Abstract
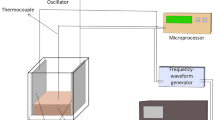
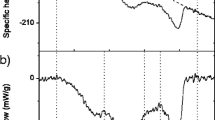
The objective of this study was to investigate the effects of ohmic (OH) and water bath (WB) cooking on shear parameters, protein degradation and ultrastructure changes of porcine longissimus dorsi muscle at the same endpoint temperatures (EPTs; range, 20–100 °C). The cooking loss and Warner–Bratzler shear force of the OH-cooked meat were significantly lower (P < 0.05) while protein solubility, pH and endothermic transition temperature were higher than those obtained by WB cooking at the same EPTs (range, 20–80 °C). Sodium dodecyl sulphate polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis analysis showed that during OH cooking, the meat had slightly fainter protein bands than that of WB-cooked ones. Less obvious shrinkage of the sarcomere and loss in the structure of Z discs were detected especially in OH-cooked meat at EPTs (100 °C). Strong correlations among pH, cooking loss, Warner–Bratzler shear force, sarcoplasmic protein solubility, T max2, and T max3 were observed in meat following OH cooking.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aktaş, N., Aksu, M. I., & Kaya, M. (2005). Changes in myofibrillar proteins during processing of pastirma (Turkish dry meat product) produced with commercial starter cultures. Food Chemistry, 90(4), 649–654.
Bertola, N., Bevilacqua, A., & Zaritzky, N. (2007). Heat treatment effect on texture changes and thermal denaturation of proteins in beef muscle. Journal of Food Processing and Preservation, 18(1), 31–46.
Bertram, H. C., Wu, Z., van den Berg, F., & Andersen, H. J. (2006). NMR relaxometry and differential scanning calorimetry during meat cooking. Meat Science, 74(4), 684–689.
Brunton, N. P., Lyng, J. G., Zhang, L., & Jacquier, J. C. (2006). The use of dielectric properties and other physical analyses for assessing protein denaturation in beef biceps femoris muscle during cooking from 5 to 85°C. Meat Science, 72(2), 236–244.
Choi, Y., Ryu, Y., Lee, S., Go, G., Shin, H., Kim, K., Rhee, M., & Kim, B. (2008). Effects of supercritical carbon dioxide treatment for sterilization purpose on meat quality of porcine longissimus dorsi muscle. LWT-Food Science and Technology, 41(2), 317–322.
Combes, S., Lepetit, J., Darche, B., & Lebas, F. (2004). Effect of cooking temperature and cooking time on Warner-Bratzler tenderness measurement and collagen content in rabbit meat. Meat Science, 66(1), 91–96.
Dai, Y., Miao, J., Yuan, S.-Z., Liu, Y., Li, X.-M., & Dai, R.-T. (2013). Colour and sarcoplasmic protein evaluation of pork following water bath and ohmic cooking. Meat Science, 93(4), 898–905.
de Huidobro, F. R., Miguel, E., Blázquez, B., & Onega, E. (2005). A comparison between two methods (Warner–Bratzler and texture profile analysis) for testing either raw meat or cooked meat. Meat Science, 69(3), 527–536.
Deng, Y., Rosenvold, K., Karlsson, A. H., Horn, P., Hedegaard, J., Steffensen, C. L., & Andersen, H. J. (2002). Relationship between thermal denaturation of porcine muscle proteins and water-holding capacity. Journal of Food Science, 67(5), 1642–1647.
den Hertog-Meischke, M. J., Smulders, F. J., Van Logtestijn, J. G., & van Knapen, F. (1997). The effect of electrical stimulation on the water-holding, capacity and protein denaturation of two bovine muscles. Journal of Animal Science, 75(1), 118–124.
Gil, M., Ramírez, J. A., Pla, M., Ariño, B., Hernández, P., Pascual, M., Blasco, A., Guerrero, L., Hajós, G., & Szerdahelyi, E. N. (2006). Effect of selection for growth rate on the ageing of myofibrils, meat texture properties and the muscle proteolytic potential of m. longissimus in rabbits. Meat Science, 72(1), 121–129.
He, Y., & Sebranek, J. G. (1996). Functional protein components in lean finely textured tissue from beef and pork. Journal of Food Science, 61(6), 1155–1159.
Huang, F., Huang, M., Xu, X., & Zhou, G. (2011). Influence of heat on protein degradation, ultrastructure and eating quality indicators of pork. Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture, 91(3), 443–448.
