Abstract
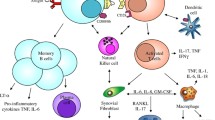
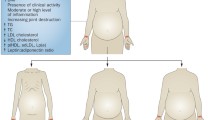
While the most obvious manifestations of rheumatoid arthritis (RA) involve inflammation and damage in the synovial joints, the systemic effects of the condition are widespread and life-threatening. Of particular interest is the ‘lipid paradox’ of RA, where patients with a numerically equivocal starting lipid profile have a significantly raised risk of cardiovascular (CV) events and response to therapy results in a ‘normalization’ of lipid levels and reduction in events. Changes in lipids can be seen before overt disease manifestations which suggest that they are closely linked to the more widespread inflammation-driven metabolic changes associated with tumour necrosis factor (TNF). Cachexia involves a shift in body mass from muscle to fat, which may or may not directly increase the cardiovascular risk. However, since TNF inhibition is associated with reduction in cardiovascular events, it does suggest that these widespread metabolic changes involving lipids are of importance. Analysis of single lipids or metabolites have been used to identify some of the key changes, but more recently, metabolomic and lipidomic approaches have been applied to identify a broad spectrum of small molecule changes and identify potentially altered metabolic pathways. Further work is needed to understand fully the metabolic changes in lipid profiles and identify novel ways of targeting desired profile changes, but work so far does suggest that a better understanding may allow management of patients to downregulate the systemic effects of their disease that puts them at risk of cardiovascular complications.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Papers of particular interest, published recently, have been highlighted as: • Of importance •• Of major importance
Humphreys JH, Verstappen SM, Hyrich KL, Chipping JR, Marshall T, Symmons DP. The incidence of rheumatoid arthritis in the UK: comparisons using the 2010 ACR/EULAR classification criteria and the 1987 ACR classification criteria. Results from the Norfolk Arthritis Register. Ann Rheum Dis. 2013;72:1315–20.
Symmons D, Turner G, Webb R, Asten P, Barrett E, Lunt M, et al. The prevalence of rheumatoid arthritis in the United Kingdom: new estimates for a new century. Rheumatology. 2002;41:793–800.
Dougados M, Soubrier M, Antunez A, Balint P, Balsa A, Buch MH, et al. Prevalence of comorbidities in rheumatoid arthritis and evaluation of their monitoring: results of an international, cross-sectional study (COMORA). Ann Rheum Dis. 2014;73:62–8. A very large study highlighting the broad range of comorbidites associated with RA, which included CVD.
Gron KL, Ornbjerg LM, Hetland ML, Aslam F, Khan NA, Jacobs JW, et al. The association of fatigue, comorbidity burden, disease activity, disability and gross domestic product in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Results from 34 countries participating in the Quest-RA program. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2014;32:869–77.
McInnes IB, Schett G. Mechanisms of disease: the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis. N Engl J Med. 2011;365:2205–19. An outstanding review of the complexities of RA molecular pathogenesis.
Demoruelle MK, Deane KD. Treatment strategies in early rheumatoid arthritis and prevention of rheumatoid arthritis. Curr Rheumatol Rep. 2012;14:472–80.
van der Linden MPM, Le Cessie S, Raza K, van der Woude D, Knevel R, Huizinga TWJ, et al. Long-term impact of delay in assessment of patients with early arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2010;62:3537–46.
Deane KD, El-Gabalawy H. Pathogenesis and prevention of rheumatic disease: focus on preclinical RA and SLE. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2014;10:212–28.
Aletaha D, Neogi T, Silman AJ, Funovits J, Felson DT, Bingham 3rd CO, et al. Rheumatoid arthritis classification criteria: an American College of Rheumatology/European League Against Rheumatism collaborative initiative. Arthritis Rheum. 2010;62:2569–81.
Rantapaa-Dahlqvist S, de Jong BA, Berglin E, Hallmans G, Wadell G, Stenlund H, et al. Antibodies against cyclic citrullinated peptide and IgA rheumatoid factor predict the development of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2003;48:2741–9.
Toms TE, Symmons DP, Kitas GD. Dyslipidaemia in rheumatoid arthritis: the role of inflammation, drugs, lifestyle and genetic factors. Curr Vasc Pharmacol. 2010;8:301–26.
Metsios GS, Stavropoulos-Kalinoglou A, Nevill AM, Douglas KM, Koutedakis Y, Kitas GD. Cigarette smoking significantly increases basal metabolic rate in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2008;67:70–3.
