Abstract
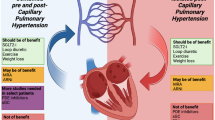
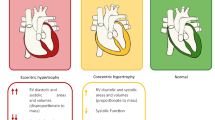
Pulmonary hypertension (PH) is a rare but life-threatening condition in antiphospholipid syndrome (APS) patients with or without systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). The definition of PH is based on hemodynamic parameters estimated by transthoracic echocardiography (TTE) and confirmed by right heart catheterization (RHC). New evidence suggests that antiphospholipid antibodies (aPL) in SLE patients increase the risk of PH; however, studies yield conflicting results. Hypotheses regarding the impact of aPL on PH include large vessel and microvascular thrombosis, and endothelial remodeling. Natural history of PH is progressive worsening mainly due to recurrent pulmonary embolism. The management in APS patients includes anticoagulation; patients undergoing pulmonary endarterectomy need to be closely monitored because of an increased risk of thrombotic complications.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Papers of particular interest, published recently, have been highlighted as: • Of importance •• Of major importance
Miyakis S, Lockshin MD, Atsumi T, Branch DW, Brey RL, Cervera R, et al. International consensus statement on an update of the classification criteria for definite antiphospholipid syndrome (APS). J Thromb Haemost. 2006;4:295–306.
Cervera R, Piette J-C, Font J, Khamashta MA, Shoenfeld Y, Camps MT, et al. Antiphospholipid syndrome: clinical and immunologic manifestations and patterns of disease expression in a cohort of 1,000 patients. Arthritis Rheum. 2002;46:1019–27.
Simonneau G, Gatzoulis MA, Adatia I, Celermajer D, Denton C, Ghofrani A, et al. Updated clinical classification of pulmonary hypertension. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2013;62:D34–41. This recent guidelines document provides the most up-to-date data regarding classification of PH together with a comprehensive review of the literature.
Kim NH, Delcroix M, Jenkins DP, Channick R, Dartevelle P, Jansa P, et al. Chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2013;62:D92–9.
Prabu A, Patel K, Yee C-S, Nightingale P, Situnayake RD, Thickett DR, et al. Prevalence and risk factors for pulmonary arterial hypertension in patients with lupus. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2009;48:1506–11.
Espínola-Zavaleta N, Vargas-Barrón J, Colmenares-Galvis T, Cruz-Cruz F, Romero-Cárdenas A, Keirns C, et al. Echocardiographic evaluation of patients with primary antiphospholipid syndrome. Am Heart J. 1999;137:973–8.
Martinuzzo ME, Pombo G, Forastiero RR, Cerrato GS, Colorio CC, Carreras LO. Lupus anticoagulant, high levels of anticardiolipin, and anti-beta2-glycoprotein I antibodies are associated with chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension. J Rheumatol. 1998;25:1313–9.
Rudski LG, Lai WW, Afilalo J, Hua L, Handschumacher MD, Chandrasekaran K, et al. Guidelines for the echocardiographic assessment of the right heart in adults: a report from the American Society of Echocardiography endorsed by the European Association of Echocardiography, a registered branch of the European Society of Cardiology, and the Canadian Society of Echocardiography. J Am Soc Echocardiogr. 2010;23:685–713.
Galiè N, Hoeper MM, Humbert M, Torbicki A, Vachiery J-L, Barbera JA, et al. Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of pulmonary hypertension: the Task Force for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Pulmonary Hypertension of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) and the European Respiratory Society (ERS), endorsed by the International Society of Heart and Lung Transplantation (ISHLT). Eur Heart J. 2009;30:2493–537.
Zuily S, Huttin O, Mohamed S, Marie P-Y, Selton-Suty C, Wahl D. Valvular heart disease in antiphospholipid syndrome. Curr Rheumatol Rep. 2013;15:320.
Zuily S, Regnault V, Selton-Suty C, Eschwège V, Bruntz J-F, Bode-Dotto E, et al. Increased risk for heart valve disease associated with antiphospholipid antibodies in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus: meta-analysis of echocardiographic studies. Circulation. 2011;124:215–24.
Chaisson NF, Hassoun PM. Systemic sclerosis-associated pulmonary arterial hypertension. Chest. 2013;144:1346–56.
Schreiber BE, Connolly MJ, Coghlan JG. Pulmonary hypertension in systemic lupus erythematosus. Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol. 2013;27:425–34.
