Abstract
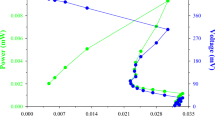
Citric acid is nowadays produced by submerged fermentation of Aspergillus niger. The process yield depends on the composition of the medium, as well as on the microorganism strain. In this work, the effect of Fe+3, Zn+2, and Mn+2 on citric acid production by A. niger NRRL 2001 is presented. The culture medium composition was glucose (120 g/L) KH2PO4 (1.0 g/L); K2HPO4 (1.0 g/L), MgSO4.7H2O (0.5 g/L), (NH4)2SO4 (3.0 g/L). The ions Fe+3, Zn+2, and Mn+2 had their concentrations changed according to an experimental design. The experiments were carried out in an orbital shaker at 200 rpm and 30°C. The strain produced an extracellular polysaccharide that was also quantified. The optimum experimental condition was found using 7.0 mg/L of Fe+3 and 6.5 mg/L of Zn+2 in absence of Mn+2. No oxalic acid formation was observed using this experimental condition. Metal contents were not significant for the production of the polysaccharide. The highest production rate (2.95 g L−1 day−1) was reached after 10 days of fermentation. After this period, the productivity decreased slightly. In 20 days, the citric acid production rate (2.44 g L−1 day−1) was 82% of the highest productivity. The conversion into citric acid increased continuously, yielding 45.8% in 20 days of fermentation.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adham, N. Z. (2002). Attempts at improving citric acid fermentation by Aspergillus niger in beet-molasses medium. Biochemical Technology, 84, 97–100.
Ali, S., Haq, I. U., Qadeer, M. A., & Iqbal, J. (2001). Biosynthesis of citric acid by locally isolated Aspergillus niger using sucrose salt media. Journal of Biological Science, 1, 178–181.
Angumeenal, A., & Venkappayya, D. (2005). Artrocarpus heterophyllus: A potential substrate for citric acid biosynthesis using Aspergillus niger. Food Science and Technology, 38, 89–93.
Bizukojc, M., & Ledakowicz, S. (2004). The kinetics of glucose uptake and product formation by Aspergillus niger in citric acid fermentation. Process Biochemistry, 39, 2261–2268.
Chinnici, F., Spinabelli, U., & Riponi, C. (2005). Optimization of the determination of organic acids and sugars in fruit juices by ion-exclusion liquid chromatography. Journal of Food Composition and Analysis, 18, 121–130.
Demirel, G., Yaykasli, K. O., & Yasar, A. (2005). The production of citric acid by using immobilized Aspergillus niger A-9 and investigation of its various effects. Food Chemistry, 89, 393–396.
Dubois, M., Gilles, K. A., Hamilton, P. A., Rebers, P. A., & Smith, F. (1956). Colorimetric method for determination of sugars and related substances. Analytical Chemistry, 28, 350–356.
Fleming, I. D., & Pegler, H. F. (1963). The determination of glucose in the presence of maltose and isomaltose by a stable, specific enzymic reagent. Analyst, 88, 967–968.
Guilherme, A. A., Dornelles, A. S., Pinto, G. A. S, & Rodrigues, S. (2006). Estudo metabólico do Aspergillus niger NRRL 2001 para produção de ácido cítrico em fermentação submersa. In XVI Congresso Brasileiro de Engenharia Química, Setembro 2006, Santos-SP-Brazil (CD-ROM).
Hang, Y. D., & Woodans, E. E. (1998). Production of citric acid from corncobs by Aspergillus niger. Bioresource Technology, 65, 251–253.
Haq, I. U., Ali, S., Qadeer, M. A., & IqBal, J. (2002). Effect of cooper ions on mould morphology and citric acid productivity by Aspergillus niger using molasses based media. Process Biochemistry, 37, 1085–1090.
Haq, I. U., Ali, S., Qadeer, M. A., & Iqbal, J. (2003). Stimulatory effect of alchohols (methanol and ethanol) on citric acid productivity by a 2-deoxy D-glucose resistant culture of Aspergillus niger GCB-47. Bioresource Technology, 86, 227–233.
Haq, I. U., Ali, S., Qadeer, M. A., & Iqbal, J. (2004). Citric acid production by selected mutants of Aspergillus niger from cane molasses. Bioresource Technology, 93, 125–130.
Imandi, S. B., Bandaru, V. V. R., Somalanka, S. R., & Garapati, H. R. (2007). Optimization of medium composition for the production of citric acid from byproduct glycerol using Doehlert experimental design. Enzyme and Microbial Technology, 40, 1367–1372.
Kirimura, K., Yusa, A. S., Rugsaseel, A. S., Nakagawa, H., Osumi, A. M., & Usami, A. S. (1999). Amylose-like polysaccharide accumulation and hyphal cell-surface structure in relation to citric acid production by Aspergillus niger in shake culture. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 52, 421–428.
Kumar, D., Jain, V. K., Shanker, G., & Srivastava, A. (2003). Citric acid production by solid state fermentation using sugar cane bagasse. Process Biochemistry, 38, 1731–1738.
Kurbanoglu, E. B. (2004). Enhancement of citric acid production with ram horn hydrolisate by Aspergillus niger. Bioresource Technology, 92, 97–101.
Papagianni, M., Mattey, M., & Kristiansen, B. (1999). The influence of glucose concentration on citric acid production and morphology of Aspergillus niger in batch and culture. Enzyme and Microbial Technology, 25, 710–717.
Sanchez-Marroquin, A., Carreno, R., & Ledezma, M. (1970). Effect of trace elements on citric acid fermentation by Aspergillus niger. Applied Microbiology, 20, 888–892.
Sankpal, N. V., Joshi, A. P., & Kulkarni, B. D. (2001). Citric acid production by Aspergillus niger immobilized on cellulose microfibrils: Influence of morphology and fermenter conditions on productivity. Process Biochemistry, 36, 1129–1139.
Soccol, C. R., Vandenberghe, L. P. S., Rodrigues, C., & Pandey, A. (2006). New perspectives for citric acid production and application. Food Technology and Biotechnology, 44, 141–149.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Conselho Nacional de Pesquisa e Desenvolvimento Cientifico e Tecnológico for the awarded scholarship and Agricultural Research Service Culture Collection for the microbial strain used in the present study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guilherme, A.A., Pinto, G.A.S. & Rodrigues, S. Optimization of Trace Metals Concentration on Citric Acid Production by Aspergillus niger NRRL 2001. Food Bioprocess Technol 1, 246–253 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-007-0009-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-007-0009-y