Myasoedova E, Crowson CS, Kremers HM, Fitz-Gibbon PD, Therneau TM, Gabriel SE. Total cholesterol and LDL levels decrease before rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2010;69:1310–4.
Amaya-Amaya J, Montoya-Sanchez L, Rojas-Villarraga A. Cardiovascular involvement in autoimmune diseases. Biomed Res Int. 2014;2014:367359.
Maradit-Kremers H, Crowson CS, Nicola PJ, Ballman KV, Roger VL, Jacobsen SJ, et al. Increased unrecognized coronary heart disease and sudden deaths in rheumatoid arthritis: a population-based cohort study. Arthritis Rheum. 2005;52:402–11.
Ogdie A, Yu Y, Haynes K, Love TJ, Maliha S, Jiang Y, et al. Risk of major cardiovascular events in patients with psoriatic arthritis, psoriasis and rheumatoid arthritis: a population-based cohort study. Ann Rheum Dis. 2015;74:326–32.
Curtis JR, John A, Baser O. Dyslipidemia and changes in lipid profiles associated with rheumatoid arthritis and initiation of anti-tumor necrosis factor therapy. Arthritis Care Res. 2012;64:1282–91. A retrospective study highlighting that RA patients are less likely to be tested for hyperlipidemia and had lower LDL cholesterol which increased after therapy.
van den Oever IA, van Sijl AM, Nurmohamed MT. Management of cardiovascular risk in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: evidence and expert opinion. Ther Adv Musculoskelet Dis. 2013;5:166–81.
Peters MJ, Symmons DP, McCarey D, Dijkmans BA, Nicola P, Kvien TK, et al. EULAR evidence-based recommendations for cardiovascular risk management in patients with rheumatoid arthritis and other forms of inflammatory arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2010;69:325–31.
Arts EE, Popa C, Den Broeder AA, Semb AG, Toms T, Kitas GD, et al. Performance of four current risk algorithms in predicting cardiovascular events in patients with early rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2015;74:668–74. An important comparison of different measures of CVD risk that shows they all underestimate the risk in RA patients.
Corrales A, Dessein PH, Tsang LD, Pina T, Blanco R, Gonzalez-Juanatey C et al. Carotid artery plaque in women with rheumatoid arthritis and low estimated cardiovascular disease risk: a cross-sectional study. Arthrit Res Ther. 2015;17. Important study focussing on the CVD risk in women, showing that plaque was highly prevalent in spite of modest rises in cholesterol.
Zampeli E, Protogerou A, Stamatelopoulos K, Fragiadaki K, Katsiari CG, Kyrkou K, et al. Predictors of new atherosclerotic carotid plaque development in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: a longitudinal study. Arthritis Res Ther. 2012;14:R44.
Sandoo A, Chanchlani N, Hodson J, Smith JP, Douglas KM, Kitas GD. Classical cardiovascular disease risk factors associate with vascular function and morphology in rheumatoid arthritis: a six-year prospective study. Arthritis Res Ther. 2013;15:R203.
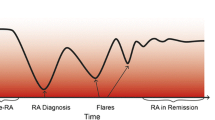
Myasoedova E, Chandran A, Ilhan B, Major BT, Michet CJ, Matteson EL et al. The role of rheumatoid arthritis (RA) flare and cumulative burden of RA severity in the risk of cardiovascular disease. Ann Rheum Dis. 2015. Online first: doi 10.1136. A large study importantly showing the strong effects of disease flares on CVD, differentiating the CVD risk in RA patients from those in the rest of the population. This highlights the need for tight control over the disease to minimise the CVD comorbidities.
Del Rincon I, Polak JF, O’Leary DH, Battafarano DF, Erikson JM, Restrepo JF, et al. Systemic inflammation and cardiovascular risk factors predict rapid progression of atherosclerosis in rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2015;74:1118–23.
Solomon DH, Reed GW, Kremer JM, Curtis JR, Farkouh ME, Harrold LR, et al. Disease activity in rheumatoid arthritis and the risk of cardiovascular events. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2015;67:1449–55.
Nurmohamed MT. Editorial: treat to target in rheumatoid arthritis: good for the joints as well as the heart? Arthritis Rheumatol. 2015;67:1412–5.
Kerekes G, Nurmohamed MT, Gonzalez-Gay MA, Seres I, Paragh G, Kardos Z, et al. Rheumatoid arthritis and metabolic syndrome. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2014;10:691–6.
