Abstract
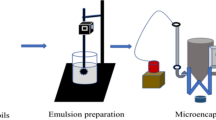
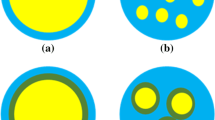
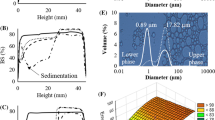
This study aimed at evaluating the potential of pectin combination with pea protein isolate (PPI) in the microencapsulation of polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFA)-rich oil by spray drying, in order to maximize encapsulation efficiency and minimize lipid oxidation. The feed emulsions used for particle production consisted of PUFA-rich oil droplets coated by either PPI (primary emulsion) or PPI–pectin (secondary emulsion). Dry emulsions characteristics and oxidative stability of microencapsulated oil as a function of relative humidity (RH; from 11 % to 75 %) were determined. Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) images revealed considerable structural changes. Oil droplets retained their shape upon drying and reconstitution. However, a shift in oil droplet size upon reconstitution indicated that oil droplet coalescence occurred within the process. Oxidation of microencapsulated oil in secondary emulsion was delayed from that of primary emulsion but followed the same pattern with regards to humidity. A high rate of oxidation was found for intermediate RH conditions (33 % and 57 % RH). The lowest rate of oxidation as followed by hydroperoxide and thiobarbituric acid reactive substances values was found at 75 % RH, a condition that is likely to diverge significantly from the monolayer moisture value. The oxidative stability of encapsulated oil was influenced by both physical state of the emulsions and the different constituents at the oil-in-water interface with PPI–pectin secondary emulsion giving the best protection of the oil.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aghbashlo, M., Mobli, H., Madadlou, A., & Rafiee, S. (2012). The correlation of wall material composition with flow characteristics and encapsulation behavior of fish oil emulsion. Food Research International, 49(1), 379–388.
Ahn, J.-H., Kim, Y.-P., Lee, Y.-M., Seo, E.-M., Lee, K.-W., & Kim, H.-S. (2008). Optimization of microencapsulation of seed oil by response surface methodology. Food Chemistry, 107(1), 98–105.
Bae, E. K., & Lee, S. J. (2008). Microencapsulation of avocado oil by spray drying using whey protein and maltodextrin. Journal of Microencapsulation, 25(8), 549–560.
Baik, M. Y., Suhendro, E. L., Nawar, W. W., McClements, D. J., Decker, E. A., & Chinachoti, P. (2004). Effects of antioxidants and humidity on the oxidative stability of microencapsulated fish oil. Journal of the American Oil Chemists’ Society, 81(4), 355–360.
Bouyer, E., Mekhloufi, G., Rosilio, V., Grossiord, J.-L., & Agnely, F. (2012). Proteins, polysaccharides, and their complexes used as stabilizers for emulsions: alternatives to synthetic surfactants in the pharmaceutical field? International Journal of Pharmaceutics, 1–2, 359–378.
Carneiro, H. C. F., Tonon, R. V., Grosso, C. R. F., & Hubinger, M. D. (2012). Encapsulation efficiency and oxidative stability of flaxseed oil microencapsulated by spray drying using different combinations of wall materials. Journal of Food Engineering, 115(4), 443–451.
Carolina, B. C., Carolina, S., Zamora, M. C., & Jorge, C. (2007). Glass transition temperatures and some physical and sensory changes in stored spray-dried encapsulated flavors. LWT - Food Science and Technology, 40(10), 1792–1797.
Charoen, R., Jangchud, A., Jangchud, K., Harnsilawat, T., Decker, E. A., & McClements, D. J. (2012). Influence of interfacial composition on oxidative stability of oil-in-water emulsions stabilized by biopolymer emulsifiers. Food Chemistry, 131(4), 1340–1346.
Chen, B., McClements, D. J., & Decker, E. A. (2010). Role of continuous phase anionic polysaccharides on the oxidative stability of Menhaden oil-in-water emulsions. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 58(6), 3779–3784.
Chen, B., Li, H., Ding, Y., & Rao, J. (2011). Improvement of physicochemical stabilities of emulsions containing oil droplets coated by non-globular protein-beet pectin complex membranes. Food Research International, 44(5), 1468–1475.
Drusch, S., & Berg, S. (2008). Extractable oil in microcapsules prepared by spray-drying: localisation, determination and impact on oxidative stability. Food Chemistry, 109(1), 17–24.
Ducel, V., Saulnier, P., Richard, J., & Boury, F. (2005). Plant protein–polysaccharide interactions in solutions: application of soft particle analysis and light scattering measurements. Colloids and Surfaces B: Biointerfaces, 41(2–3), 95–102.
Fuchs, M., Turchiuli, C., Bohin, M., Cuvelier, M. E., Ordonnaud, C., Peyrat-Maillard, M. N., et al. (2006). Encapsulation of oil in powder using spray drying and fluidised bed agglomeration. Journal of Food Engineering, 75(1), 27–35.
