Abstract
Whole-genome linkage and association studies of bipolar disorder are beginning to provide some compelling evidence for the involvement of several chromosomal regions and susceptibility genes in the pathogenesis of bipolar disorder. Developments in genotyping technology and efforts to combine data from different studies have helped in identifying chromosomes 6q16-q25, 13q, and 16p12 as probable susceptibility loci for bipolar disorder and confirmed CACNA1C and ANK3 as susceptibility genes for bipolar disorder. However, a lack of replication is still apparent in the literature. New studies focusing on copy number variants as well as new analytical approaches utilizing pathway analysis offer a new direction in the study of the genetics of bipolar disorder.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Papers of particular interest, published recently, have been highlighted as: • Of importance •• Of major importance
Goodwin FK, Jamison KR. Manic-depressive illness. New York: Oxford University Press; 1990.
McGuffin P, Rijsdijk F, Andrew M, Sham P, Katz R, Cardno A. The heritability of bipolar affective disorder and the genetic relationship to unipolar depression. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2003;60(5):497–502.
Sham P, McGuffin P. Linkage and association. In: McGuffin P, Owen MJ, Gottesman II, editors. Psychiatric genetics & genomics. Oxford: Oxford University Press; 2002. p. 55–75.
Badner JA, Gershon ES. Meta-analysis of whole-genome linkage scans of bipolar disorder and schizophrenia. Mol Psychiatry. 2002;7(4):405–11.
Wigg K, Feng Y, Gomez L, Kiss E, Kapornai K, Tamas Z, et al. Genome scan in sibling pairs with juvenile-onset mood disorders: evidence for linkage to 13q and xq. Am J Med Genet B: The Official Publication of the International Society of Psychiatric Genetics. 2009;150B(5):638–46.
Xu H, Cheng R, Juo SH, Liu J, Loth JE, Endicott J, et al. Fine mapping of candidate regions for bipolar disorder provides strong evidence for susceptibility loci on chromosomes 7q. Am J Med Genet B: The Official Publication of the International Society of Psychiatric Genetics. 2011;156(2):168–76.
McGuffin P, Knight J, Breen G, Brewster S, Boyd PR, Craddock N, et al. Whole genome linkage scan of recurrent depressive disorder from the depression network study. Hum Mol Genet. 2005;14(22):3337–45.
Chen YS, Akula N, Detera-Wadleigh SD, Schulze TG, Thomas J, Potash JB, et al. Findings in an independent sample support an association between bipolar affective disorder and the g72/g30 locus on chromosome 13q33. Mol Psychiatry. 2004;9(1):87–92. image 85.
Detera-Wadleigh SD, McMahon FJ. G72/g30 in schizophrenia and bipolar disorder: review and meta-analysis. Biol Psychiatry. 2006;60(2):106–14.
Hattori E, Liu C, Badner JA, Bonner TI, Christian SL, Maheshwari M, et al. Polymorphisms at the g72/g30 gene locus, on 13q33, are associated with bipolar disorder in two independent pedigree series. Am J Hum Genet. 2003;72(5):1131–40.
Prata D, Breen G, Osborne S, Munro J, St Clair D, Collier D. Association of DAO and g72(DAOA)/g30 genes with bipolar affective disorder. Am J Med Genet B: The Official Publication of the International Society of Psychiatric Genetics. 2008;147B(6):914–7.
Schumacher J, Jamra RA, Freudenberg J, Becker T, Ohlraun S, Otte AC, et al. Examination of g72 and d-amino-acid oxidase as genetic risk factors for schizophrenia and bipolar affective disorder. Mol Psychiatry. 2004;9(2):203–7.
Segurado R, Detera-Wadleigh SD, Levinson DF, Lewis CM, Gill M, Nurnberger Jr JI, et al. Genome scan meta-analysis of schizophrenia and bipolar disorder, part III: Bipolar disorder. Am J Hum Genet. 2003;73(1):49–62.
Palo OM, Soronen P, Silander K, Varilo T, Tuononen K, Kieseppa T, et al. Identification of susceptibility loci at 7q31 and 9p13 for bipolar disorder in an isolated population. Am J Med Genet B: The Official Publication of the International Society of Psychiatric Genetics. 2010;153B(3):723–35.
Bennett P, Segurado R, Jones I, Bort S, McCandless F, Lambert D, et al. The Wellcome Trust UK-Irish bipolar affective disorder sibling-pair genome screen: first stage report. Mol Psychiatry. 2002;7(2):189–200.