Amezaga Urruela M, Suarez-Almazor ME. Lipid paradox in rheumatoid arthritis: changes with rheumatoid arthritis therapies. Curr Rheumatol Rep. 2012;14:428–37.
Choy E, Sattar N. Interpreting lipid levels in the context of high-grade inflammatory states with a focus on rheumatoid arthritis: a challenge to conventional cardiovascular risk actions. Ann Rheum Dis. 2009;68:460–9.
Myasoedova E, Crowson CS, Nicola PJ, Maradit-Kremers H, Davis 3rd JM, Roger VL, et al. The influence of rheumatoid arthritis disease characteristics on heart failure. J Rheumatol. 2011;38:1601–6.
Charles-Schoeman C, Lee YY, Grijalva V, Amjadi S, FitzGerald J, Ranganath VK, et al. Cholesterol efflux by high density lipoproteins is impaired in patients with active rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2012;71:1157–62.
Liao KP, Playford MP, Frits M, Coblyn JS, Iannaccone C, Weinblatt ME, et al. The association between reduction in inflammation and changes in lipoprotein levels and HDL cholesteroleEfflux capacity in rheumatoid arthritis. J Am Heart Assoc. 2015;4:e001588. The lipid flux changes they observed give new insights into mechanisms underlying the shift in lipids in RA.
Toms TE, Panoulas VF, Kitas GD. Dyslipidaemia in rheumatological autoimmune diseases. Open Cardiovasc Med J. 2011;5:64–75.
Davis LA, Whitfield E, Cannon GW, Wolff RK, Johnson DS, Reimold AM, et al. Association of rheumatoid arthritis susceptibility gene with lipid profiles in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatology. 2014;53:1014–21.
Toms TE, Panoulas VF, Smith JP, Douglas KMJ, Metsios GS, Stavropoulos-Kalinoglou A, et al. Rheumatoid arthritis susceptibility genes associate with lipid levels in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2011;70:1025–32.
Norata GD, Pirillo A, Ammirati E, Catapano AL. Emerging role of high density lipoproteins as a player in the immune system. Atherosclerosis. 2012;220:11–21.
Haque UJ, Bathon JM, Giles JT. Association of vitamin D with cardiometabolic risk factors in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Care Res. 2012;64:1497–504.
Jeffery LE, Burke F, Mura M, Zheng Y, Qureshi OS, Hewison M, et al. 1,25-Dihydroxyvitamin D-3 and IL-2 combine to inhibit T cell production of inflammatory cytokines and promote development of regulatory T cells expressing CTLA-4 and FoxP3. J Immunol. 2009;183:5458–67.
Moraitis AG, Freeman LA, Shamburek RD, Wesley R, Wilson W, Grant CM, et al. Elevated interleukin-10: a new cause of dyslipidemia leading to severe HDL deficiency. J Clin Lipidol. 2015;9:81–90.
Daien CI, Duny Y, Barnetche T, Daures JP, Combe B, Morel J. Effect of TNF inhibitors on lipid profile in rheumatoid arthritis: a systematic review with meta-analysis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2012;71:862–8.
Chen DY, Chen YM, Hsieh TY, Hsieh CW, Lin CC, Lan JL. Significant effects of biologic therapy on lipid profiles and insulin resistance in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Res Ther. 2015;17:559.
Ljung L, Askling J, Rantapaa-Dahlqvist S, Jacobsson L. The risk of acute coronary syndrome in rheumatoid arthritis in relation to tumour necrosis factor inhibitors and the risk in the general population: a national cohort study. Arthritis Res Ther. 2014;16:R127.
McInnes IB, Thompson L, Giles JT, Bathon JM, Salmon JE, Beaulieu AD, et al. Effect of interleukin-6 receptor blockade on surrogates of vascular risk in rheumatoid arthritis: MEASURE, a randomised, placebo-controlled study. Ann Rheum Dis. 2015;74:694–702. An imporant study showing how one of the newer biologic therapies may have specific benefits for CVD risk by altering lipids profiles.
De Sanctis S, Marcovecchio ML, Gaspari S, Del Torto M, Mohn A, Chiarelli F, et al. Etanercept improves lipid profile and oxidative stress measures in patients with juvenile idiopathic arthritis. J Rheumatol. 2013;40:943–8.
Desai RJ, Eddings W, Liao KP, Solomon DH, Kim SC. Disease-modifying antirheumatic drug use and the risk of incident hyperlipidemia in patients with early rheumatoid arthritis: a retrospective cohort study. Arthritis Care Res. 2015;67:457–66.