Gharsallaoui, A., Roudaut, G., Chambin, O., Voilley, A., & Saurel, R. (2007). Applications of spray-drying in microencapsulation of food ingredients: an overview. Food Research International, 40(9), 1107–1121.
Gharsallaoui, A., Cases, E., Chambin, O., & Saurel, R. (2009). Interfacial and emulsifying characteristics of acid-treated pea protein. Food Biophysics, 4(4), 273–280.
Gharsallaoui, A., Saurel, R., Chambin, O., Cases, E., Voilley, A., & Cayot, P. (2010a). Utilisation of pectin coating to enhance spray-dry stability of pea protein-stabilised oil-in-water emulsions. Food Chemistry, 122(2), 447–454.
Gharsallaoui, A., Yamauchi, K., Chambin, O., Cases, E., & Saurel, R. (2010b). Effect of high methoxyl pectin on pea protein in aqueous solution and at oil/water interface. Carbohydrate Polymers, 80(3), 817–827.
Gharsallaoui, A., Roudaut, G., Beney, L., Chambin, O., Voilley, A., & Saurel, R. (2012). Properties of spray-dried food flavours microencapsulated with two-layered membranes: roles of interfacial interactions and water. Food Chemistry, 132(4), 1713–1720.
Gray, D. A., Bowen, S. E., Farhat, I., & Hill, S. E. (2008). Lipid oxidation in glassy and rubbery-state starch extrudates. Food Chemistry, 106(1), 227–234.
Gueguen, J., & Barbot, J. (1988). Quantitative and qualitative variability of pea (Pisum sativum L.) protein composition. Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture, 42(3), 209–224.
Gueguen, J., Vu, A. T., & Schaeffer, F. (1984). Large-scale purification and characterisation of pea globulins. Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture, 35(9), 1024–1033.
Gueguen, J., Chevalier, M., And, J. B., & Schaeffer, F. (1988). Dissociation and aggregation of pea legumin induced by pH and ionic strength. Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture, 44(2), 167–182.
Guzey, D., & McClements, D. J. (2006). Formation, stability and properties of multilayer emulsions for application in the food industry. Advances in Colloid and Interface Science, 128–130, 227–248.
Jafari, S. M., Assadpoor, E., Bhandari, B., & He, Y. (2008). Nano-particle encapsulation of fish oil by spray drying. Food Research International, 41(2), 172–183.
Jimenez, M., Garcia, H. S., & Beristain, C. I. (2004). Spray-drying microencapsulation and oxidative stability of conjugated linoleic acid. European Food Research and Technology, 219(6), 588–592.
Jumaa, M., & Müller, B. W. (1998). The effect of oil components and homogenization conditions on the physicochemical properties and stability of parenteral fat emulsions. International Journal of Pharmaceutics, 163(1–2), 81–89.
Karel, M., Labuza, T. P., & Maloney, J. F. (1967). Chemical changes in freeze-dried foods and model systems. Cryobiology, 3, 288–296.
Katsuda, M. S., McClements, D. J., Miglioranza, L. H. S., & Decker, E. A. (2008). Physical and oxidative stability of fish oil-in-water emulsions stabilized with β-lactoglobulin and pectin. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 56(14), 5926–5931.
Keogh, M. K., & O’Kennedy, B. T. (1999). Milk fat microencapsulation using whey proteins. International Dairy Journal, 9(9), 657–663.
Keogh, M. K., O’Kennedy, B. T., Kelly, J., Auty, M. A., Kelly, P. M., Fureby, A., et al. (2001). Stability to oxidation of spray-dried fish oil powder microencapsulated using milk ingredients. Journal of Food Science, 66(2), 217–224.
Klinkesorn, U., Sophanodora, P., Chinachoti, P., McClements, D. J., & Decker, E. A. (2005). Stability of spray-dried tuna oil emulsions encapsulated with two-layered interfacial membranes. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 53(21), 8365–8371.
Klinkesorn, U., Sophanodora, P., Chinachoti, P., Decker, E. A., & McClements, D. J. (2006). Characterization of spray-dried tuna oil emulsified in two-layered interfacial membranes prepared using electrostatic layer-by-layer deposition. Food Research International, 39(4), 449–457.
Labuza, T. P. (1968). Sorption phenomena in foods. Food Technology, 22, 15–24.
Levine, H., & Slade, L. (1986). A polymer physico-chemical approach to the study of commercial starch hydrolysis products (SHPs). Carbohydrate Polymers, 6(3), 213–244.
Liu, X.-D., Atarashi, T., Furuta, T., Yoshii, H., Aishima, S., Ohkawara, M., et al. (2001). Microencapsulation of emulsified hydrophobic flavors by spray drying. Drying Technology, 19(7), 1361–1374.
Liu, S., Elmer, C., Low, N. H., & Nickerson, M. T. (2010). Effect of pH on the functional behaviour of pea protein isolate-gum Arabic complexes. Food Research International, 43(2), 489–495.
Makri, E. A., & Doxastakis, G. I. (2006). Emulsifying and foaming properties of Phaseolus vulgaris and coccineus proteins. Food Chemistry, 98(3), 558–568.
