Abstract
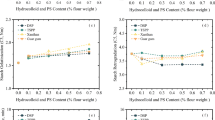
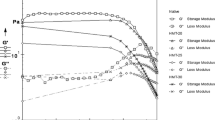
Five different hydrocolloids (amidated low-methoxyl [ALM] and high-methoxyl [HM] pectins, kappa- and iota-carrageenans [κ-C and ι-C], and xanthan gum [XG]) and two dairy proteins (whey protein [WP] and sodium caseinate [SC]) were added at five different concentrations to fresh (F) and frozen/thawed (F/T) mashed potatoes to investigate ways of improving the effects of freezing and thawing. It was found that each hydrocolloid and protein, depending on the concentration, affected the viscoelastic properties of F and F/T mashed potatoes in a different way. Color, drip loss (DL), total soluble solid (TSS) content, and overall acceptability (OA) were also determined. All systems showed weak gel behavior, although the F samples exhibited higher values of G′ and G″ as compared to F/T counterparts. However, the effects were highly dependent on the type and level of biopolymer added. F and F/T mashed potatoes with added WP presented higher values of G′ and G″, and values were lowest in both when XG was added. After freezing and thawing, the addition of ingredients (3 to 5 g kg−1 ALM and HM, 3 to 8 g kg−1 κ-C, and 1.5 g kg−1 WP) had the effect of thickening the mash and thus improving freeze/thaw stability. Processed samples were darker than F samples, although this darkening was not detected by the panelists. Color was affected less by κ-C or ι-C than by the other ingredients added. ALM pectin, κ-C and ι-C, XG, and SC all exhibited water-holding capability, whereas HM and WP did not. The product yielded by XG was softer than controls without added cryoprotectants in both F and F/T samples, but samples containing 0.5 and 1.5 g kg−1 added XG were judged more acceptable than the F control because of the creamy mouth-feel it produced.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmed, J., & Ramaswamy, H. S. (2006). Viscoelastic properties of sweet potato puree infant food. Journal of Food Engineering, 74, 376–382.
Alvarez, M. D., & Canet, W. (1999). Rheological properties of mashed potatoes made from dehydrated flakes: effect of ingredients and freezing. European Food Research & Technology, 209, 335–342.
Alvarez, M. D., Canet, W., & Fernández, C. (2005). Effect of freezing/thawing conditions and long-term frozen storage on the quality of mashed potatoes. Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture, 85, 2327–2340.
Alvarez, M. D., Canet, W., & Fernández, C. (2007a). Effect of modified starch concentration and freezing and thawing rates on properties of mashed potatoes (cv. Kennebec). Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture, 87, 1108–1122.
Alvarez, M. D., Canet, W., & Fernández, C. (2007b). Effect of temperature, geometry, gap and surface friction on oscillatory rheological properties of mashed potatoes. Journal of Food Process and Engineering, 30, 267–292.
Baeza, R. I., Carp, D. J., Pérez, O. E., & Pilosof, A. M. R. (2002). k-Carrageenan–protein interactions: effect of proteins on polysaccharide gelling and textural properties. Lebensmittel-Wissenschaft und-Technologie, 35, 741–747.
Basak, S., & Ramaswamy, H. S. (1994). Simultaneous evaluation of shear rate and time dependency of stirred yogurt rheology as influenced by added pectin and strawberry concentrate. Journal of Food Engineering, 21, 385–393.
Bolliger, S., Wildmoser, H., Goff, H. D., & Tharp, B. W. (2000). Relationship between ice cream mix viscoelasticity and ice crystal growth in ice cream. International Dairy Journal, 10, 791–797.
Canet, W., Alvarez, M. D., Fernández, C., & Tortosa, M. E. (2005). The effect of sample temperature on instrumental and sensory properties of mashed potato products. International Journal of Food Science and Technology, 40, 481–493.
Chaisawang, M., & Suphantharika, M. (2005). Effects of guar gum and xanthan gum additions on physical and rheological properties of cationic tapioca starch. Carbohydrate Polymers, 61, 288–295.
Chaisawang, M., & Suphantharika, M. (2006). Pasting and rheological properties of native and anionic tapioca starches as modified by guar gum and xanthan gum. Food Hydrocolloids, 20, 641–649.
Chen, J. S., Dickinson, E., & Edwards, M. (1999). Rheology of acid-induced sodium caseinate stabilized emulsion gels. Journal of Texture Studies, 30, 377–396.
CIE. (1978). Recommendations on uniform colour spaces–colour difference equations, psychometric colour terms. Supplement No. 2 to CIE Publication No. 15(E-1-3.1) 1971/(TC-1-3). CIE, Paris.
