Abstract
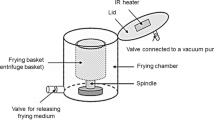
This paper explores the possibility of combining moderate vacuum frying followed by post-frying high vacuum application during the oil drainage stage, with the aim to reduce oil content in potato chips. Potato slices were initially vacuum fried under two operating conditions (140 °C, 20 kPa and 162 °C, 50.67 kPa) until the moisture content reached 10 and 15 % (wet basis), prior to holding the samples in the head space under high vacuum level (1.33 kPa). This two-stage process was found to lower significantly the amount of oil taken up by potato chips by an amount as high as 48 %, compared to drainage at the same pressure as the frying pressure. Reducing the pressure value to 1.33 kPa reduced the water saturation temperature (11 °C), causing the product to continuously lose moisture during the course of drainage. Continuous release of water vapour prevented the occluded surface oil from penetrating into the product structure and released it from the surface of the product. When frying and drainage occurred at the same pressure, the temperature of the product fell below the water saturation temperature soon after it was lifted out of the oil, which resulted in the oil getting sucked into the product. Thus, lowering the pressure after frying to a value well below the frying pressure is a promising method to lower oil uptake by the product.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmad Tarmizi, A. H., & Niranjan, K. (2010). The possibility of lowering oil content of potato chips by combining atmospheric frying with postfrying vacuum application. Journal of Food Science, 75(9), E572–E579.
Ahmad Tarmizi, A. H., & Niranjan, K. (2011). Post-frying oil drainage from potato chips and French fries: a comparative study of atmospheric and vacuum drainage. Food & Bioprocess Technology. doi:10.1007/s11947-011-0685-5.
Al-Khusaibi, M., & Niranjan, K. (2011). The impact of blanching and high-pressure pre-treatments on oil uptake of fried potato slices. Food & Bioprocess Technology. doi:10.1007/s11947-011-0562-2.
Aladedunye, F., & Przybylski, R. (2009). Protecting oil during frying: a comparative study. European Journal of Lipid Science and Technology, 111(9), 893–901.
Bouchon, P. (2002). Modelling oil uptake during frying. PhD Thesis. Department of Food Biosciences. University of Reading: Reading, UK.
Bouchon, P., Aguilera, J. M., & Pyle, D. L. (2003). Structure oil—absorption relationships during deep-fat frying. Journal of Food Science, 68(9), 2711–2716.
Bouchon, P., & Pyle, D. L. (2004). Studying oil absorption in restructured potato chips. Journal of Food Science, 69(3), FEP115–FEP122.
Costa, R. M., Oliveira, F. A. R., & Boutcheva, G. (2001). Structural changes and shrinkage of potato during frying. Journal of Food Science and Technology, 36(1), 11–23.
Dana, D., & Saguy, I. S. (2001). Frying of nutritious food: obstacles and feasibility. Food Science and Technology Research, 7(4), 265–279.
Dueik, V., Robert, P., & Bouchon, P. (2010). Vacuum frying reduces oil uptake and improves the quality parameters of carrot crisps. Food Chemistry, 119(3), 1143–1149.
Firestone, D. (2009). Official methods and recommended practices of the AOCS (5th ed.). Champaign: American Oil Chemists' Society.
Gamble, M. H., Rice, P., & Selman, J. D. (1987). Relationship between oil uptake and moisture loss during frying of potato slices from c.V. Record Tobers. International Journal of Food Science and Technology, 22(3), 233–241.
Garayo, J., & Moreira, R. (2002). Vacuum frying of potato chips. Journal of Food Engineering, 55(2), 181–191.
Granda, C., Moreira, R., & Tichy, S. E. (2004). Reduction of acrylamide formation in potato chips by low-temperature vacuum frying. Journal of Food Science, 69(8), E405–E411.
Khalil, A. H. (1999). Quality of French fried potatoes as influenced by coating with hydrocolloids. Food Chemistry, 66(2), 201–208.
