Abstract
Chronic daily headache (CDH) is a common neurological condition that affects 1–4 % of the general population. Most individuals with CDH originally suffered from episodic headaches, but over time, this developed into CDH. Although the pathophysiology of CDH is not fully understood, recent clinical and epidemiological studies suggest some risk factors that are associated with an increased risk of transformation from episodic headaches. If risk factors can be identified, they could provide a base for aggressive preventive intervention and thus decrease the transformation from episodic headaches to eventual CDH. In this article, we review and summarize the current data on risk factors for CDH.

Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AMPP:
-
American Migraine Prevalence and Prevention
- CDH:
-
Chronic daily headache
- CM:
-
Chronic migraine
- CGRP:
-
Calcium-gene-related peptide
- CTTH:
-
Chronic tension-type headache
- EM:
-
Episodic migraine
- HR:
-
Hazard ratio
- ICHD-2:
-
The second edition of the International Classification of Headache Disorder
- ICHD-3 beta:
-
The third beta edition of the International Classification of Headache Disorder
- ICD-9-CM:
-
The International Classification of Diseases, Ninth Revision, Clinical Modification
- OR:
-
Odds ratio
- SES:
-
Socioeconomic status
- TM:
-
Transformed migraine
- TMD:
-
Temporomandibular disorders
References
Papers of particular interest, published recently, have been highlighted as: • Of importance •• Of major importance
Castillo J, Muñoz P, Guitera V, Pascual J. Epidemiology of chronic daily headache in the general population. Headache. 1999;39(3):190–6.
Lu S, Fuh J, Chen W, Juang K, Wang S. Chronic daily headache in Taipei, Taiwan: prevalence, follow-up and outcome predictors. Cephalalgia. 2001;21(10):980–6.
Stark RJ, Ravishankar K, Siow HC, Lee KS, Pepperle R, Wang S-J. Chronic migraine and chronic daily headache in the Asia-Pacific region: a systematic review. Cephalalgia. 2013;33(4):266–83.
Wang S-J, Fuh J-L, Lu S-R, Liu C-Y, Hsu L-C, Wang P-N, et al. Chronic daily headache in Chinese elderly: prevalence, risk factors, and biannual follow-up. Neurology. 2000;54(2):314–9.
Prencipe M, Casini A, Ferretti C, Santini M, Pezzella F, Scaldaferri N, et al. Prevalence of headache in an elderly population: attack frequency, disability, and use of medication. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2001;70(3):377–81.
Bekkelund SI, Salvesen R. Prevalence of head trauma in patients with difficult headache: the North Norway Headache Study. Headache. 2003;43(1):59–62.
Manzoni G, Granella F, Sandrini G, Cavallini A, Zanferrari C, Nappi G. Classification of chronic daily headache by International Headache Society criteria: limits and new proposals. Cephalalgia. 1995;15(1):37–43.
Mathew NT. Chronic daily headache. Handbook of Headache. 2005:113–38.
Mathew NT, Reuveni U, Perez F. Transformed or evolutive migraine. Headache. 1987;27(2):102–6.
Solomon S, Lipton RB, Newman LC. Clinical features of chronic daily headache. Headache. 1992;32(7):325–9.
Von Korff M, Galer BS, Stang P. Chronic use of symptomatic headache medications. Pain. 1995;62(2):179–86.
Silberstein SD, Lipton RB. Chronic daily headache, including transformed migraine, chronic tension-type headache, and medication overuse. Wolff’s Headache Head Pain. 2001;7:247–82.
Silberstein SD, Lipton RB, Sliwinski M. Classification of daily and near-daily headaches field trial of revised IHS criteria. Neurology. 1996;47(4):871–5.
Scher AI, Stewart WF, Liberman J, Lipton RB. Prevalence of frequent headache in a population sample. Headache. 1998;38(7):497–506.
Olesen J, Steiner T. The International Classification of Headache Disorders, 2nd edn (ICDH-II). J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2004;75(6):808.
Headache Classification Committee of the International Headache Society. The international classification of headache disorders, (beta version). Cephalalgia. 2013;33(9):629–808.
Scher A, Stewart W, Ricci J, Lipton R. Factors associated with the onset and remission of chronic daily headache in a population-based study. Pain. 2003;106(1):81–9.
Wiendels NJ, Neven AK, Rosendaal FR, Spinhoven P, Zitman FG, Assendelft WJ, et al. Chronic frequent headache in the general population: prevalence and associated factors. Cephalalgia. 2006;26(12):1434–42.
Wang S-J, Fuh J-L, Lu S-R, Juang K-D. Outcomes and predictors of chronic daily headache in adolescents: a 2-year longitudinal study. Neurology. 2007;68(8):591–6.