Berrettini WH, Ferraro TN, Goldin LR, Detera-Wadleigh SD, Choi H, Muniec D, et al. A linkage study of bipolar illness. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1997;54(1):27–35.
Detera-Wadleigh SD, Badner JA, Berrettini WH, Yoshikawa T, Goldin LR, Turner G, et al. A high-density genome scan detects evidence for a bipolar-disorder susceptibility locus on 13q32 and other potential loci on 1q32 and 18p11.2. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1999;96(10):5604–9.
Fallin MD, Lasseter VK, Wolyniec PS, McGrath JA, Nestadt G, Valle D, et al. Genomewide linkage scan for bipolar-disorder susceptibility loci among Ashkenazi Jewish families. Am J Hum Genet. 2004;75(2):204–19.
Lin JP, Bale SJ. Parental transmission and d18s37 allele sharing in bipolar affective disorder. Genet Epidemiol. 1997;14(6):665–8.
Stine OC, Xu J, Koskela R, McMahon FJ, Gschwend M, Friddle C, et al. Evidence for linkage of bipolar disorder to chromosome 18 with a parent-of-origin effect. Am J Hum Genet. 1995;57(6):1384–94.
Mulle JG, Fallin MD, Lasseter VK, McGrath JA, Wolyniec PS, Pulver AE. Dense SNP association study for bipolar I disorder on chromosome 18p11 suggests two loci with excess paternal transmission. Mol Psychiatry. 2007;12(4):367–75.
Nothen MM, Cichon S, Rohleder H, Hemmer S, Franzek E, Fritze J, et al. Evaluation of linkage of bipolar affective disorder to chromosome 18 in a sample of 57 German families. Mol Psychiatry. 1999;4(1):76–84.
McQueen MB, Devlin B, Faraone SV, Nimgaonkar VL, Sklar P, Smoller JW, et al. Combined analysis from eleven linkage studies of bipolar disorder provides strong evidence of susceptibility loci on chromosomes 6q and 8q. Am J Hum Genet. 2005;77(4):582–95.
Middleton FA, Pato MT, Gentile KL, Morley CP, Zhao X, Eisener AF, et al. Genomewide linkage analysis of bipolar disorder by use of a high-density single-nucleotide-polymorphism (snp) genotyping assay: a comparison with microsatellite marker assays and finding of significant linkage to chromosome 6q22. Am J Hum Genet. 2004;74(5):886–97.
Schumacher J, Kaneva R, Jamra RA, Diaz GO, Ohlraun S, Milanova V, et al. Genomewide scan and fine-mapping linkage studies in four European samples with bipolar affective disorder suggest a new susceptibility locus on chromosome 1p35-p36 and provides further evidence of loci on chromosome 4q31 and 6q24. Am J Hum Genet. 2005;77(6):1102–11.
Venken T, Claes S, Sluijs S, Paterson AD, van Duijn C, Adolfsson R, et al. Genomewide scan for affective disorder susceptibility loci in families of a Northern Swedish isolated population. Am J Hum Genet. 2005;76(2):237–48.
Ewald H, Flint T, Kruse TA, Mors O. A genome-wide scan shows significant linkage between bipolar disorder and chromosome 12q24.3 and suggestive linkage to chromosomes 1p22-21, 4p16, 6q14-22, 10q26 and 16p13.3. Mol Psychiatry. 2002;7(7):734–44.
Lambert D, Middle F, Hamshere ML, Segurado R, Raybould R, Corvin A, et al. Stage 2 of the Wellcome Trust UK-Irish bipolar affective disorder sibling-pair genome screen: evidence for linkage on chromosomes 6q16-q21, 4q12-q21, 9p21, 10p14-p12 and 18q22. Mol Psychiatry. 2005;10(9):831–41.
Service S, Molina J, Deyoung J, Jawaheer D, Aldana I, Vu T, et al. Results of a SNP genome screen in a large Costa Rican pedigree segregating for severe bipolar disorder. Am J Med Genet B: The Official Publication of the International Society of Psychiatric Genetics. 2006;141B(4):367–73.
Cheng R, Juo SH, Loth JE, Nee J, Iossifov I, Blumenthal R, et al. Genome-wide linkage scan in a large bipolar disorder sample from the National Institute of Mental Health genetics initiative suggests putative loci for bipolar disorder, psychosis, suicide, and panic disorder. Mol Psychiatry. 2006;11(3):252–60.