Cefle A, Inanc M, Sayarlioglu M, Kamali S, Gul A, Ocal L, et al. Pulmonary hypertension in systemic lupus erythematosus: relationship with antiphospholipid antibodies and severe disease outcome. Rheumatol Int. 2011;31:183–9. This study reports results from a small cohort a significant association between aPL-positivity and PH in SLE patients.
Foïs E, Le Guern V, Dupuy A, Humbert M, Mouthon L, Guillevin L. Noninvasive assessment of systolic pulmonary artery pressure in systemic lupus erythematosus: retrospective analysis of 93 patients. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2010;28:836–41.
Houman MH, Smiti-Khanfir M, Ben Ghorbell I, Miled M. Systemic lupus erythematosus in Tunisia: demographic and clinical analysis of 100 patients. Lupus. 2004;13:204–11.
Kamel SR, Omar GM, Darwish AF, Asklany HT, Ellabban AS. Asymptomatic pulmonary hypertension in systemic lupus erythematosus. Clin Med Insights Arthritis Musculoskelet Disord. 2011;4:77–86.
Lee JH, Im Cho K. Arterial stiffness, antiphospholipid antibodies, and pulmonary arterial hypertension in systemic lupus erythematosus. J Cardiol. 2014.
Lian F, Chen D, Wang Y, Ye Y, Wang X, Zhan Z, et al. Clinical features and independent predictors of pulmonary arterial hypertension in systemic lupus erythematosus. Rheumatol Int. 2012;32:1727–31.
Tanaseanu C, Tudor S, Tamsulea I, Marta D, Manea G, Moldoveanu E. Vascular endothelial growth factor, lipoporotein-associated phospholipase A2, sP-selectin and antiphospholipid antibodies, biological markers with prognostic value in pulmonary hypertension associated with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and systemic lupus erithematosus. Eur J Med Res. 2007;12:145–51.
Akdogan A, Kilic L, Dogan I, Okutucu S, Er E, Kaya B, et al. Pulmonary hypertension in systemic lupus erythematosus: pulmonary thromboembolism is the leading cause. J Clin Rheumatol. 2013;19:421–5.
Bourre-Tessier J, Huynh T, Clarke A, Bernatsky S, Joseph L, Belisle P, et al. Features associated with cardiac abnormalities in systemic lupus erythematosus. Lupus. 2011;20:1518–25.
Farzaneh-Far A, Roman MJ, Lockshin MD, Devereux RB, Paget SA, Crow MK, et al. Relationship of antiphospholipid antibodies to cardiovascular manifestations of systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 2006;54:3918–25.
Hübbe-Tena C, Gallegos-Nava S, Márquez-Velasco R, Castillo-Martínez D, Vargas-Barrón J, Sandoval J, et al. Pulmonary hypertension in systemic lupus erythematosus: echocardiography-based definitions predict 6-year survival. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2014;53:1256–63.
Johnson SR, Gladman DD, Urowitz MB, Ibañez D, Granton JT. Pulmonary hypertension in systemic lupus. Lupus. 2004;13:506–9.
Asherson RA, Morgan SH, Harris N, Gharavi AE, Hughes GR, Millar AB. Pulmonary hypertension and chronic cutaneous lupus erythematosus: association with the lupus anticoagulant. Arthritis Rheum. 1985;28:118.
Petri M, Rheinschmidt M, Whiting-O’Keefe Q, Hellmann D, Corash L. The frequency of lupus anticoagulant in systemic lupus erythematosus. A study of sixty consecutive patients by activated partial thromboplastin time, Russell viper venom time, and anticardiolipin antibody level. Ann Intern Med. 1987;106:524–31.
De Laat B, Derksen RHWM, Urbanus RT, de Groot PG. IgG antibodies that recognize epitope Gly40-Arg43 in domain I of beta 2-glycoprotein I cause LAC, and their presence correlates strongly with thrombosis. Blood. 2005;105:1540–5.
Giannakopoulos B, Krilis SA. The pathogenesis of the antiphospholipid syndrome. N Engl J Med. 2013;368:1033–44.
Asherson RA, Khamashta MA, Ordi-Ros J, Derksen RH, Machin SJ, Barquinero J, et al. The “primary” antiphospholipid syndrome: major clinical and serological features. Medicine (Baltimore). 1989;68:366–74.
Badui E, Solorio S, Martinez E, Bravo G, Enciso R, Barile L, et al. The heart in the primary antiphospholipid syndrome. Arch Med Res. 1995;26:115–20.
