Abstract
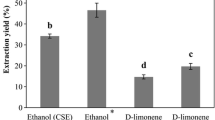
After processing, every extraction process generates huge amount of unintended wastes, especially from fruits and vegetables which represent a major disposal problem for the food industry. They are promising sources of bioactive compounds that could be used for their favourable nutritional properties. Sea buckthorn juice production results in generation of large amount of by-products, which are suggested to contain substantial amounts of valuable natural antioxidants. Extracts obtained by solvent-free microwave hydrodiffusion and gravity (MHG) technique and conventional solvent extraction (CSE) method were analysed with HPLC for quantification of flavonoids along with evaluating their phenolic contents by Folin-Ciocalteu method and reducing power by the reduction of 2,2-diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl (DPPH) radical. MHG is a green extraction method which offers important advantages like shorter extraction time (15 min), cleaner feature (no solvent or water used) and extraction of valuable flavonoids (Isorhamnetin, isorhamnetin 3-O-glucoside, isorhamnetin 3-O-rutinoside and quercetin 3-O-glucoside) at optimised power (400 W). Along with extracting similar flavonols in enough concentratioin, MHG extract has shown much higher phenolic contents (1,147 milligram gallic acid equivalents (GAE) per gram) against CSE extract (741 mg GAE/g) with greater antioxidant activity determined by DPPH assay.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abert-Vian, M., Fernandez, X., Visinoni, F., & Chemat, F. (2008). Microwave hydrodiffusion and gravity, a new technique for extraction of essential oils. Journal of Chromatography A, 1190, 14–17.
Arimboor, R., Kumar, K. S., & Arumughan, C. (2008). Simultaneous estimation of phenolic acids in sea buckthorn (Hippophaë rhamnoides) using RP-HPLC with DAD. Journal of Pharmaceutical and Biomedical Analysis, 47, 31–38.
Bélanger, J. M. R., & Paré, J. R. J. (2008) Microwave-assisted processes in food analysis. Handbook of Food Analysis Instruments, S, Ötles, Ed., Taylor & Francis–CRC Press.
Beveridge, T., Li, T. S.-C., Dave, O.-B., & Smith, A. (1999). Sea buckthorn products: manufacture and composition. Journal of Agriculture and Food Chemistry, 47, 3480–3488.
Bilaloglu, G.-V., Gul, M., & Yildirim, A. (2004). Hippophaë rhamnoides L.: chromatographic to determine chemical composition, use in traditional medicine and pharmacological effects. Journal of Chromatography B, 812, 291–307.
Chemat, F., Lucchesi, M. E., Smadja, J., Favretto, L., Colnaghi, G., & Visinoni, F. (2006). Microwave accelerated steam distillation of essential oil from lavender: a rapid, clean and environmentally friendly approach. Analytica Chimica Acta, 555, 157–160.
Chen, C., Zhang, H., Xiao, W., Yong, Z.-P., & Bai, N. (2007). High-performance liquid chromatographic fingerprint analysis for different origins of sea buckthorn berries. Journal of Chromatography A, 1154, 250–259.
Craveiro, A. A., Matos, F. J. A., Alencar, J. W., & Plumel, M. M. (1989). Microwave extraction of an essential oil. Flavour Fragrance Journal, 4, 43–44.
Diouf, P. N., Stevanovic, T., & Cloutier, A. (2009). Study on chemical composition, antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activities of hot water extract from Picea mariana bark and its proanthocyanidin-rich fractions. Food Chemistry, 113, 897–902.
Dufour, C., Loonis, M., & Dangles, O. (2007). Inhibition of the peroxidation of linoleic acid by the flavonoid quercetin with in their complex with human serum albumin. Free Radical Biology & Medicine, 43, 241–252.
Ercisli, S., Orhan, E., Ozdemir, O., & Sengul, M. (2007). The genotypic effects on the chemical composition and antioxidant activity of sea buckthorn (Hippophaë rhamnoides L.) berries grown in Turkey. Scientia Horticulturae, 115, 27–33.
Ferhat, M. A., Meklati, B. Y., Smadja, J., & Chemat, F. (2006). An improved microwave Clevengervapparatus for distillation of essential oils from orange peel. Journal of Chromatography A, 1112, 121–126.
Ferhat, M. A., Tigrine-Kordjani, N., Chemat, S., Meklati, B. Y., & Chemat, F. (2007). Rapid extraction of volatile compounds using a new simultaneous microwave distillation: solvent extraction device. Chromatographia, 65, 217–222.
Ganzler, K., Salgo, A., & Valko, K. (1986). Microwave extraction: a novel sample preparation method for chromatography. Journal of Chromatography A, 371, 299–306.