Comfort, S., & Howell, N. K. (2002). Gelation properties of soya and whey protein isolate mixtures. Food Hydrocolloids, 16, 661–672.
DeFreitas, Z., Sebranek, J. G., Olson, D. G., & Carr, J. M. (1997). Carrageenan effects on salt-soluble meat proteins in model systems. Journal of Food Science, 62, 539–543.
Dickinson, E. (1998). Stability and rheological implications of electrostatic milk protein–polysaccharide interactions. Trends in Food Science & Technology, 9, 347–354.
Dobies, M., Kozak, M., & Jurga, S. (2004). Studies of gelation process investigated by fast field cycling relaxometry and dynamical rheology: the case of aqueous low methoxyl pectin solution. Solid State Nuclear Magnetic Resonance, 25, 188–193.
Dolz, M., Hernández, M. J., & Delegido, J. (2006). Oscillatory measurements for salad dressings stabilized with modified starch, xanthan gum, and locust bean gum. Journal of Applied Polymer Science, 102, 897–903.
Downey, G. (2002). Quality changes in frozen and thawed, cooked puréed vegetables containing hydrocolloids, gums and dairy powders. International Journal of Food Science & Technology, 37, 869–877.
Downey, G. (2003). Effects of cryoprotectant mixtures on physical properties of frozen and thawed puréed cooked potatoes: some introductory studies. International Journal of Food Science & Technology, 38, 857–868.
Drohan, D. D., Tziboula, A., McNulty, D., & Horne, D. S. (1997). Milk proteins carrageenan interactions. Food Hydrocolloids, 11, 101–107.
Eliasson, A. C., & Kim, H. R. (1992). Changes in rheological properties of hydroxypropyl potato starch pastes during freeze–thaw treatments I. A rheological approach for evaluation of freeze–thaw stability. Journal of Texture Studies, 23, 279–295.
Faria-Tischer, P. C. S., Noseda, M. D., de Freitas, R. A., Sierakowski, M. R., & Duarte, M. E. R. (2006). Effects of iota-carrageenan on the rheological properties of starches. Carbohydrate Polymers, 65, 49–57.
Fernández, C., Alvarez, M. D., Canet, W. (2007). Steady shear and yield stress of fresh and frozen/thawed mashed potatoes: effect of biopolymers addition. Food Hydrocolloids. DOI 10.1016/j.foodhyd.2007.08.003.
Garnier, C., Axelos, M. A. V., & Thibault, J. F. (1993). Phase-diagrams of pectin–calcium systems. Influence of pH, ionic-strength, and temperature on the gelation of pectins with different degrees of methylation. Carbohydrate Research, 240, 219–232.
Gilsenan, P. M., Richardson, R. K., & Morris, E. R. (2000). Thermally reversible acid-induced gelation of low-methoxy pectin. Carbohydrate Polymers, 41, 339–349.
Hirashima, M., Takahashi, R., & Nishimari, K. (2004). Effects of citric acid on the viscoelasticity of corn starch pastes. Journal of Agriculture and Food Chemistry, 52, 2929–2933.
Koksoy, A., & Kilic, M. (2004). Use of hydrocolloids in textural stabilization of a yoghurt drink, ayran. Food Hydrocolloids, 18, 593–600.
Korus, J., Juszczak, L., Witczak, M., & Achremowicz, B. (2004). Influence of selected hydrocolloids on triticale starch rheological properties. International Journal of Food Science & Technology, 39, 641–652.
Lai, V. M. F., Huang, A. L., & Lii, C. Y. (1999). Rheological properties and phase transition of red algal polysaccharides–starch composites. Food Hydrocolloids, 13, 409–418.
Liehr, M., & Kuliche, W. M. (1996). Rheological examination of the influence of hydrocolloids on the freeze-thaw-stability of starch gels. Starke (Weinheim), 48, 52–57.
Lundin, L., & Hermansson, A. M. (1998). Multivariate analysis of the influences of locus beam gum, α s-casein, k-casein on viscoelastic properties of Na-k-carrageenan gels. Food Hydrocolloids, 12, 175–187.
Mandala, I. (2005). Physical properties of fresh and frozen stored, microwave-reheated breads, containing hydrocolloids. Journal of food Engineering, 63, 291–300.
Mandala, I. G., & Bayas, E. (2004). Xanthan effect on swelling, solubility and viscosity of wheat starch dispersions. Food Hydrocolloids, 18, 191–201.
Mandala, I., Michon, C., & Launay, B. (2004). Phase and rheological behaviors of xanthan/amylose and xanthan/starch mixed systems. Carbohydrate Polymers, 58, 285–292.
Marcotte, M., Taherian, A. R., Trigui, M., & Ramaswamy, H. S. (2001). Evaluation of rheological properties of selected salt enriched food hydrocolloids. Journal of Food Engineering, 48, 157–167.
