Abstract
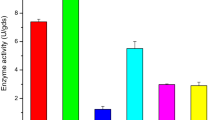
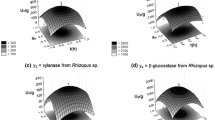
Seven strains of the genus Kluyveromyces were screened for β-galactosidase activity and Kluyveromyces marxianus ATCC 16045 was selected as the best enzyme producer for culture medium optimization. The production of β-galactosidase by submerged cultivation was evaluated using a factorial design and response surface methodology. The culture medium containing whey and parboiled rice effluent was formulated to maximize the production of β-galactosidase. The effects of the initial pH and the concentrations of whey lactose, peptone, (NH4)2SO4, yeast extract, and parboiled rice effluent on enzyme production were studied using a 2 6-2IV fractional design. A CCRD (24 trials plus axial and central points) was used for the four variables selected from the fractional design (lactose, peptone, (NH4)2SO4 and yeast extract), with β-galactosidase activity as the response. The optimum conditions established for production were a whey (lactose) concentration of 120 g/L, a yeast extract concentration of 5 g/L, a peptone concentration of 15 g/L, a (NH4)2SO4 concentration of 15 g/L, a parboiled rice effluent concentration of 30 g/L, and a pH value of 4.0. Under these conditions, the highest enzymatic activity of 10.4 U/mL was measured, being 9.5–9.7 as the values predicted by the proposed model, showing an enzymatic activity increase of 30% using alternative sources of lactose and nitrogen for β-galactosidase production.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adeniran, H. A., Abiose, S. H., & Ogunsua, A. O. (2010). Production of fungal b-amylase and amyloglucosidase on some nigerian agricultural residues. Food and Bioprocess Technology, 3, 693–698.
Aktas, N., Boyaci, I. H., Mutlu, M., & Tanyolac, A. (2006). Optimization of lactose utilization in deproteinated whey by Kluyveromyces marxianus using response surface methodology (RSM). Bioresource Technology, 97, 2252–2259.
Alves, F. G., Maugeri, F., Burkert, J. F. M., & Kalil, S. J. (2010). Maximization of b-galactosidase production: a simultaneous investigation of agitation and aeration effects. Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 160, 1528–1539.
Burkert, J. F. M., Kalil, S. J., Maugeri, F., & Rodrigues, M. I. (2006). Parameters optimization for enzymatic assays using experimental design. Brazilian Journal of Chemical Engineering, 23, 163–170.
Dubois, M., Gilles, K. A., Hamilton, J. K., Rebers, P. A., & Smith, F. (1956). Colorimetric method for determination of sugars and related substances. Analytical Chemistry, 28, 350–356.
Francis, F., Sabu, A., Nampoothiri, K. M., Ramachandran, S., Ghosh, S., Szakacs, G., et al. (2003). Use of response surface methodology for optimizing process parameters for the production of [alpha]-amylase by Aspergillus oryzae. Biochemical Engineering Journal, 15, 107–115.
Furlan, S. A., Schneider, A. L. S., Merkle, R., Carvalho-Jonas, M. F., & Jonas, R. (2000). Formulation of a lactose-free, low-cost culture medium for the production of beta-d-galactosidase by Kluyveromyces marxianus. Biotechnology Letters, 22, 589–593.
Hsu, C. A., Lee, S. L., & Chou, C. C. (2007a). Enzymatic production of galactooligosaccharides by beta-galactosidase from Bifidobacterium longum BCRC 15708. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 55, 2225–2230.
Hsu, C. A., Yu, R. C., Lee, S. L., & Chou, C. C. (2007b). Cultural condition affecting the growth and production of beta-galactosidase by Bifidobacterium longum CCRC 15708 in ajar fermenter. International Journal of Food Microbiology, 116, 186–189.
Inchaurrondo, V. A., Yautorno, O. M., & Voget, C. E. (1994). Yeast growth and b-galactosidase production during Aerobic batch cultures in lactose-limited synthetic medium. Process Biochemistry, 29, 47–54.
Kalil, S. J., Maugeri, F., & Rodrigues, M. I. (2000). Response surface analysis and simulation as a tool for bioprocess design and optimization. Process Biochemistry, 35, 539–550.
