Abstract
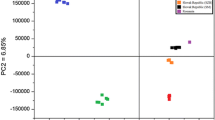
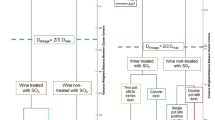
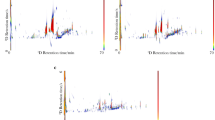
The volatiles of Chinese spirits were evaluated using a fast gas chromatography analyzer (zNose™). The first derivative profile, retention time, and peak area were used to discriminate samples at various grades. Principal component analysis and canonical discriminant analysis were adopted for data analyses, where 100% classification was achieved. A network analyzer was also included in this study in order to explore the possibility of estimating the concentration of alcohol using the spirit’s dielectric properties. The dielectric constant and loss factor of 0–100% ethanol–water mixtures in 10% interval and 42%, 50%, 53%, 62%, and 64% ethanol–water mixtures, as well as spirits samples were measured and compared.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Boyaci, I. H., Sumnu, G., & Sakiyan, O. (2008). Estimation of dielectric properties of cakes based on porosity, moisture content, and formulations using statistical methods and artificial neural network. Food and Bioprocess Technology. doi:10.1007/s11947-008-0064-z.
Fenjiu Group (2007). Available at: www.fenjiu.com.cn. Accessed 25 March 2007.
Gan, H. L., Che Man, Y. B., Tan, C. P., NorAini, I., & Nazimah, S. A. H. (2005). Characterization of vegetable oils by surface acoustic wave sensing electronic nose. Food Chemistry, 89, 507–518. doi:10.1016/j.foodchem.2004.03.005.
Kuang, W., & Nelson, S. O. (1997). Dielectric relaxation characteristics of fresh fruits and vegetables from 3 to 20 GHz. Journal of Microwave power & Electromagnetic Energy, 32(2), 114–122.
Lammertyn, J., Veraverbeke, E. A., & Irudayaraj, J. (2004). zNose technology for the classification of honey based on rapid aroma profiling. Sensors Actuators B, 98, 54–62. doi:10.1016/j.snb.2003.09.012.
Li, C., Heinemann, P., & Sherry, R. (2006a). Neural network and Bayesian network fusion models to fuse electronic nose and surface acoustic wave sensor data for apple defect detection. Sensors and Actuators. B, Chemical, 125, 301–310 (2007).
Li, Z., Wang, N., & Vigneault, C. (2006b). Electronic nose and electronic tongue in food production and processing. Stewart Postharvest Review, 4(7), 1–6. doi:10.2212/spr.2006.4.7.
Liao, X., Raghavan, G. S. V., & Yaylayan, V. A. (2001). Dielectric properties of Alcohols (C1-C5) at 2450 MHz and 945 MHz. Journal of Molecular Liquids, 94, 51–60. doi:10.1016/S0167-7322(01)00241-0.
Nelson, S. O. (1977). Use of electrical properties for grain-moisture measurement. Journal of Microwave Power, 12(1), 67–72.
Nelson, S. O. (1999). Dielectric properties measurement techniques and application. Transactions of the ASAE, 42(2), 523–529.
Nigmatullin, R. R., & Nelson, S. O. (2006). Recognition of the ‘‘fractional’’ kinetics in complex systems: Dielectric properties of fresh fruits and vegetables from 0.01 to 1.8 GHz. Signal Processing, 86, 2744–2759. doi:10.1016/j.sigpro.2006.02.018.
Smith, R. L., Lee, S. B., Komori, H., & Arai, K. (1998). Relative permittivity and dielectric relaxation in aqueous alcohol solutions. Fluid Phase Equilibria, 144, 315–322. doi:10.1016/S0378-3812(97)00275-6.
Wu, S. (2001). Research on correlations and trace components of five flavour types of liquor. Liquor-Making Science & Technology, 106, 82–85 in Chinese.
Zhang, Q., Xie, C., Zhang, S., Wang, A., Zhu, B., Wang, L., et al. (2005). Identification and pattern recognition analysis of Chinese liquors doped nano ZnO gas sensor array. Sensors Actuators B, 110, 370–376. doi:10.1016/j.snb.2005.02.017.
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge financial support from Canada Foundation of Innovation (CFI) and Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada (NSERC). The Fenjiu Group is also acknowledged for supplying samples.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Z., Wang, N., Raghavan, G.S.V. et al. Volatiles Evaluation and Dielectric Properties Measurements of Chinese Spirits for Quality Assessment. Food Bioprocess Technol 4, 247–253 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-008-0162-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-008-0162-y