Pardos-Gea J, Avegliano G, Evangelista A, Vilardell M, Ordi-Ros J. Cardiac manifestations other than valvulopathy in antiphospholipid syndrome: long-time echocardiography follow-up study. Int J Rheum Dis. 2013. This prospective study published follow-up data in APS patients with chronic thromboembolic PH.
Vianna JL, Khamashta MA, Ordi-Ros J, Font J, Cervera R, Lopez-Soto A, et al. Comparison of the primary and secondary antiphospholipid syndrome: a European Multicenter Study of 114 patients. Am J Med. 1994;96:3–9.
Colorio CC, Martinuzzo ME, Forastiero RR, Pombo G, Adamczuk Y, Carreras LO. Thrombophilic factors in chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension. Blood Coagul Fibrinolysis. 2001;12:427–32.
D’Armini AM, Totaro P, Nicolardi S, Morsolini M, Silvaggio G, Toscano F, et al. Impact of high titre of antiphospholipid antibodies on postoperative outcome following pulmonary endarterectomy. Interact Cardiovasc Thorac Surg. 2010;10:418–22.
Wolf M, Boyer-Neumann C, Parent F, Eschwege V, Jaillet H, Meyer D, et al. Thrombotic risk factors in pulmonary hypertension. Eur Respir J. 2000;15:395–9.
Wong CL, Szydlo R, Gibbs S, Laffan M. Hereditary and acquired thrombotic risk factors for chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension. Blood Coagul Fibrinolysis. 2010;21:201–6.
Morrisroe KB, Stevens W, Nandurkar H, Prior D, Thakkar V, Roddy J, et al. The association of antiphospholipid antibodies with cardiopulmonary manifestations of systemic sclerosis. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2014.
Vegh J, Szodoray P, Kappelmayer J, Csipo I, Udvardy M, Lakos G, et al. Clinical and immunoserological characteristics of mixed connective tissue disease associated with pulmonary arterial hypertension. Scand J Immunol. 2006;64:69–76.
Miyata M, Suzuki K, Sakuma F, Watanabe H, Kaise S, Nishimaki T, et al. Anticardiolipin antibodies are associated with pulmonary hypertension in patients with mixed connective tissue disease or systemic lupus erythematosus. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 1993;100:351–4.
Yanai-Landau H, Amital H, Bar-Dayan Y, Levy Y, Gur H, Lin HC, et al. Autoimmune aspects of primary pulmonary hypertension. Pathobiology. 1995;63:71–5.
Sasaki N, Kamataki A, Sawai T. A histopathological study of pulmonary hypertension in connective tissue disease. Allergol Int. 2011;60:411–7.
Tuder RM, Archer SL, Dorfmüller P, Erzurum SC, Guignabert C, Michelakis E, et al. Relevant issues in the pathology and pathobiology of pulmonary hypertension. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2013;62:D4–12.
Yutani C, Imakita M, Ishibashi-Ueda H, Nakamura Y, Sekino T, Iida K, et al. Pulmonary thromboembolic hypertension in systemic lupus erythematosus with lupus anticoagulant: histopathological analysis of localization and distribution of thromboemboli in pulmonary vasculature. Intern Med. 1995;34:1030–4.
Brucato A, Baudo F, Barberis M, Redaelli R, Casadei G, Allegri F, et al. Pulmonary hypertension secondary to thrombosis of the pulmonary vessels in a patient with the primary antiphospholipid syndrome. J Rheumatol. 1994;21:942–4.
Fishman AP. Changing concepts of the pulmonary plexiform lesion. Physiol Res. 2000;49:485–92.
Runo JR, Loyd JE. Primary pulmonary hypertension. Lancet. 2003;361:1533–44.
Stevens T. Molecular and cellular determinants of lung endothelial cell heterogeneity. Chest. 2005;128:558S–64.
Luchi ME, Asherson RA, Lahita RG. Primary idiopathic pulmonary hypertension complicated by pulmonary arterial thrombosis. Association with antiphospholipid antibodies. Arthritis Rheum. 1992;35:700–5.
Karmochkine M, Cacoub P, Dorent R, Laroche P, Nataf P, Piette JC, et al. High prevalence of antiphospholipid antibodies in precapillary pulmonary hypertension. J Rheumatol. 1996;23:286–90.
