Abstract
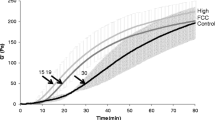
This study was conducted to investigate the effect of freeze-dried mechanically deboned spent laying hen hydrolysate on the quality and antioxidative characteristics of boiled fish paste during storage. Boiled fish paste samples were divided into three treatments: control (commercial fish paste), T1(1 % freeze-dried mechanically deboned spent laying hen hydrolysate), and T2(3 % freeze-dried mechanically deboned spent laying hen hydrolysate). Moisture, crude protein, and crude fat were not significantly different among samples in the 0 day. T1 and T2 had lower pH, lightness, and whiteness than the control during storage. Volatile basic nitrogen was increased in T1 and T2 during storage. The breaking force, deformation, gel strength, and jelly strength values were higher in the control than in T1 and T2 during storage. Sensory evaluation showed that color, flavor, springiness, and overall acceptability were lower and more nonelastic in T1 and T2 than in control samples after storage. The 2,2-diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl hydrate radical scavenging activity of boiled fish paste was dose-dependently increased in T1 and T2 during storage.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
AOAC, (1995). Official methods of analysis. Association of Office Analytical Chemists.
Badii, F., & Howell, N. K. (2002). Changes in the texture and structure of cod and haddock fillets during frozen storage. Food Hydrocolloids, 16, 313–319.
Bhaskar, N., Modi, V. K., Govindaraju, K., Radha, C., & Lalitha, R. G. (2007). Utilization of meat industry by products: protein hydrolysate from sheep visceral mass. Bioresource Technology., 98(2), 388–394.
Brandwilliams, W., Cuvelier, M. E., & Berset, C. (1995). Use of a free-radical method to evaluate antioxidant activity. Food Science and Technology LEB, 28(1), 25–30.
Bueno-Solano, C., Lopez-Cervantes, J., Campas-Baypoli, O. N., Lauterio-Garcia, R., Adan-Bante, N. P., & Sanchez-Machado, D. I. (2009). Chemical and biological characteristics of protein hydrolysates from fermented shrimp by-products. Food Chemistry, 1112, 671–675.
Cavalheiro, C. P., Ludtke, F. L., Stefanello, F. S., Kubata, e. H., Terra, N. N., & Fries, L. L. M. (2014). Replacement of mechanically deboned chicken meat with its protein hydrolysate in mortadella-type sausages. Food Science and Technology, 34, 478–484.
Chen, G. T., Zhao, L., Zhao, L. Y., Cong, T., & Bao, S. F. (2006). In vitro study on antioxidant activities of peanut protein hydrolysate. Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture, 87, 357–362.
Cross, H. R., Moen, R., & Stanfield, M. S. (1978). Training and testing of judges for sensory analysis of meat quality. Food Technology, 32, 48–54.
Dong, S., Zeng, M., Wang, D., Liu, Z., Zhao, Y., & Yang, H. (2008). Antioxidant and biochemical properties of protein hydrolysates prepared from Silver carp (Hypophthalmichthys molitrix). Food Chemistry, 107, 1485–1493.
Fernandez-Lopez, J., Sayas-Barbera, E., Perez-Alvarez, J. A., & Aranda-Catala, V. (2003). Effect of sodium chloride, sodium tripolyphosphate and pH on color properties of pork meat. Color Research and Application, 29, 67–74.
Je, J. Y., Park, P. J., & Kim, S. K. (2005). Antioxidant activity of a peptide isolated from Alaska pollack (Theragra chalcogramma) frame protein hydrolysate. Food Research International, 38, 45–50.
Jin, S. K., Park, J. H., & Hur, S. J. (2014a). Effect of substituting surimi with spent laying hen meat on the physicochemical characteristics of fried fish paste. Food and Bioprocess Technology, 7, 901–908.
Jin, S. K., Hwang, J. W., Moon, S., Choi, Y. J., Kim, G. D., Jung, E. Y., & Yang, H. S. (2014b). The effects of mechanically deboned chicken hydrolysates on the characteristics of imitation crab stick. Korean Journal for Food Science of Animal Resources, 34(2), 192–199.
