruminant Research, 51(2), 165–173. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.smallrumres.2003.08.007
El Galiou, O., Zantar, S., Bakkali, M., Laglaoui, A., Centeno, J. A., & Carballo, J. (2015). Chemical and microbiological characteristics of traditional homemade fresh goat cheeses from northern Morocco. Small Ruminant Research, 129, 108–113. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.smallrumres.2015.06.005
FAO/WHO (2001). Evaluation of health and nutritional properties of probiotics in food including powder milk with live lactic acid bacteria. In R. o. A. J. F. W. E. Consultation (Ed.). Córdoba, Argentina, .
Figueroa-González, I., Quijano, G., Ramírez, G., & Cruz-Guerrero, A. (2011). Probiotics and prebiotics—perspectives and challenges. Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture, 91(8), 1341–1348. https://doi.org/10.1002/jsfa.4367
Furtado, M. M. (1986). Fabricação de queijo de leite de cabra. São Paulo: Nobel.
Gomes, A. A., Braga, S. P., Cruz, A. G., Cadena, R. S., Lollo, P. C. B., Carvalho, C., Amaya-Farfán, J., Faria, J. A. F., & Bolini, H. M. A. (2011). Effect of the inoculation level of Lactobacillus acidophilus in probiotic cheese on the physicochemical features and sensory performance compared with commercial cheeses. Journal of Dairy Science, 94(10), 4777–4786. https://doi.org/10.3168/jds.2011-4175
Haenlein, G. F. W. (2004). Goat milk in human nutrition. Small Ruminant Research, 51(2), 155–163. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.smallrumres.2003.08.010
Haenlein, G. F. W., & Anke, M. (2011). Mineral and trace element research in goats: a review. Small Ruminant Research, 95(1), 2–19. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.smallrumres.2010.11.007
Hill, C., Guarner, F., Reid, G., Gibson, G. R., Merenstein, D. J., Pot, B., Morelli, L., Canani, R. B., Flint, H. J., Salminen, S., Calder, P. C., & Sanders, M. E. (2014). Expert consensus document: The International Scientific Association for Probiotics and Prebiotics consensus statement on the scope and appropriate use of the term probiotic. [consensus statement]. Nature Reviews. Gastroenterology & Hepatology, 11(8), 506–514. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrgastro.2014.66
IAL. (2008). Métodos Físico-Químicos para Análise de Alimentos (Vol. 4). São Paulo: Instituto Adolfo Lutz.
Karimi, R., Sohrabvandi, S., & Mortazavian, A. M. (2012). Review article: sensory characteristics of probiotic cheese. Comprehensive Reviews in Food Science and Food Safety, 11(5), 437–452. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1541-4337.2012.00194.x
Madureira, A. R., Pereira, C. I., Truszkowska, K., Gomes, A. M., Pintado, M. E., & Malcata, F. X. (2005). Survival of probiotic bacteria in a whey cheese vector submitted to environmental conditions prevailing in the gastrointestinal tract. International Dairy Journal, 15(6–9), 921–927. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.idairyj.2004.08.025
Madureira, A. R., Amorim, M., Gomes, A. M., Pintado, M. E., & Malcata, F. X. (2011). Protective effect of whey cheese matrix on probiotic strains exposed to simulated gastrointestinal conditions. Food Research International, 44(1), 465–470. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodres.2010.09.010
Meira, Q. G. S., Magnani, M., de Medeiros Júnior, F. C., de Cássia Ramos do Egito Queiroga, R., Madruga, M. S., Gullón, B., et al. (2015). Effects of added Lactobacillus acidophilus and Bifidobacterium lactis probiotics on the quality characteristics of goat ricotta and their survival under simulated gastrointestinal conditions. Food Research International, 76(Part 3), 828–838. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodres.2015.08.002
Padilha, M. (2013). Queijo petit-suisse probiótico e simbiótico: características tecnológicas e emprego de técnicas independentes de cultivo na avaliação da sobrevivência dos probióticos no produto e em ensaios de sobrevivência in vitro. São Paulo: Universidade de São Paulo.
Padilha, M., Villarreal Morales, M. L., Vieira, A. D. S., Costa, M. G. M., & Saad, S. M. I. (2016). A prebiotic mixture improved lactobacillus acidophilus and Bifidobacterium animalis gastrointestinal in vitro resistance in petit-suisse. [10.1039/C5FO01592H]. Food & Function, 7(5), 2312–2319. https://doi.org/10.1039/C5FO01592H
Park, Y. W., Juárez, M., Ramos, M., & Haenlein, G. F. W. (2007). Physico-chemical characteristics of goat and sheep milk. Small Ruminant Research, 68(1–2), 88-113, doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.smallrumres.2006.09.013.