Del Papa N, Guidali L, Sala A, Buccellati C, Khamashta MA, Ichikawa K, et al. Endothelial cells as target for antiphospholipid antibodies. Human polyclonal and monoclonal anti-beta 2-glycoprotein I antibodies react in vitro with endothelial cells through adherent beta 2-glycoprotein I and induce endothelial activation. Arthritis Rheum. 1997;40:551–61.
Bordron A, Dueymes M, Levy Y, Jamin C, Ziporen L, Piette JC, et al. Anti-endothelial cell antibody binding makes negatively charged phospholipids accessible to antiphospholipid antibodies. Arthritis Rheum. 1998;41:1738–47.
Dueymes M, Levy Y, Ziporen L, Jamin C, Piette JC, Shoenfeld Y, et al. Do some antiphospholipid antibodies target endothelial cells? Ann Med Interne (Paris). 1996;147 Suppl 1:22–3.
Allen KL, Fonseca FV, Betapudi V, Willard B, Zhang J, McCrae KR. A novel pathway for human endothelial cell activation by antiphospholipid/anti-β2 glycoprotein I antibodies. Blood. 2012;119:884–93.
Satta N, Kruithof EKO, Fickentscher C, Dunoyer-Geindre S, Boehlen F, Reber G, et al. Toll-like receptor 2 mediates the activation of human monocytes and endothelial cells by antiphospholipid antibodies. Blood. 2011;117:5523–31.
Riboldi P, Gerosa M, Raschi E, Testoni C, Meroni PL. Endothelium as a target for antiphospholipid antibodies. Immunobiology. 2003;207:29–36.
Arends SJ, Damoiseaux JGMC, Duijvestijn AM, Debrus-Palmans L, Boomars KA, Brunner-La Rocca H-P, et al. Functional implications of IgG anti-endothelial cell antibodies in pulmonary arterial hypertension. Autoimmunity. 2013;46:463–70.
Arends SJ, Damoiseaux JGMC, Duijvestijn AM, Debrus-Palmans L, Vroomen M, Boomars KA, et al. Immunoglobulin G anti-endothelial cell antibodies: inducers of endothelial cell apoptosis in pulmonary arterial hypertension? Clin Exp Immunol. 2013;174:433–40.
Arends SJ, Damoiseaux J, Duijvestijn A, Debrus-Palmans L, Boomars K, Broers B, et al. Prevalence of anti-endothelial cell antibodies in idiopathic pulmonary arterial hypertension. Eur Respir J. 2010;35:923–5.
Chen Y, Chen G, Zhu C, Lu X, Ye S, Yang C. Severe systemic lupus erythematosus in emergency department: a retrospective single-center study from China. Clin Rheumatol. 2011;30:1463–9.
Cervera R, Serrano R, Pons-Estel GJ, Ceberio-Hualde L, Shoenfeld Y, de Ramón E, et al. Morbidity and mortality in the antiphospholipid syndrome during a 10-year period: a multicentre prospective study of 1000 patients. Ann Rheum Dis. 2014. This European study reported follow-up data including outcomes and causes of death of 1000 APS patients.
Chow SL, Chandran V, Fazelzad R, Johnson SR. Prognostic factors for survival in systemic lupus erythematosus associated pulmonary hypertension. Lupus. 2012;21:353–64. This systematic review identified that anticardiolipin antibodies-positivity was a predictive factor of decreased survival in SLE patients with PH.
Zavaleta NE, Montes RM, Soto ME, Vanzzini NA, Amigo M-C. Primary antiphospholipid syndrome: a 5-year transesophageal echocardiographic followup study. J Rheumatol. 2004;31:2402–7.
Fuster V, Steele PM, Edwards WD, Gersh BJ, McGoon MD, Frye RL. Primary pulmonary hypertension: natural history and the importance of thrombosis. Circulation. 1984;70:580–7.
Morris TA, Marsh JJ, Chiles PG, Magaña MM, Liang N-C, Soler X, et al. High prevalence of dysfibrinogenemia among patients with chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension. Blood. 2009;114:1929–36.
Miniati M, Fiorillo C, Becatti M, Monti S, Bottai M, Marini C, et al. Fibrin resistance to lysis in patients with pulmonary hypertension other than thromboembolic. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2010;181:992–6.
Galiè N, Corris PA, Frost A, Girgis RE, Granton J, Jing ZC, et al. Updated treatment algorithm of pulmonary arterial hypertension. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2013;62:D60–72.