Matsuno, R., & Adachi, S. (1993). Lipid encapsulation technology — techniques and applications to food. Trends in Food Science and Technology, 4(8), 256–261.
McClements, D. J. (2010). Emulsion design to improve the delivery of functional lipophilic components. Annual Review of Food Science and Technology, 1(1), 241–269.
McClements, D. J., & Decker, E. A. (2000). Lipid oxidation in oil-in-water emulsions: impact of molecular environment on chemical reactions in heterogeneous food systems. Journal of Food Science, 65(8), 1270–1282.
Millqvist-Fureby, A. (2003). Characterisation of spray-dried emulsions with mixed fat phases. Colloids and Surfaces B: Biointerfaces, 31(1–4), 65–79.
O’Kane, F. E., Happe, R. P., Vereijken, J. M., Gruppen, H., & van Boekel, M. A. J. S. (2004). Characterization of Pea Vicilin. 2. Consequences of compositional heterogeneity on heat-induced gelation behavior. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 52(10), 3149–3154.
Partanen, R., Raula, J., Seppänen, R., Buchert, J., Kauppinen, E., & Forssell, P. (2008). Effect of relative humidity on oxidation of flaxseed oil in spray dried whey protein emulsions. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 56(14), 5717–5722.
Pedersen, G. P., Fäldt, P., Bergenstahl, B., & Kristensen, H. G. (1998). Solid state characterisation of a dry emulsion: a potential drug delivery system. International Journal of Pharmaceutics, 171(2), 257–270.
Raymundo, A., Gouveia, L., Batista, A. P., Empis, J., & Sousa, I. (2005). Fat mimetic capacity of Chlorella vulgaris biomass in oil-in-water food emulsions stabilized by pea protein. Food Research International, 38(8–9), 961–965.
Roos, Y. (1995). Phase transitions in foods. New York, USA: Academic Press.
Serfert, Y., Drusch, S., Schmidt-Hansberg, B., Kind, M., & Schwarz, K. (2009a). Process engineering parameters and type of n-octenylsuccinate-derivatised starch affect oxidative stability of microencapsulated long chain polyunsaturated fatty acids. Journal of Food Engineering, 95(3), 386–392.
Serfert, Y., Drusch, S., & Schwarz, K. (2009b). Chemical stabilisation of oils rich in long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acids during homogenisation, microencapsulation and storage. Food Chemistry, 113(4), 1106–1112.
Serfert, Y., Schröder, J., Mescher, A., Laackmann, J., Rätzke, K., Shaikh, M. Q., et al. (2013). Spray drying behaviour and functionality of emulsions with β-lactoglobulin/pectin interfacial complexes. Food Hydrocolloids, 31(2), 438–445.
Sheu, T. Y., & Rosenberg, M. (1998). Microstructure of microcapsules consisting of whey proteins and carbohydrates. Journal of Food Science, 63(3), 491–494.
Soottitantawat, A., Yoshii, H., Furuta, T., Ohkawara, M., & Linko, P. (2003). Microencapsulation by spray drying: influence of emulsion size on the retention of volatile compounds. Journal of Food Science, 68(7), 2256–2262.
Soottitantawat, A., Bigeard, F., Yoshii, H., Furuta, T., Ohkawara, M., & Linko, P. (2005). Influence of emulsion and powder size on the stability of encapsulated d-limonene by spray drying. Innovative Food Science and Emerging Technologies, 6(1), 107–114.
Thakur, B. R., Singh, R. K., Handa, A. K., & Rao, M. A. (1997). Chemistry and uses of pectin — a review. Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition, 37(1), 47–73.
Thomas, M. E. C., Scher, J. L., Desobry-Banon, S., & Desobry, S. P. (2004). Milk powders ageing: effect on physical and functional properties. Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition, 44(5), 297–322.
Velasco, J., Dobarganes, C., & Márquez-Ruiz, G. (2003). Variables affecting lipid oxidation in dried microencapsulated oils. Grasas y Aceites (Sevilla), 54, 304–314.
Viroben, G., Barbot, J., Mouloungui, Z., & Guéguen, J. (2000). Preparation and characterization of films from pea protein. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 48(4), 1064–1069.
Zamora, R., & Hidalgo, F. J. (2005). Coordinate contribution of lipid oxidation and Maillard reaction to the nonenzymatic food browning. Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition, 45(1), 49–59.
Acknowledgments
Funds for this research were provided by the “Conseil regional de Bourgogne” France. We greatly thank Aline Bonnotte from the CM-DImaCell (Centre de Microscopie INRA/Université de Bourgogne, Plateforme DimaCell, BP 86510, F-21000 Dijon, France) for the SEM micrographs.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Aberkane, L., Roudaut, G. & Saurel, R. Encapsulation and Oxidative Stability of PUFA-Rich Oil Microencapsulated by Spray Drying Using Pea Protein and Pectin. Food Bioprocess Technol 7, 1505–1517 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-013-1202-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-013-1202-9