Ranadheera, C. S., Evans, C. A., Adams, M. C., & Baines, S. K. (2012a). In vitro analysis of gastrointestinal tolerance and intestinal cell adhesion of probiotics in goat’s milk ice cream and yogurt. Food Research International, 49(2), 619–625. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodres.2012.09.007
Ranadheera, C. S., Evans, C. A., Adams, M. C., & Baines, S. K. (2012b). Probiotic viability and physico-chemical and sensory properties of plain and stirred fruit yogurts made from goat’s milk. Food Chemistry, 135(3), 1411–1418. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2012.06.025
Rolim, F. R. L., dos Santos, K. M. O., Barcelos, S. C., Egito, A. S. d., Ribeiro, T. S., Conceição, M. L. d., et al. (2015). Survival of Lactobacillus rhamnosus EM1107 in simulated gastrointestinal conditions and its inhibitory effect against pathogenic bacteria in semi-hard goat cheese. LWT - Food Science and Technology, 63(2), 807–813. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lwt.2015.05.004
Saad, N., Delattre, C., Urdaci, M., Schmitter, J. M., & Bressollier, P. (2013). An overview of the last advances in probiotic and prebiotic field. LWT - Food Science and Technology, 50(1), 1–16. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lwt.2012.05.014
Santos, T. D. R. (2011). Avaliação de queijos “Boursin” de leite de cabras das raças Saanen e Parda Alpina submetidas a diferentes dietas. In Dissertação. Bahia, ITAPETINGA: Universidade Estadual do Sudoeste da.
Santos, B. M., de Oliveira, M. E. G., de Sousa, Y. R. F., Madureira, A. R. M. F. M., Pintado, M. M. E., Gomes, A. M. P., et al. (2011). Caracterização físico-química e sensorial de queijo coalho produzido com mistura de leite de cabra e leite de vaca. Revista Instituto Adolfo Lutz, 70(3), 302–310.
Shah, N. P. (2000). Probiotic bacteria: selective enumeration and survival in dairy foods. Journal of Dairy Science, 83(4), 894–907. https://doi.org/10.3168/jds.S0022-0302(00)74953-8
Silanikove, N., Leitner, G., Merin, U., & Prosser, C. G. (2010). Recent advances in exploiting goat’s milk: quality, safety and production aspects. Small Ruminant Research, 89(2–3), 110–124. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.smallrumres.2009.12.033
Soukoulis, C., Behboudi-Jobbehdar, S., Yonekura, L., Parmenter, C., & Fisk, I. (2014). Impact of milk protein type on the viability and storage stability of microencapsulated lactobacillus acidophilus NCIMB 701748 using spray drying. [journal article]. Food and Bioprocess Technology, 7(5), 1255–1268. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-013-1120-x
Stone, H., & Sidel, J. L. (1992). Sensory evaluation practices. San Diego, California: Academic Press.
Tharmaraj, N., & Shah, N. P. (2003). Selective enumeration of Lactobacillus delbrueckii ssp. bulgaricus, Streptococcus thermophilus, Lactobacillus acidophilus, Bifidobacteria, Lactobacillus casei, Lactobacillus rhamnosus, and Propionibacteria. Journal of Dairy Science, 86(7), 2288–2296. https://doi.org/10.3168/jds.S0022-0302(03)73821-1
Tripathi, M. K., & Giri, S. K. (2014). Probiotic functional foods: survival of probiotics during processing and storage. Journal of Functional Foods, 9(supplement C), 225-241. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jff.2014.04.030
Verruck, S., Prudêncio, E. S., Vieira, C. R. W., Amante, E. R., & Amboni, R. D. d. M. C. (2015). The buffalo minas Frescal cheese as a protective matrix of Bifidobacterium BB-12 under in vitro simulated gastrointestinal conditions. LWT - Food Science and Technology, 63(2), 1179–1183. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lwt.2015.04.014
Vinderola, C. G., & Reinheimer, J. A. (1999). Culture media for the enumeration of Bifidobacterium bifidum and Lactobacillus acidophilus in the presence of yoghurt bacteria. International Dairy Journal, 9(8), 497–505. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0958-6946(99)00120-X
Wang, J., Guo, Z., Zhang, Q., Yan, L., Chen, W., Liu, X. M., & Zhang, H. P. (2009). Fermentation characteristics and transit tolerance of probiotic Lactobacillus casei Zhang in soymilk and bovine milk during storage. Journal of Dairy Science, 92(6), 2468–2476. https://doi.org/10.3168/jds.2008-1849
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Martins, I.B.A., Deliza, R., dos Santos, K.M.O. et al. Viability of Probiotics in Goat Cheese During Storage and Under Simulated Gastrointestinal Conditions. Food Bioprocess Technol 11, 853–863 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-018-2060-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-018-2060-2