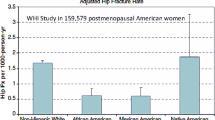
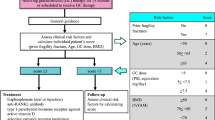
Abstract
Purpose of Review
Osteoporosis in axial spondyloarthritis may be modified by therapy. The purpose of this systematic review is to describe (i) the effect of TNFi on BMD, (ii) the effect of secukinumab on BMD, and (iii) the effect of secukinumab on radiographic disease progression in axSpA.
Recent Findings
We searched PubMed, Embase, and Cochrane using the following retrieval languages: spondyloarthritis, ankylosing spondylitis, TNF, IL-17, x-rays, and osteoporosis. Twenty-nine studies were included; 27 re: TNFi and BMD, and 2 re: IL-17 blockers and x-ray progression. TNFi over 2–4 years increased BMD of the lumbar spine (3.2–14.9%) and hip (2.26–4.7%) without reducing vertebral fractures. Secukinumab reduced radiographic progression; none (73%) and minimal (79%) at 4 years. No data on IL-17 blockade and bone were found.
Summary
TNFi therapy improves bone density but not vertebral fracture rates. Secukinumab improves symptoms and may slow radiographic progression. Data is lacking regarding the effects of secukinumab on BMD and fractures. These are important questions which may impact the choice of therapy.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- axSpA:
-
Axial spondyloarthritis
- AS:
-
Ankylosing spondylitis
- TNFi:
-
Tumor necrosis factor (TNF) inhibitor
- RCT:
-
Randomized control trial
- PRISMA:
-
Preferred reporting items for systematic review and meta-analysis
- mSASSS:
-
Modified Stoke Ankylosing Spondylitis Spinal Score
- ACR:
-
American College of Rheumatology
- LS:
-
Lumbar spine
- TH:
-
Total hip
- FN:
-
Femoral neck
- VFx:
-
Vertebral fractures
- OTW:
-
Occiput to wall
- BASFI:
-
Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Functional Index
- VEs:
-
Vertebral edges
References
Papers of particular interest, published recently, have been highlighted as: • Of importance •• Of major importance
Calin A. Osteoporosis and ankylosing spondylitis. Br J Rheumatol. 1991;30(4):318–9.
Reid DM, Nicoll JJ, Kennedy NS, Smith MA, Tothill P, Nuki G. Bone mass in ankylosing spondylitis. J Rheumatol. 1986;13(5 SRC - BaiduScholar):932–5.
Will R, Palmer R, Bhalla AK, Ring F, Calin A. Osteoporosis in early ankylosing spondylitis: a primary pathological event? Lancet (London, England). 1989;2:1483–5 SRC - BaiduScholar:8678–8679.
El Maghraoui A, Borderie D, Cherruau B, Edouard R, Dougados M, Roux C. Osteoporosis, body composition, and bone turnover in ankylosing spondylitis. J Rheumatol. 1999;26(10):2205–9.
Arends S, Spoorenberg A, Houtman PM, Leijsma MK, Bos R, Kallenberg CG, et al. The effect of three years of TNFalpha blocking therapy on markers of bone turnover and their predictive value for treatment discontinuation in patients with ankylosing spondylitis: a prospective longitudinal observational cohort study. Arthritis Res Ther. 2012;14(2):R98.
Briot K, Gossec L, Kolta S, Dougados M, Roux C. Prospective assessment of body weight, body composition, and bone density changes in patients with spondyloarthropathy receiving anti-tumor necrosis factor-alpha treatment. J Rheumatol. 2008;35(5):855–61.
Durnez A, Paternotte S, Fechtenbaum J, Landewe RB, Dougados M, Roux C, et al. Increase in bone density in patients with spondyloarthritis during anti-tumor necrosis factor therapy: 6-year followup study. J Rheumatol. 2013;40(10):1712–8.
Haroon N, Inman RD, Learch TJ, Weisman MH, Lee M, Rahbar MH, et al. The impact of tumor necrosis factor alpha inhibitors on radiographic progression in ankylosing spondylitis. Arthritis Rheum. 2013;65(10):2645–54.
Maas F, Arends S, Brouwer E, Essers I, van der Veer E, Efde M, et al. Reduction in spinal radiographic progression in ankylosing spondylitis patients receiving prolonged treatment with tumor necrosis factor inhibitors. Arthritis Care Res. 2017;69(7):1011–9.