Myasoedova E, Gabriel SE, Green AB, Matteson EL, Crowson CS. Impact of statin use on lipid levels in statin-naive patients with rheumatoid arthritis versus non-rheumatoid arthritis subjects: results from a population-based study. Arthritis Care Res. 2013;65:1592–9.
Marks JL, Edwards CJ. Protective effect of methotrexate in patients with rheumatoid arthritis and cardiovascular comorbidity. Ther Adv Musculoskelet Dis. 2012;4:149–57.
Morris SJ, Wasko MC, Antohe JL, Sartorius JA, Kirchner HL, Dancea S, et al. Hydroxychloroquine use associated with improvement in lipid profiles in rheumatoid arthritis patients. Arthritis Care Res. 2011;63:530–4.
Toussirot E. Effects of TNFalpha inhibitors on adiposity and other cardiovascular risk factors: implications for the cardiovascular prognosis in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Expert Opin Drug Saf. 2015;14:525–32.
van Halm VP, Nurmohamed MT, Twisk JW, Dijkmans BA, Voskuyl AE. Disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs are associated with a reduced risk for cardiovascular disease in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: a case control study. Arthritis Res Ther. 2006;8:R151.
Chung CP, Giles JT, Petri M, Szklo M, Post W, Blumenthal RS, et al. Prevalence of traditional modifiable cardiovascular risk factors in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: comparison with control subjects from the multi-ethnic study of atherosclerosis. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2012;41:535–44.
Gross RW, Han X. Lipidomics at the interface of structure and function in systems biology. Chem Biol. 2011;18:284–91.
Atilla-Gokcumen GE, Eggert US. A comparative LC-MS based profiling approach to analyze lipid composition in tissue culture systems. Methods Mol Biol. 2015;1232:103–13.
Sud M, Fahy E, Cotter D, Dennis EA, Subramaniam S. LIPID MAPS-Nature Lipidomics Gateway: an online resource for students and educators interested in lipids. J Chem Educ. 2012;89:291–2.
Wishart DS, Jewison T, Guo AC, Wilson M, Knox C, Liu Y, et al. HMDB 3.0—the human metabolome database in 2013. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013;41:D801–7.
Ananth L, Prete PE, Kashyap ML. Apolipoproteins A-I and B and cholesterol in synovial fluid of patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Metabolism. 1993;42:803–6.
Dennis Jr G, Holweg CT, Kummerfeld SK, Choy DF, Setiadi AF, Hackney JA, et al. Synovial phenotypes in rheumatoid arthritis correlate with response to biologic therapeutics. Arthritis Res Ther. 2014;16:R90.
Giera M, Ioan-Facsinay A, Toes R, Gao F, Dalli J, Deelder AM, et al. Lipid and lipid mediator profiling of human synovial fluid in rheumatoid arthritis patients by means of LC-MS/MS. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2012;1821:1415–24. One of the first papers to rigorously apply lipidomics to RA and suggests this is the way to go in the future.
Metsios GS, Stavropoulos-Kalinoglou A, Panoulas VF, Koutedakis Y, Nevill AM, Douglas KM, et al. New resting energy expenditure prediction equations for patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2008;47:500–6.
Elkan AC, Hakansson N, Frostegard J, Cederholm T, Hafstrom I. Rheumatoid cachexia is associated with dyslipidemia and low levels of atheroprotective natural antibodies against phosphorylcholine but not with dietary fat in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: a cross-sectional study. Arthritis Res Ther. 2009;11:R37.
Roubenoff R, Roubenoff RA, Cannon JG, Kehayias JJ, Zhuang H, Dawson-Hughes B, et al. Rheumatoid cachexia: cytokine-driven hypermetabolism accompanying reduced body cell mass in chronic inflammation. J Clin Invest. 1994;93:2379–86.
Arshad A, Rashid R, Benjamin K. The effect of disease activity on fat-free mass and resting energy expenditure in patients with rheumatoid arthritis versus noninflammatory arthropathies/soft tissue rheumatism. Mod Rheumatol. 2007;17:470–5.
Binymin K, Herrick A, Carlson G, Hopkins S. The effect of disease activity on body composition and resting energy expenditure in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. J Inflamm Res. 2011;4:61–6.
Heymsfield SB, Gallagher D, Kotler DP, Wang Z, Allison DB, Heshka S. Body-size dependence of resting energy expenditure can be attributed to nonenergetic homogeneity of fat-free mass. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metabol. 2002;282:E132–8.