Mleko, S., Li-Chan, E. C. Y., & Pikus, S. (1997). Interactions of k-carragenan with whey protein in gels formed at different pH. Food Research International, 30, 427–433.
Montero, P., & Pérez-Mateos, M. (2002). Effects of Na+, K+ and Ca2+ on gels formed from fish mince containing a carrageenan or alginate. Food Hydrocolloids, 16, 375–385.
Morikawa, K., & Nishinari, K. (2000). Effects of concentration dependence of retrogradation behaviour of dispersions for native and chemically modified potato starch. Food Hydrocolloids, 14, 395–401.
Norton, I. T., & Frith, W. J. (2001). Microstructure design in mixed biopolymer composites. Food Hydrocolloids, 15, 543–553.
Norton, I. T., Goodall, D. M., Frangou, S. A., & Morris, E. R. (1984). Mechanism and dynamics of conformational ordering in xanthan polysaccharide. Journal of Molecular Biology, 175, 371–394.
O'Leary, E., Gormley, T. R., Butler, F., & Shilton, N. (2000). The effect of freeze-chilling on the quality of ready-meal components. Lebensmittel-Wissenschaft und-Technologie, 33, 217–224.
Ould Eleya, M. M., & Turgeon, S. L. (2000). Rheology of k-carrageenan and β-lactoglobulin mixed gels. Food Hydrocolloids, 14, 29–40.
Picullel, L. (1991). Effects of ions on the disorder–order transitions of gel-forming polysaccharides. Food Hydrocolloids, 5, 57–69.
Racape, E., Thibault, J. F., Reitsma, J. C. E., & Pilnik, W. (1989). Properties of amidated pectin II. Polyelectrolyte behaviour and calcium binding of amidated pectins and amidated pectic acids. Biopolymers, 28, 1435–1448.
Ramaswamy, H. S., & Basak, S. (1992). Pectin and strawberry concentrate effects on the rheology of stirred commercial yogurt. Journal of Food Science, 57, 357–360.
Rao, M. A., & Cooley, H. J. (1992). Rheological behaviour of tomato pastes in steady and dynamic shear. Journal of Texture Studies, 23, 415–425.
Rico, R., Alvarez, M. D., & Canet, W. (1995). Sistema de adquisición y análisis de datos. Eurofach Electrónica, 18, 60–65.
Shand, P. J., Sofos, J. N., & Schmidt, G. R. (1994). Kappa-carrageenan, sodium chloride and temperature affect yield and texture of structured beef rolls. Journal of Food Science, 59, 282–287.
Shi, X. H., & BeMiller, J. M. (2002). Effects of food gums on viscosities of starch suspensions during pasting. Carbohydrate Polymers, 50, 7–18.
Smith, O. (1987). Transport and storage of potatoes. In Potato processing (pp. 203–285). New York: Van Nostrand Reinhold.
Stanley, N. F. (1990). Carrageenans. In Food gels (pp. 79–119). London: Elsevier.
Sudhakar, V., Singhal, R. S., & Kulkarmi, P. R. (1995). Studies on starch–hydrocolloid interactions: effect of salts. Food Chemistry, 53, 405–408.
Sych, J., Lacroix, C., Adambounou, L. T., & Castaigne, F. (1990). Cryoprotective effect of lactitol, palatinit and polydextrose on cod surimi proteins during frozen storage. Journal of Food Science, 55, 356–360.
Tárrega, A., Costell, E., & Rao, M. A. (2006). Vane yield stress of native and cross-linked starch dispersions in skimmed milk: effect of starch concentration and λ-carrageenan addition. Food Science & Technology International, 12, 253–260.
Tavares, C., Monteiro, S. R., Moreno, N., & Lopes da Silva, J. A. (2005). Does the branching degree of galactomannans influence their effect on whey protein gelation. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 270–271, 213–219.
Tecante, A., & Doublier, J. L. (1999). Steady flow and viscoelastic behavior of crosslinked waxy corn starch-kappa-carrageenan pastes and gels. Carbohydrate Polymers, 40, 221–231.
Acknowledgements
The authors wish to thank the Spanish Ministry of Education and Science for the financial support (AGL2004-01780) and Premium Ingredients, SL for the donation of ingredients. The author C. Fernández wishes to thank the CAM for the fellowship awarded for her doctoral thesis.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Alvarez, M.D., Fernández, C. & Canet, W. Oscillatory Rheological Properties of Fresh and Frozen/Thawed Mashed Potatoes as Modified by Different Cryoprotectants. Food Bioprocess Technol 3, 55–70 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-007-0051-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-007-0051-9