Hughes, M. C., Kerry, J. P., Arendt, E. K., Kenneally, P. M., McSweeney, P. L. H., & O’Neill, E. E. (2002). Characterization of proteolysis during the ripening of semi-dry fermented sausages. Meat Science, 62(2), 205–216.
Kong, F., Tang, J., Lin, M., & Rasco, B. (2008). Thermal effects on chicken and salmon muscles: tenderness, cook loss, area shrinkage, collagen solubility and microstructure. LWT- Food Science and Technology, 41(7), 1210–1222.
Li, C., Wang, D., Xu, W., Gao, F., & Zhou, G. (2013). Effect of final cooked temperature on tenderness, protein solubility and microstructure of duck breast muscle. LWT-Food Science and Technology, 51(1), 266–274.
McKenna, B., Lyng, J., Brunton, N., & Shirsat, N. (2006). Advances in radio frequency and ohmic heating of meats. Journal of Food Engineering, 77(2), 215–229.
Murphy, R., & Marks, B. (2000). Effect of meat temperature on proteins, texture, and cook loss for ground chicken breast patties. Poultry Science, 79(1), 99–104.
Qiao, M., Fletcher, D., Smith, D., & Northcutt, J. (2001). The effect of broiler breast meat color on pH, moisture, water-holding capacity, and emulsification capacity. Poultry Science, 80(5), 676–680.
Sante-Lhoutellier, V., Aubry, L., & Gatellier, P. (2007). Effect of oxidation on in vitro digestibility of skeletal muscle myofibrillar proteins. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 55(13), 5343–5348.
Shin, H.-G., Choi, Y.-M., Kim, H.-K., Ryu, Y.-C., Lee, S.-H., & Kim, B.-C. (2008). Tenderization and fragmentation of myofibrillar proteins in bovine longissimus dorsi muscle using proteolytic extract from Sarcodon aspratus. LWT-Food Science and Technology, 41(8), 1389–1395.
Shirsat, N., Brunton, N. P., Lyng, J. G., & McKenna, B. (2004). Water holding capacity, dielectric properties and light microscopy of conventionally and ohmically cooked meat emulsion batter. European Food Research and Technology, 219(1), 1–5.
Sotelo, I., Pérez-Munuera, I., Quiles, A., Hernando, I., Larrea, V., & Lluch, M. A. (2004). Microstructural changes in rabbit meat wrapped with Pteridium aquilinum fern during postmortem storage. Meat Science, 66(4), 823–829.
Supavititpatana, T., & Apichartsrangkoon, A. (2007). Combination effects of ultra-high pressure and temperature on the physical and thermal properties of ostrich meat sausage (yor). Meat Science, 76(3), 555–560.
Tadpitchayangkoon, P., Park, J. W., & Yongsawatdigul, J. (2012). Gelation characteristics of tropical surimi under water bath and ohmic heating. LWT-Food Science and Technology, 46(1), 97–103.
Thorarinsdottir, K. A., Arason, S., Geirsdottir, M., Bogason, S. G., & Kristbergsson, K. (2002). Changes in myofibrillar proteins during processing of salted cod (Gadus morhua) as determined by electrophoresis and differential scanning calorimetry. Food Chemistry, 77(3), 377–385.
Tornberg, E. (2005). Effects of heat on meat proteins-Implications on structure and quality of meat products. Meat Science, 70(3), 493–508.
Vasanthi, C., Venkataramanujam, V., & Dushyanthan, K. (2007). Effect of cooking temperature and time on the physico-chemical, histological and sensory properties of female carabeef (buffalo) meat. Meat Science, 76(2), 274–280.
Wattanachant, S., Benjakul, S., & Ledward, D. A. (2005). Effect of heat treatment on changes in texture, structure and properties of Thai indigenous chicken muscle. Food Chemistry, 93(2), 337–348.
Zell, M., Lyng, J. G., Cronin, D. A., & Morgan, D. J. (2009). Ohmic cooking of whole beef muscle—optimisation of meat preparation. Meat Science, 81(4), 693–698.
Zell, M., Lyng, J. G., Cronin, D. A., & Morgan, D. J. (2010). Ohmic cooking of whole turkey meat—effect of rapid ohmic heating on selected product parameters. Food Chemistry, 120(3), 724–729.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (no. 31271894) and the Ministry of Agriculture of China (no. 200903012).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dai, Y., Zhang, Qn., Wang, L. et al. Changes in Shear Parameters, Protein Degradation and Ultrastructure of Pork Following Water Bath and Ohmic Cooking. Food Bioprocess Technol 7, 1393–1403 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-013-1145-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-013-1145-1