Raza K, Falciani F, Curnow SJ, Ross EJ, Lee CY, Akbar AN, et al. Early rheumatoid arthritis is characterized by a distinct and transient synovial fluid cytokine profile of T cell and stromal cell origin. Arthritis Res Ther. 2005;7:R784–95.
Yeo L, Adlard N, Biehl M, Juarez M, Smallie T, Snow M et al. Expression of chemokines CXCL4 and CXCL7 by synovial macrophages defines an early stage of rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2015;Online First:doi:10.1136.
Stavropoulos-Kalinoglou A, Metsios GS, Panoulas VF, Nightingale P, Koutedakis Y, Kitas GD. Anti-tumour necrosis factor alpha therapy improves insulin sensitivity in normal-weight but not in obese patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Res Ther. 2012;14:R160.
Kay J, Morgacheva O, Messing SP, Kremer JM, Greenberg JD, Reed GW, et al. Clinical disease activity and acute phase reactant levels are discordant among patients with active rheumatoid arthritis: acute phase reactant levels contribute separately to predicting outcome at one year. Arthritis Res Ther. 2014;16:R40.
van Wietmarschen H, van der Greef J. Metabolite space of rheumatoid arthritis. Br J Med Med Res. 2012;2:469–83.
Kobayashi T, Okada M, Ito S, Kobayashi D, Shinhara A, Muramatsu T, et al. Amino acid profiles in relation to chronic periodontitis and rheumatoid arthritis. Open J Stomatol. 2014;4:49–55.
Dunn WB, Broadhurst DI, Atherton HJ, Goodacre R, Griffin JL. Systems level studies of mammalian metabolomes: the roles of mass spectrometry and nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Chem Soc Rev. 2011;40:387–426.
Tufts L, Shet Vishnudas K, Fu E, Kurhanewicz J, Ries M, Alliston T, et al. Correlating high-resolution magic angle spinning NMR spectroscopy and gene analysis in osteoarthritic cartilage. NMR Biomed. 2015;28:523–8.
Kim K, Mall C, Taylor SL, Hitchcock S, Zhang C, Wettersten HI, et al. Mealtime, temporal, and daily variability of the human urinary and plasma metabolomes in a tightly controlled environment. PLoS ONE. 2014;9:e86223.
Yousri NA, Kastenmuller G, Gieger C, Shin SY, Erte I, Menni C, et al. Long term conservation of human metabolic phenotypes and link to heritability. Metabolomics. 2014;10:1005–17.
Zhang A, Sun H, Wu X, Wang X. Urine metabolomics. Clin Chim Acta. 2012;414:65–9.
Duarte IF, Diaz SO, Gil AM. NMR metabolomics of human blood and urine in disease research. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2014;93:17–26.
Trifonova O, Lokhov P, Archakov A. Postgenomics diagnostics: metabolomics approaches to human blood profiling. OMICS. 2013;17:550–9.
Le Gall G, Noor SO, Ridgway K, Scovell L, Jamieson C, Johnson IT, et al. Metabolomics of fecal extracts detects altered metabolic activity of gut microbiota in ulcerative colitis and irritable bowel syndrome. J Proteome Res. 2011;10:4208–18.
Dona AC, Jimenez B, Schafer H, Humpfer E, Spraul M, Lewis MR, et al. Precision high-throughput proton NMR spectroscopy of human urine, serum, and plasma for large-scale metabolic phenotyping. Anal Chem. 2014;86:9887–94.
Smolinska A, Blanchet L, Buydens LM, Wijmenga SS. NMR and pattern recognition methods in metabolomics: from data acquisition to biomarker discovery: a review. Anal Chim Acta. 2012;750:82–97.
Smith R, Mathis AD, Ventura D, Prince JT. Proteomics, lipidomics, metabolomics: a mass spectrometry tutorial from a computer scientist’s point of view. BMC Bioinforma. 2014;15:S7–9.
Want EJ, Masson P, Michopoulos F, Wilson ID, Theodoridis G, Plumb RS, et al. Global metabolic profiling of animal and human tissues via UPLC-MS. Nat Protoc. 2013;8:17–32.
Huang Y, Zhu M, Li Z, Sa R, Chu Q, Zhang Q, et al. Mass spectrometry-based metabolomic profiling identifies alterations in salivary redox status and fatty acid metabolism in response to inflammation and oxidative stress in periodontal disease. Free Radic Biol Med. 2014;70:223–32.