Ladero, M., Santos, A., & Garcia-Ochoa, F. (2000). Kinetic modeling of lactose hydrolysis with an immobilized [beta]-galactosidase from Kluyveromyces fragilis. Enzyme and Microbial Technology, 27, 583–592.
Mahoney, R. R. (1998). Galactosyl-oligosaccharide formation during lactose hydrolysis: a review. Food Chemistry, 63, 147–154.
Manera, A. P., Ores, J. C., Ribeiro, V. A., Burkert, C. A. V., & Kalil, S. J. (2008). Optimization of the culture medium for the production of b-galactosidase from Kluyveromyces marxianus CCT 7082. Food Technology and Biotechnology, 46, 66–72.
Nor, Z. M., Melih, I. T., Mehrab, M., Jeno, M. S., Moo-Young, M., & Jervis, E. J. (2001). Improvement of intracellular beta-galactosidase production in fed-batch culture of Kluyveromyces fragilis. Biotechnology Letters, 23, 845–849.
Numanoglu, Y., & Sungur, S. (2004). b-Galactosidase from Kluyveromyces lactis cell disruption and enzyme immobilization using a cellulose-gelatin carrier system. Process Biochemistry, 39, 703–709.
Pinheiro, R., Belo, I., & Mota, M. (2003). Growth and b-galactosidase activity in cultures of Kluyveromyces marxianus under increased air pressure. Letters in Applied Microbiology, 37, 438–442.
Queiroz, M. I., Lopes, E. J., Zepka, L. Q., Bastos, R. G., & Goldbeck, R. (2007). The kinetics of the removal of nitrogen and organic matter from parboiled rice effluent by cyanobacteria in a stirred batch reactor. Bioresource Technology, 98, 2163–2169.
Rajoka, M. I., Latif, F., Khan, S., & Shahid, R. (2004). Kinetics of improved productivity of beta-galactosidase by a cycloheximide-resistant mutant of Kluyveromyces marxianus. Biotechnology Letters, 26, 741–746.
Rech, R., & Ayub, M. A. Z. (2007). Simplified feeding strategies for fed-batch cultivation of Kluyveromyces marxianus in cheese whey. Process Biochemistry, 42, 873–877.
Rech, R., Cassini, C. F., Secchi, A., & Ayub, M. A. Z. (1999). Utilization of protein-hydrolyzed cheese whey for production of b-galactosidase by Kluyveromyces marxianus. Journal of Industrial Microbiology & Biotechnology, 23, 91–96.
Rodriguez, A. P., Leiro, R. F., Trillo, M. C., Cerdan, M. E., Siso, M. I. G., & Becerra, M. (2006). Secretion and properties of a hybrid Kluyveromyces lactis–Aspergillus niger beta-galactosidase. Micro Cell Fact, 5, 1–13.
Santos, A., Ladero, M., & Garcia-Ochoa, F. (1998). Kinetic modeling of lactose hydrolysis by a [beta]-galactosidase from Kluyveromices Fragilis. Enzyme and Microbial Technology, 22, 558–567.
Shankar, T. J., Sokhansanj, S., Bandyopadhyay, S., & Bawa, A. S. (2010). A case study on optimization of biomass flow during single-screw extrusion cooking using genetic algorithm (GA) and response surface method (RSM). Food and Bioprocess Technology, 3, 498–510.
Siso, M. I. G. (1996). The biotechnological utilization of cheese whey: a review. Bioresource Technology, 57, 1–11.
Szczodrak, J. (2000). Hydrolysis of lactose in whey permeate by immobilized [beta]-galactosidase from Kluyveromyces fragilis. Journal of Molecular Catalysis. B, Enzymatic, 10, 631–637.
Whitaker, J. R. (1994). Principles of enzymology for the food science. New York: Marcel Dekker.
Acknowledgments
The present work was carried out with the financial support of FAPERGS, CNPq, and CAPES, entities of the Brazilian government.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Braga, A.R.C., Gomes, P.A. & Kalil, S.J. Formulation of Culture Medium with Agroindustrial Waste for β-Galactosidase Production from Kluyveromyces marxianus ATCC 16045. Food Bioprocess Technol 5, 1653–1663 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-011-0511-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-011-0511-0