Faraone SV, Lasky-Su J, Glatt SJ, Van Eerdewegh P, Tsuang MT. Early onset bipolar disorder: possible linkage to chromosome 9q34. Bipolar Disord. 2006;8(2):144–51.
Abou Jamra R, Fuerst R, Kaneva R, Orozco Diaz G, Rivas F, Mayoral F, et al. The first genomewide interaction and locus-heterogeneity linkage scan in bipolar affective disorder: strong evidence of epistatic effects between loci on chromosomes 2q and 6q. Am J Hum Genet. 2007;81(5):974–86.
Stine OC, McMahon FJ, Chen L, Xu J, Meyers DA, MacKinnon DF, et al. Initial genome screen for bipolar disorder in the NIMH genetics initiative pedigrees: chromosomes 2, 11, 13, 14, and x. Am J Med Genet. 1997;74(3):263–9.
Zubenko GS, Maher B, Hughes 3rd HB, Zubenko WN, Stiffler JS, Kaplan BB, et al. Genome-wide linkage survey for genetic loci that influence the development of depressive disorders in families with recurrent, early-onset, major depression. Am J Med Genet B: The Official Publication of the International Society of Psychiatric Genetics. 2003;123B(1):1–18.
Curtis D, Kalsi G, Brynjolfsson J, McInnis M, O’Neill J, Smyth C, et al. Genome scan of pedigrees multiply affected with bipolar disorder provides further support for the presence of a susceptibility locus on chromosome 12q23-q24, and suggests the presence of additional loci on 1p and 1q. Psychiatr Genet. 2003;13(2):77–84.
Dawson E, Parfitt E, Roberts Q, Daniels J, Lim L, Sham P, et al. Linkage studies of bipolar disorder in the region of the Darier’s disease gene on chromosome 12q23-24.1. Am J Med Genet. 1995;60(2):94–102.
Degn B, Lundorf MD, Wang A, Vang M, Mors O, Kruse TA, et al. Further evidence for a bipolar risk gene on chromosome 12q24 suggested by investigation of haplotype sharing and allelic association in patients from the Faroe Islands. Mol Psychiatry. 2001;6(4):450–5.
Ekholm JM, Kieseppa T, Hiekkalinna T, Partonen T, Paunio T, Perola M, et al. Evidence of susceptibility loci on 4q32 and 16p12 for bipolar disorder. Hum Mol Genet. 2003;12(15):1907–15.
Ewald H, Degn B, Mors O, Kruse TA. Significant linkage between bipolar affective disorder and chromosome 12q24. Psychiatr Genet. 1998;8(3):131–40.
Maziade M, Roy MA, Rouillard E, Bissonnette L, Fournier JP, Roy A, et al. A search for specific and common susceptibility loci for schizophrenia and bipolar disorder: a linkage study in 13 target chromosomes. Mol Psychiatry. 2001;6(6):684–93.
Morissette J, Villeneuve A, Bordeleau L, Rochette D, Laberge C, Gagne B, et al. Genome-wide search for linkage of bipolar affective disorders in a very large pedigree derived from a homogeneous population in Quebec points to a locus of major effect on chromosome 12q23-q24. Am J Med Genet. 1999;88(5):567–87.
Shink E, Morissette J, Sherrington R, Barden N. A genome-wide scan points to a susceptibility locus for bipolar disorder on chromosome 12. Mol Psychiatry. 2005;10(6):545–52.
Craddock N, Owen M, Burge S, Kurian B, Thomas P, McGuffin P. Familial cosegregation of major affective disorder and Darier’s disease (keratosis follicularis). Brit J Psychiat: J Ment Sci. 1994;164(3):355–8.
Green E, Elvidge G, Jacobsen N, Glaser B, Jones I, O’Donovan MC, et al. Localization of bipolar susceptibility locus by molecular genetic analysis of the chromosome 12q23-q24 region in two pedigrees with bipolar disorder and Darier’s disease. Am J Psychiatry. 2005;162(1):35–42.
Jones I, Jacobsen N, Green EK, Elvidge GP, Owen MJ, Craddock N. Evidence for familial cosegregation of major affective disorder and genetic markers flanking the gene for Darier’s disease. Mol Psychiatry. 2002;7(4):424–7.
Abkevich V, Camp NJ, Hensel CH, Neff CD, Russell DL, Hughes DC, et al. Predisposition locus for major depression at chromosome 12q22-12q23.2. Am J Hum Genet. 2003;73(6):1271–81.