Putri SP, Yamamoto S, Tsugawa H, Fukusaki E. Current metabolomics: technological advances. J Biosci Bioeng. 2013;116:9–16.
Holmes E, Wilson ID, Nicholson JK. Metabolic phenotyping in health and disease. Cell. 2008;134:714–7.
Nicholson JK, Holmes E, Kinross JM, Darzi AW, Takats Z, Lindon JC. Metabolic phenotyping in clinical and surgical environments. Nature. 2012;491:384–92.
Gowda GA, Zhang S, Gu H, Asiago V, Shanaiah N, Raftery D. Metabolomics-based methods for early disease diagnostics. Expert Rev Mol Diagn. 2008;8:617–33.
Zhang A, Sun H, Wang P, Han Y, Wang X. Recent and potential developments of biofluid analyses in metabolomics. J Proteome. 2012;75:1079–88.
Priori R, Scrivo R, Brandt J, Valerio M, Casadei L, Valesini G, et al. Metabolomics in rheumatic diseases: the potential of an emerging methodology for improved patient diagnosis, prognosis, and treatment efficacy. Autoimmun Rev. 2013;12:1022–33.
Madsen RK, Lundstedt T, Gabrielsson J, Sennbro CJ, Alenius GM, Moritz T, et al. Diagnostic properties of metabolic perturbations in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Res Ther. 2011;13:R19.
van Wietmarschen HA, Dai WD, van der Kooij AJ, Reijmers TH, Schroen Y, Wang M, et al. Characterization of rheumatoid arthritis subtypes using symptom profiles, clinical chemistry and metabolomics measurements. PLoS ONE. 2012;7:e44331.
Vorkas PA, Shalhoub J, Isaac G, Want EJ, Nicholson JK, Holmes E, et al. Metabolic phenotyping of atherosclerotic plaques reveals latent associations between free cholesterol and ceramide metabolism in atherogenesis. J Proteome Res. 2015;14:1389–99. A very thorough analysis of the lipid profile of plaques, which reveals potential new effects of the lipids found and mitochondrial function, suggesting this approach may be important for future understanding of the complex changes in lipids in disease.
Wang ZG, Chen Z, Yang SS, Wang Y, Yu LF, Zhang BC, et al. H-1 NMR-based metabolomic analysis for identifying serum biomarkers to evaluate methotrexate treatment in patients with early rheumatoid arthritis. Exp Ther Med. 2012;4:165–71.
Kapoor SR, Filer A, Fitzpatrick M, Fisher BA, Taylor PC, Buckley CD, et al. Metabolic profiling predicts response to anti-TNFα therapy in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2013;65:1448–56.
Young SP, Kapoor SR, Viant MR, Byrne JJ, Filer A, Buckley CD, et al. The impact of inflammation on metabolomic profiles in patients with arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2013;65:2015–23.
Lodhi IJ, Wei X, Yin L, Feng C, Adak S, Abou-Ezzi G, et al. Peroxisomal lipid synthesis regulates inflammation by sustaining neutrophil membrane phospholipid composition and viability. Cell Metab. 2015;21:51–64. Proposes a method of immune regulation by constraining neutrophil numbers through selective targetting of lipid biogenesis in a murine model.
Deo RC, Hunter L, Lewis GD, Pare G, Vasan RS, Chasman D, et al. Interpreting metabolomic profiles using unbiased pathway models. PLoS Comp Biol. 2010;6:e1000692.
Kell DB, Goodacre R. Metabolomics and systems pharmacology: why and how to model the human metabolic network for drug discovery. Drug Discov Today. 2014;19:171–82.
Leichtle AB, Dufour JF, Fiedler GM. Potentials and pitfalls of clinical peptidomics and metabolomics. Swiss Med Wkly. 2013;143:w13801.
Compliance with Ethics Guidelines
Conflict of Interest
Catherine M. McGrath is a National Institute for Health Research (NIHR) Academic Clinical Fellow. She reports that during 1997-2005, she was employed by bcm (Alliance Boots) and Wyeth Biopharma (now Pfizer) and with whom she has preserved pensions.
Stephen P. Young declares no conflict of interest.
Human and Animal Rights and Informed Consent
This article does not contain any studies with human or animal subjects performed by the authors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This article is part of the Topical Collection on Rheumatoid Arthritis
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
McGrath, C.M., Young, S.P. Lipid and Metabolic Changes in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Curr Rheumatol Rep 17, 57 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11926-015-0534-z
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11926-015-0534-z