Luo, Y. K., Kuwahara, R., Kaneniwa, M., Murata, Y., & Yokoyama, M. (2001). Comparison of gel properties of surimi from Alaska Pollock and three freshwater fish species: effects of thermal processing and protein concentration. Journal of Food Science, 66, 548–554.
Luo, Y., Kuwahara, R., Kaneniwa, M., Murata, Y., & Yokoyama, M. (2004). Effect of soy protein isolate on gel properties of Alaska pollock and common carp surimi at different setting conditions. Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture, 84, 663–671.
Nurkhoeriyati, T., Huda, N., & Ahmad, R. (2011). Gelation properties of spent duck meat surimi-like material produced using acid-alkaline solubilization methods. Journal of Food Science, 76, S48–S55.
Ochiai, Y., Ochiai, L., Hashimoto, K., & Watabe, S. (2001). Quantitative estimation of dark muscle content in the mackerel meat paste and its products using antisera against myosin light chains. Journal of Food Science, 66, 1301–1305.
Okada, M. (1992). History of surimi technology in Japan. In T. C. Lanier & C. M. Lee (Eds.), Surimi technology (pp. 3–22). New York: Marcel Dekker Inc.
Park, S., Brewer, M. S., Novakofski, J., Bechtel, P. J., & McKeith, F. K. (1996). Process and characteristics for a surimi-like material made from beef or pork. Journal of Food Science, 61, 422–427.
Phatcharat, S., Benjakul, S., & Visessanguan, W. (2006). Effects of washing with oxidising agents on the gel-forming ability and physicochemical properties of surimi produced from bigeye snapper (Priacanthus tayenus). Food Chemistry, 98, 431–439.
Qian, Z. J., Jung, W. K., & Kim, S. K. (2008). Free radical scavenging activity of a novel antioxidative peptide purified from hydrolysate of bullfrog skin, Rana catesbeiana Shaw. Bioresource Technology, 99, 1690–1698.
Saiga, A., Tanabe, S., & Nishimura, T. (2003). Antioxidant activity of peptides obtained from porcine myofibrillar proteins by protease treatment. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 51(12), 3661–3667.
Sakanaka, S., & Tachibana, Y. (2006). Active oxygen scavenging activity of egg-yolk protein hydrolysates and their effects on lipid oxidation in beef and tuna homogenates. Food Chemistry, 95, 243–249.
Sheih, I. C., Wu, T. K., & Fang, T. J. (2009). Antioxidant properties of a new antioxidative peptide from algae protein waste hydrolysate in different oxidation systems. Bioresource Technology, 100, 3419–3425.
Siriangkanakun, S., & Yongsawatdigul, J. (2012). Trypsin inhibitory activity and gel-enhancing effect of sarcoplasmic proteins from common carp. Journal of Food Science, 77(10), C1124–C1130.
Spellman, D., Cuinn, G. O., & FitzGerald, R. J. (2009). Bitterness in Bacillus protein hydrolysates of whey proteins. Food Chemistry, 114, 440–446.
Uresti, R. M., Velazquez, G., Ramírez, J. A., Vázquez, M., & Torres, J. A. (2004). Effect of high-pressure treatments on mechanical and functional properties of restructured products from arrowtooth flounder (Atheresthes stomias). Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture, 84, 1741–1749.
Wu, H. C., Chen, H. M., & Shiau, C. Y. (2003). Free amino acids and peptides as related to antioxidant properties in protein hydrolysates of mackerel (Scomber austriasicus). Food Research International, 36, 949–957.
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the Technology Development Program; Ministry for Food, Agriculture, Forestry, and Fisheries; Republic of Korea (2009, 109158-3) and by the Priority Research Centers Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea funded by the Ministry of Education, Science, and Technology (2009-0093813).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hur, S.J., Choi, J.S. & Jin, S.K. Effect of Freeze-Dried Mechanically Deboned Spent Laying Hen Hydrolysates on the Quality Characteristics of Boiled Fish Paste. Food Bioprocess Technol 9, 1169–1176 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-016-1707-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-016-1707-0