Molnar C, Scherer A, Baraliakos X, de Hooge M, Micheroli R, Exer P, et al. TNF blockers inhibit spinal radiographic progression in ankylosing spondylitis by reducing disease activity: results from the Swiss clinical quality management cohort. Ann Rheum Dis. 2018;77(1):63–9.
Paine A, Ritchlin CT. Targeting the interleukin-23/17 axis in axial spondyloarthritis. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2016;28(4):359–67.
Patel DD, Kuchroo VK. Th17 cell pathway in human immunity: lessons from genetics and therapeutic interventions. Immunity. 2015;43(6):1040–51.
Wellcome Trust Case Control C, Australo-Anglo-American spondylitis C, Burton PR, Clayton DG, Cardon LR, Craddock N, et al. Association scan of 14,500 nonsynonymous SNPs in four diseases identifies autoimmunity variants. Nat Genet. 2007;39(11):1329–37.
Sherlock JP, Joyce-Shaikh B, Turner SP, Chao CC, Sathe M, Grein J, et al. IL-23 induces spondyloarthropathy by acting on ROR-gammat+ CD3+CD4-CD8- entheseal resident T cells. Nat Med. 2012;18(7):1069–76.
Tseng HW, Pitt ME, Glant TT, McRae AF, Kenna TJ, Brown MA, Pettit AR, Thomas GP: Inflammation-driven bone formation in a mouse model of ankylosing spondylitis: sequential not parallel processes. Arthritis Res Ther 2016, 18:0.
• Mansoori MN, Shukla P, Singh D. Combination of PTH (1–34) with anti-IL17 prevents bone loss by Inhibiting IL-17/ N-cadherin mediated disruption of PTHR1/LRP-6 interaction. Bone. 2017;105:226–36 This study investigates the mechanism of action by which IL-17 promotes bone loss and provides data demonstrating that the bone loss occurs through up-regulation of N-cadherin and inhibition of wnt signaling. This provides a rationale for the hypothesis that blockade of IL-17 may be beneficial in preventing osteoporosis.
Tyagi AM, Mansoori MN, Srivastava K, Khan MP, Kureel J, Dixit M, et al. Enhanced immunoprotective effects by anti-IL-17 antibody translates to improved skeletal parameters under estrogen deficiency compared with anti-RANKL and anti-TNF-alpha antibodies. J Bone Miner Res Off J Am Soc Bone Miner Res. 2014;29(9):1981–92.
Molnar I, Bohaty I, Somogyine-Vari E. IL-17A-mediated sRANK ligand elevation involved in postmenopausal osteoporosis. Osteoporosis Int. 2014;25(2 SRC - BaiduScholar):783–6.
Azizieh F, Raghupathy R, Shehab D, Al-Jarallah K, Gupta R: Cytokine profiles in osteoporosis suggest a proresorptive bias. Menopause (New York, NY) 2017, 24(9):1057–1064.
•• Braun J, Baraliakos X, Deodhar A, Baeten D, Sieper J, Emery P, et al. Effect of secukinumab on clinical and radiographic outcomes in ankylosing spondylitis: 2-year results from the randomized phase III MEASURE 1 study. Ann Rheum Dis. 2017;76(6):1070–7 This study describes the results of the Phase 3 secukinumab study in AS demonstrating both improvement in AS signs and symptoms through 2 years of therapy as well as low mean progression of spinal radiographic progression.
Braun J, Baraliakos X, Deodhar AA, Poddubnyy D, Emery P, Delicha EM, Talloczy Z, Porter B: Secukinumab demonstrates low radiographic progression and sustained efficacy through 4 years in patients with active ankylosing spondylitis. Arhtritis Rheumatol 2017, 69(suppl 10).
Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J, Altman DG. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement. Ann Intern Med. 2009;151(4):264–9 w264.
van der Linden S, Valkenburg HA, Cats A. Evaluation of diagnostic criteria for ankylosing spondylitis. A proposal for modification of the New York criteria. Arthritis Rheum. 1984;27(4):361–8.
Rudwaleit M, van der Heijde D, Landewe R, Akkoc N, Brandt J, Chou CT, et al. The assessment of SpondyloArthritis International Society classification criteria for peripheral spondyloarthritis and for spondyloarthritis in general. Ann Rheum Dis. 2011;70(1):25–31.
Haroon NN, Sriganthan J, Al Ghanim N, Inman RD, Cheung AM. Effect of TNF-alpha inhibitor treatment on bone mineral density in patients with ankylosing spondylitis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2014;44(2):155–61.