Fallin MD, Lasseter VK, Avramopoulos D, Nicodemus KK, Wolyniec PS, McGrath JA, et al. Bipolar I disorder and schizophrenia: a 440-single-nucleotide polymorphism screen of 64 candidate genes among Ashkenazi Jewish case-parent trios. Am J Hum Genet. 2005;77(6):918–36.
Lyons-Warren A, Chang JJ, Balkissoon R, Kamiya A, Garant M, Nurnberger J, et al. Evidence of association between bipolar disorder and citron on chromosome 12q24. Mol Psychiatry. 2005;10(9):807–9.
Barden N, Harvey M, Gagne B, Shink E, Tremblay M, Raymond C, et al. Analysis of single nucleotide polymorphisms in genes in the chromosome 12q24.31 region points to p2rx7 as a susceptibility gene to bipolar affective disorder. Am J Med Genet B: The Official Publication of the International Society of, Psychiatric Genetics. 2006;141B(4):374–82.
McQuillin A, Bass NJ, Choudhury K, Puri V, Kosmin M, Lawrence J, et al. Case-control studies show that a non-conservative amino-acid change from a glutamine to arginine in the p2rx7 purinergic receptor protein is associated with both bipolar- and unipolar-affective disorders. Mol Psychiatry. 2009;14(6):614–20.
Hejjas K, Szekely A, Domotor E, Halmai Z, Balogh G, Schilling B, et al. Association between depression and the gln460arg polymorphism of p2rx7 gene: a dimensional approach. Am J Med Genet B: The Official Publication of the International Society of Psychiatric Genetics. 2009;150B(2):295–9.
Lucae S, Salyakina D, Barden N, Harvey M, Gagne B, Labbe M, et al. P2rx7, a gene coding for a purinergic ligand-gated ion channel, is associated with major depressive disorder. Hum Mol Genet. 2006;15(16):2438–45.
Green EK, Grozeva D, Raybould R, Elvidge G, Macgregor S, Craig I, et al. P2rx7: a bipolar and unipolar disorder candidate susceptibility gene? Am J Med Genet B: The Official Publication of the International Society of Psychiatric Genetics. 2009;150B(8):1063–9.
Grigoroiu-Serbanescu M, Herms S, Muhleisen TW, Georgi A, Diaconu CC, Strohmaier J, et al. Variation in p2rx7 candidate gene (rs2230912) is not associated with bipolar I disorder and unipolar major depression in four European samples. Am J Med Genet B: The Official Publication of the International Society of Psychiatric Genetics. 2009;150B(7):1017–21.
Baum AE, Akula N, Cabanero M, Cardona I, Corona W, Klemens B, et al. A genome-wide association study implicates diacylglycerol kinase eta (dgkh) and several other genes in the etiology of bipolar disorder. Mol Psychiatry. 2008;13(2):197–207.
Altshuler D, Daly MJ, Lander ES. Genetic mapping in human disease. Science. 2008;322(5903):881–8.
The Wellome Trust Case Control Consortium. Genome-wide association study of 14,000 cases of seven common diseases and 3,000 shared controls. Nature. 2007;447(7145):661–78.
Dick DM, Foroud T, Edenberg HJ, Miller M, Bowman E, Rau NL, et al. Apparent replication of suggestive linkage on chromosome 16 in the NIMH genetics initiative bipolar pedigrees. Am J Med Genet. 2002;114(4):407–12.
Maziade M, Roy MA, Chagnon YC, Cliche D, Fournier JP, Montgrain N, et al. Shared and specific susceptibility loci for schizophrenia and bipolar disorder: a dense genome scan in Eastern Quebec families. Mol Psychiatry. 2005;10(5):486–99.
Merette C, Roy MA, Bureau A, Fournier A, Emond C, Cliche D, et al. Replication of linkage with bipolar disorder on chromosome 16p in the Eastern Quebec population. Am J Med Genet B: The Official Publication of the International Society of Psychiatric Genetics. 2008;147B(6):737–44.
Sklar P, Smoller JW, Fan J, Ferreira MA, Perlis RH, Chambert K, et al. Whole-genome association study of bipolar disorder. Mol Psychiatry. 2008;13(6):558–69.
Liu Y, Blackwood DH, Caesar S, de Geus EJ, Farmer A, Ferreira MA, et al. Meta-analysis of genome-wide association data of bipolar disorder and major depressive disorder. Mol Psychiatry. 2011;16(1):2–4.