Olsson KM, Delcroix M, Ghofrani HA, Tiede H, Huscher D, Speich R, et al. Anticoagulation and survival in pulmonary arterial hypertension: results from the Comparative, Prospective Registry of Newly Initiated Therapies for Pulmonary Hypertension (COMPERA). Circulation. 2014;129:57–65. This prospective registry recently confirmed the benefit of anticoagulation in idiopathic pulmonary arterial hypertension but not in connective tissue disease-associated pulmonary arterial hypertension.
Reynaud Q, Lega J-C, Mismetti P, Chapelle C, Wahl D, Cathébras P, et al. Risk of venous and arterial thrombosis according to type of antiphospholipid antibodies in adults without systemic lupus erythematosus: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Autoimmun Rev. 2014;13:595–608.
Lockshin M, Tenedios F, Petri M, McCarty G, Forastiero R, Krilis S, et al. Cardiac disease in the antiphospholipid syndrome: recommendations for treatment. Committee consensus report. Lupus. 2003;12:518–23.
De la Mata J, Gomez-Sanchez MA, Aranzana M, Gomez-Reino JJ. Long-term iloprost infusion therapy for severe pulmonary hypertension in patients with connective tissue diseases. Arthritis Rheum. 1994;37:1528–33.
Humbert M, Sanchez O, Fartoukh M, Jagot JL, Le Gall C, Sitbon O, et al. Short-term and long-term epoprostenol (prostacyclin) therapy in pulmonary hypertension secondary to connective tissue diseases: results of a pilot study. Eur Respir J. 1999;13:1351–6.
Heresi GA, Minai OA. Lupus-associated pulmonary hypertension: long-term response to vasoactive therapy. Respir Med. 2007;101:2099–107.
Pulido T, Adzerikho I, Channick RN, Delcroix M, Galiè N, Ghofrani H-A, et al. Macitentan and morbidity and mortality in pulmonary arterial hypertension. N Engl J Med. 2013;369:809–18.
Ghofrani H-A, D’Armini AM, Grimminger F, Hoeper MM, Jansa P, Kim NH, et al. Riociguat for the treatment of chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension. N Engl J Med. 2013;369:319–29.
Sandoval J, Amigo MC, Barragan R, Izaguirre R, Reyes PA, Martinez-Guerra ML, et al. Primary antiphospholipid syndrome presenting as chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension. Treatment with thromboendarterectomy. J Rheumatol. 1996;23:772–5.
Camous J, Decrombecque T, Louvain-Quintard V, Doubine S, Dartevelle P, Stéphan F. Outcomes of patients with antiphospholipid syndrome after pulmonary endarterectomy. Eur J CardioThorac Surg. 2014;46:116–20. In this prospective study of patients undergoing pulmonary endarterectomy, Camous et al. revealed the very high-risk of these procedures for patients with APS in terms of thrombotic complications.
Auger WR, Permpikul P, Moser KM. Lupus anticoagulant, heparin use, and thrombocytopenia in patients with chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension: a preliminary report. Am J Med. 1995;99:392–6.
Saunders KH, Erkan D, Lockshin MD. Perioperative management of antiphospholipid antibody-positive patients. Curr Rheumatol Rep. 2014;16:426.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to acknowledge Dr. Heymonet, Dr. Huttin, Dr. Mandry, Dr. Mohamed, Dr. Selton-Suty, Pr. Chabot, Pr. Chaouat, and Pr. Kaminsky for their involvement in multidisciplinary APS-related PH patient management.
Compliance with Ethics Guidelines
ᅟ
Conflict of Interest
Stéphane Zuily and Denis Wahl declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Human and Animal Rights and Informed Consent
This article does not contain any studies with human or animal subjects performed by any of the authors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This article is part of the Topical Collection on Antiphospholipid Syndrome
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zuily, S., Wahl, D. Pulmonary Hypertension in Antiphospholipid Syndrome. Curr Rheumatol Rep 17, 4 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11926-014-0478-8
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11926-014-0478-8
Keywords
- Antiphospholipid syndrome
- Antiphospholipid antibodies
- Systemic lupus erythematosus
- Pulmonary hypertension
- Chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension
- Pulmonary arterial hypertension
- Transthoracic echocardiography
- Right heart catheterization
- Pulmonary embolism
- Anticoagulant
- Cardiac surgery
- Pulmonary endarterectomy
- Thrombosis