Khiari, Z., Makris, D. P., & Kefalas, P. (2009). An investigation on the recovery of antioxidant phenolics from onion solid wastes employing water/ethanol-based solvent systems. Food and Bioprocess Technology, 2, 337–343. doi:10.1007/s11947-007-0044-8.
Lettelier, M., & Budzinski, H. (1999). Microwave assisted extraction of organic compounds. Analusis, 27, 259–270.
Lucchesi, M. E., Chemat, F., & Smadja, J. (2004). Solvent-free microwave extraction of essential oil from aromatic herbs: comparison with conventional hydro-distillation. Journal of Chromatography A, 1043, 323–327.
Mengal, P., & Mompon, B. (1996). Method and apparatus for solvent free microwave extraction of natural products. Eur. Pat. P. EP 698 076 B1.
Monzocco, L., Anese, M., & Nicoli, M. C. (1998). Antioxidant properties of tea extracts as affected by processing. Lebensmittel-Wissenschaft und Technologie, 31, 694–698.
Paré, J. R. J., & Bélanger, J. M. R. (1997). Microwave-assisted process: principles and applications. In J. R. J. Paré & J. M. R. Bélanger (Eds.), Instrumental methods in food analysis (Vol. 18). Amsterdam: Elsevier Science.
Patras, A., Brunton, N. P., Tiwari, B. K., & Butler, F. (2009). Stability and degradation kinetics of bioactive compounds and colour in strawberry jam during storage. Food and Bioprocess Technology. doi:10.1007/s11947-009-0226-7.
Rosch, D., Krumbein, A., & Kroh, L.-W. (2004). Antioxidant gallocatechins, dimeric and trimeric proanthocyanidins from sea buckthorn (Hippophae rhamnoides) pomace. European Food Research and Technology, 219, 605–613.
Sahraoui, N., Abert-Vian, M., Bornard, I., Boutekdjiret, C., & Chemat, F. (2008). Improved microwave steam distillation appatus for isolation of essential oils: Comparison with conventional steam distillation. Journal of Chromatography A, 1210, 229–233.
Sajfrtova, M., Lickova, L., Wimmerova, M., Sovova, H., & Wimmer, Z. (2010). β-Sitosterol: supercritical carbon dioxide extraction from Sea Buckthorn (Hippophaë rhamnoides L.) Seeds. International Journal of Molecular Science, 11, 1842–1850.
Sharma, U.-K., Sharma, K., Sharma, N., Singh, H.-P., & Sinha, A.-K. (2008). Microwave-assisted efficient extraction of different parts of Hippophaë rhamnoids for the comparative evaluation of antioxidant activity and qualification of its phenolic constituents by reverse-phase high performance liquid chromatography. Journal of Agriculture and Food Chemistry, 56, 374–379.
Stashenko, E. E., Jaramillo, B. E., & Martinez, J. R. (2004). Comparison of different extraction methods for the analysis of volatile secondary metabolites of Lippia alba (Mill.) N.E. Brown, grown in Colombia, and evaluation of its in vitro antioxidant activity. Journal of Chromatography A, 1025, 93–103.
Upendra, K., Kapril, S., Nnandini, S., & Abhishe, S. (2008). Microwave-assisted efficient extraction of different parts of Hippophaë rhamnoides for the comparative evaluation of antioxidant activity and quantification of its phenolic constituents by RP- HPLC. Journal of Agriculture and Food Chemistry, 56, 374–379.
Vinson, J. A., & Hontz, B. A. (1995). Phenol antioxidant index: comparative antioxidant effectiveness of red and white wines. Journal of Agriculture and Food Chemistry, 43, 401–403.
Yuangang, Z., Chunying, L., Yujie, F., & Chunying, Z. (2006). Simultaneous determination of catechin, rutin, quercetin, kaempferol and isorhamnetin in the extraction of sea buchthorn (Hippophae rhamnoides L.) leaves by RP-HPLC with DAD. Journal of Pharmaceutical and Biomedical Analysis, 41, 714–719.
Zill-e-Huma, Abert-Vian M., Mangonnat, J. F., & Chemat, F. (2009). Clean recovery of antioxidant flavonoids from onions: optimising solvent free microwave extraction method. Journal of Chromatography A, 1216, 7700–7707.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Périno-Issartier, S., Zill-e-Huma, Abert-Vian, M. et al. Solvent Free Microwave-Assisted Extraction of Antioxidants from Sea Buckthorn (Hippophae rhamnoides) Food By-Products. Food Bioprocess Technol 4, 1020–1028 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-010-0438-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-010-0438-x