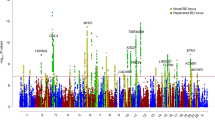
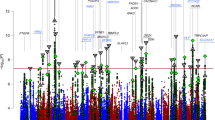
•• Ferreira MA, O’Donovan MC, Meng YA, Jones IR, Ruderfer DM, Jones L, Fan J, Kirov G, Perlis RH, Green EK, Smoller JW et al. Collaborative genome-wide association analysis supports a role for ANK3 and CACNA1C in bipolar disorder. Nat Genet. 2008;40(9):1056–8. This study combined data from two previously published GWAS and one new GWAS to provide adequate power for the detection of common genetic variants. It was the first study to identify the role of ANK3 in BD and to support the previously reported role of CACNA1C in BD. It emphasized the importance of collaborations between different centers.
Smith EN, Bloss CS, Badner JA, Barrett T, Belmonte PL, Berrettini W, et al. Genome-wide association study of bipolar disorder in European American and African American individuals. Mol Psychiatry. 2009;14(8):755–63.
Hattori E, Toyota T, Ishitsuka Y, Iwayama Y, Yamada K, Ujike H, et al. Preliminary genome-wide association study of bipolar disorder in the Japanese population. Am J Med Genet B: The Official Publication of the International Society of Psychiatric Genetics. 2009;150B(8):1110–7.
Lee MT, Chen CH, Lee CS, Chen CC, Chong MY, Ouyang WC, Chiu NY, Chuo LJ, Chen CY, Tan HK, Lane HY et al. Genome-wide association study of bipolar I disorder in the Han Chinese population. Mol Psychiatr. 2010.
McMahon FJ, Akula N, Schulze TG, Muglia P, Tozzi F, Detera-Wadleigh SD, et al. Meta-analysis of genome-wide association data identifies a risk locus for major mood disorders on 3p21.1. Nat Genet. 2010;42(2):128–31.
Breen G, Lewis CM, Vassos E, Pergadia ML, Blackwood DH, Boomsma DI, et al. Replication of association of 3p21.1 with susceptibility to bipolar disorder but not major depression. Nat Genet. 2011;43(1):3–5. author reply 5.
Pinto D, Pagnamenta AT, Klei L, Anney R, Merico D, Regan R, et al. Functional impact of global rare copy number variation in autism spectrum disorders. Nature. 2010;466(7304):368–72.
Need AC, Ge D, Weale ME, Maia J, Feng S, Heinzen EL, et al. A genome-wide investigation of SNPs and CNVs in schizophrenia. PLoS Genet. 2009;5(2):e1000373.
• Zhang D, Cheng L, Qian Y, Alliey-Rodriguez N, Kelsoe JR, Greenwood T, Nievergelt C, Barrett TB, McKinney R, Schork N, Smith EN et al. Singleton deletions throughout the genome increase risk of bipolar disorder. Mol Psychiatry 2009;14(4):376–80. This genome-wide CNV study was the first to suggest that very rare singleton (appear once in the data) deletions increase the risk of BD in cases versus controls.
• Grozeva D, Kirov G, Ivanov D, Jones IR, Jones L, Green EK, St Clair DM, Young AH, Ferrier N, Farmer AE, McGuffin P et al: Rare copy number variants: a point of rarity in genetic risk for bipolar disorder and schizophrenia. Arch Gen Psychiatry 2010;67(4):318–27. In contrast to the study by Zhang et al. [71•], this genome-wide CNV study found no significant increase in rare CNVs in cases versus controls and reported a trend toward a reduced rate of deletions in BD. As a pair, this and the paper by Zhang et al. [71•] have opened up a new and interesting controversy about the role of CNVs in major adult psychiatric disorders.
Askland K, Read C, Moore J. Pathways-based analyses of whole-genome association study data in bipolar disorder reveal genes mediating ion channel activity and synaptic neurotransmission. Hum Genet. 2009;125(1):63–79.
Le-Niculescu H, Patel SD, Bhat M, Kuczenski R, Faraone SV, Tsuang MT, et al. Convergent functional genomics of genome-wide association data for bipolar disorder: comprehensive identification of candidate genes, pathways and mechanisms. Am J Med Genet B: The Official Publication of the International Society of Psychiatric Genetics. 2009;150B(2):155–81.
Disclosure
No potential conflicts of interest relevant to this article were reported.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Margarita Rivera and Peter McGuffin contributed equally to this paper.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Alsabban, S., Rivera, M. & McGuffin, P. Genome-Wide Searches for Bipolar Disorder Genes. Curr Psychiatry Rep 13, 522–527 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11920-011-0226-y
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11920-011-0226-y