Kita, A., & Figiel, A. (2008). Effect of post-drying method on selected properties of potato chips. Acta Agrophysica, 11(1), 91–100.
Kleinbaum, D. G., Kupper, L. L., Nizam, A., & Muller, K. E. (2008). Applied regression analysis and other multivariable methods (4th ed.). Belmont: Duxbury Series Applied.
Krokida, M. K., Oreopoulou, V., Maroulis, Z. B., & Marinos-Kuris, D. (2001). Effect of osmotic dehydration pretreatment on quality of French fries. Journal of Food Engineering, 49(4), 339–345.
Mariscal, M., & Bouchon, P. (2008). Comparison between atmospheric and vacuum frying of apple slices. Food Chemistry, 107(4), 1561–1569.
Mir-Bel, J., Oria, R., & Salvador, M. L. (2009). Influence of vacuum break conditions on oil uptake during potato post-frying cooling. Journal of Food Engineering, 95(3), 416–422.
Moreira, R., Da Silva, P. F., & Gomes, C. (2009). The effect of a de-oiling mechanism on the production of high quality vacuum fried potato chips. Journal of Food Engineering, 92(3), 297–304.
Pandey, A., & Moreira, R. (2011). Batch vacuum frying system analysis for potato chips. Journal of Food Process Engineering. doi:10.1111/j.1745-4530.2011.00635.x.
Rajkumar, V., Moreira, R., & Barrufet, M. (2003). Modelling the structural changes of tortilla chips during frying. Journal of Food Engineering, 60(2), 167–175.
Rayner, M., Ciolfi, V., Maves, B., Stedman, P., & Mittal, G. S. (2000). Development and application of soy-protein films to reduce fat intake in deep-fat foods. Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture, 80(6), 777–782.
Saguy, I. S., & Dana, D. (2003). Integrated approach to deep fat frying: engineering, nutrition, health and consumer aspect. Journal of Food Engineering, 56(2–3), 143–152.
Shyu, S., Hau, L., & Hwang, L. S. (1998). Effect of vacuum frying on the oxidative stability of oils. Journal of the American Oil Chemists' Society, 75(10), 1393–1398.
Shyu, S., & Hwang, L. S. (2001). Effects of processing conditions on the quality of vacuum fried apple chips. Food Research International, 34, 133–142.
Tan, K. J., & Mittal, G. S. (2006). Physicochemical properties changes in donuts during vacuum frying. International Journal of Food Properties, 9(1), 85–98.
Troncoso, E., & Pedreschi, F. (2009). Modelling water loss and oil uptake during vacuum frying of pre-treated potato slices. LWT- Food Science and Technology, 42(6), 1164–1173.
Troncoso, E., Pedreschi, F., & Zúñiga, R. N. (2009). Comparative study of physical and sensory properties of pre-treated potato slices during vacuum and atmospheric frying. LWT- Food Science and Technology, 42(1), 187–195.
Vanivambal, R., & Jayas, D. S. (2007). Changes in quality of microwave-treated agricultural products—a review. Biosystems Engineering, 98(1), 1–16.
Yagua, C. V., & Moreira, R. (2011). Physical and thermal properties of potato chips during vacuum frying. Journal of Food Engineering, 104(2), 272–283.
Ziaiifar, A. M., Achir, N., Courtois, F., Trezzani, I., & Trystram, G. (2008). Review on mechanisms, conditions, and factors involved in the oil uptake phenomenon during deep-fat frying process. International Journal of Food Science and Technology, 43(8), 1410–1423.
Acknowledgments
The authors express gratitude to (1) The Malaysian Palm Oil Board and (2) the technicians and colleagues of the Department of Food and Nutritional Sciences.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ahmad Tarmizi, A.H., Niranjan, K. Combination of Moderate Vacuum Frying with High Vacuum Drainage—Relationship Between Process Conditions and Oil Uptake. Food Bioprocess Technol 6, 2600–2608 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-012-0921-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-012-0921-7