Li H, Li Q, Chen X, Ji C, Gu J. Anti-tumor necrosis factor therapy increased spine and femoral neck bone mineral density of patients with active ankylosing spondylitis with low bone mineral density. J Rheumatol. 2015;42(8):1413–7.
Venceviciene L, Butrimiene I, Vencevicius R, Sadauskiene E, Kasiulevicius V, Sapoka V. Factors associated with bone mineral density loss in patients with spondyloarthropathies: a 4-year follow-up study. Medicina (Kaunas, Lithuania). 2015;51(5):272–9.
Briot K, Etcheto A, Miceli-Richard C, Dougados M, Roux C. Bone loss in patients with early inflammatory back pain suggestive of spondyloarthritis: results from the prospective DESIR cohort. Rheumatology (Oxford, England). 2016;55(2):335–42.
• van der Weijden MA, van Denderen JC, Lems WF, Nurmohamed MT, Dijkmans BA, van der Horst-Bruinsma IE. Etanercept increases bone mineral density in ankylosing spondylitis, but does not prevent vertebral fractures: results of a prospective observational cohort study. J Rheumatol. 2016;43(4):758–64 This study highlights the dichotomy of increased bone density at the hip and spine with the anti-TNF agent Etanercept in AS patients but also reports increased incidence of vertebral fracture in this group of patients.
Maas F, Spoorenberg A, Brouwer E, Schilder AM, Chaudhry RN, Wink F, et al. Radiographic vertebral fractures develop in patients with ankylosing spondylitis during 4 years of TNF-alpha blocking therapy. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2016;34(2):191–9.
Balshem H, Helfand M, Schunemann HJ, Oxman AD, Kunz R, Brozek J, et al. GRADE guidelines: 3. Rating the quality of evidence. J Clin Epidemiol. 2011;64(4):401–6.
Dischereit G, Tarner IH, Muller-Ladner U, Lange U. Infliximab improves bone metabolism and bone mineral density in rheumatoid arthritis and ankylosing spondylitis: a prospective 2-year study. Clin Rheumatol. 2013;32(3):377–81.
Beek K, van der Weijden M, Lems W, van Denderen W, Nurmohamed M, Van der Horst-Buinsma I. Long-term effects of TNF-alpha inhibitors on bone mineral density and the incidence of vertebral fractures in patients with ankylosing spondylitis. Arthritis Rheum. 2017;69(suppl 10).
Baeten D, Baraliakos X, Braun J, Sieper J, Emery P, van der Heijde D, et al. Anti-interleukin-17A monoclonal antibody secukinumab in treatment of ankylosing spondylitis: a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet (London, England). 2013;382(9906):1705–13.
Baraliakos X, Borah B, Braun J, Baeten D, Laurent D, Sieper J, et al. Long-term effects of secukinumab on MRI findings in relation to clinical efficacy in subjects with active ankylosing spondylitis: an observational study. Ann Rheum Dis. 2016;75(2):408–12.
Braun J, Buehring, B., Baraliakos, X., Gensler, LS., Porter, B., Shete, A., Quebe-Fehling, E., Haemmerle S.: Bone mineral density and serum biomarkers of bone turnover in ankylosing spondylitis patients treated with Secukinumab: 2-year data from the pivotal phase 3 study. Arthritis Rheum 2018, 70(S10).
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Haley Tornberg—research assistant.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
DA, EMS, and SMG contributed to the conception and design of the review and assessed all papers, data extraction, and quality assessment. DA, EMG, RG, and SMG performed the literature search. DA drafted the paper; EMS and SMG revised the article for important intellectual content. All authors gave final approval of the version to be published.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
Dr. Goodman reports grants from Novartis, personal fees from Novartis, personal fees from Pfizer, personal fees from UCB, grants from Horizon, outside the submitted work.
Dr. Ashany reports grants from Novartis, outside the submitted work.
Emily M. Stein and Rie Goto declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Human and Animal Rights and Informed Consent
This article does not contain any studies with human or animal subjects performed by any of the authors.
Ethics Approval and Consent to Participate
Not applicable.
Consent for Publication
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Topical Collection on Spondyloarthritis
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ashany, D., Stein, E.M., Goto, R. et al. The Effect of TNF Inhibition on Bone Density and Fracture Risk and of IL17 Inhibition on Radiographic Progression and Bone Density in Patients with Axial Spondyloarthritis: a Systematic Literature Review. Curr Rheumatol Rep 21, 20 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11926-019-0818-9
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11926-019-0818-9