Manack A, Buse D, Serrano D, Turkel C, Lipton R. Rates, predictors, and consequences of remission from chronic migraine to episodic migraine. Neurology. 2011;76(8):711–8. A population-based study investigating factors associated with remission from CM to EM.
Bigal ME, Lipton RB. Modifiable risk factors for migraine progression. Headache. 2006;46(9):1334–43.
Buse DC, Manack A, Serrano D, Turkel C, Lipton RB. Sociodemographic and comorbidity profiles of chronic migraine and episodic migraine sufferers. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2010;81(4):428–32.
Blumenfeld AM, Varon SF, Wilcox TK, Buse DC, Kawata AK, Manack A, et al. Disability, HRQoL and resource use among chronic and episodic migraineurs: results from the International Burden of Migraine Study (IBMS). Cephalalgia. 2011;31(3):301–15.
Chen YC, Tang CH, Ng K, Wang SJ. Comorbidity profiles of chronic migraine sufferers in a national database in Taiwan. J Headache Pain. 2012;13(4):311–9. This article showed multiple comorbidities of CM compared to non-migraineurs and other migraine subtypes using Taiwan National Health Insurance Research Database and emphasized the higher risk of depression, anxiety, bipolar, and other medical illness in CM sufferers.
Pakalnis A, Butz C, Splaingard D, Kring D, Fong J. Emotional problems and prevalence of medication overuse in pediatric chronic daily headache. J Child Neurol. 2007;22(12):1356–9.
Buse DC, Silberstein SD, Manack AN, Papapetropoulos S, Lipton RB. Psychiatric comorbidities of episodic and chronic migraine. J Neurol. 2013;260(8):1960–9. A comprehensive review article summarized the association between psychiatric comorbidity and CM in comparison with EM, using recent data.
Houle TT, Butschek RA, Turner DP, Smitherman TA, Rains JC, Penzien DB. Stress and sleep duration predict headache severity in chronic headache sufferers. Pain. 2012;153(12):2432–40.
Radat F, Creac’h C, Swendsen J, Lafittau M, Irachabal S, Dousset V, et al. Psychiatric comorbidity in the evolution from migraine to medication overuse headache. Cephalalgia. 2005;25(7):519–22.
Breslau N, Davis GC, Schultz LR, Peterson EL. Joint 1994 Wolff Award Presentation. Migraine and major depression: a longitudinal study. Headache. 1994;34(7):387–93.
Rueda-Sanchez M, Diaz-Martinez LA. Prevalence and associated factors for episodic and chronic daily headache in the Colombian population. Cephalalgia. 2008;28(3):216–25.
Scher A, Lipton R, Stewart W. Habitual snoring as a risk factor for chronic daily headache. Neurology. 2003;60(8):1366–8.
Fernandes G, Franco AL, Goncalves DA, Speciali JG, Bigal ME, Camparis CM. Temporomandibular disorders, sleep bruxism, and primary headaches are mutually associated. J Orofac Pain. 2013;27(1):14–20. This article showed the mutual association between painful TMD, sleep bruxism, and CM. TMD or sleep bruxism increased risk of CM. Otherwise diagnosis of CM increased risk of TMD with/without sleep bruxism.
Barbanti P, Aurilia C, Egeo G, Fofi L, Vanacore N. A case-control study on excessive daytime sleepiness in chronic migraine. Sleep Med. 2013;14(3):278–81.
Stuginski-Barbosa J, Macedo HR, Bigal ME, Speciali JG. Signs of temporomandibular disorders in migraine patients: a prospective, controlled study. Clin J Pain. 2010;26(5):418–21.
Goncalves DA, Camparis CM, Speciali JG, Franco AL, Castanharo SM, Bigal ME. Temporomandibular disorders are differentially associated with headache diagnoses: a controlled study. Clin J Pain. 2011;27(7):611–5.
Bevilaqua-Grossi D, Lipton RB, Napchan U, Grosberg B, Ashina S, Bigal ME. Temporomandibular disorders and cutaneous allodynia are associated in individuals with migraine. Cephalalgia. 2010;30(4):425–32.
Bigal ME, Lipton RB. Obesity is a risk factor for transformed migraine but not chronic tension-type headache. Neurology. 2006;67(2):252–7.
Lu SR, Fuh JL, Wang SJ, Juang KD, Chen SP, Liao YC, et al. Incidence and risk factors of chronic daily headache in young adolescents: a school cohort study. Pediatrics. 2013;132(1):e9–16. The role of obesity on the new onset CDH in young adolescents using a school cohort.
Alessi MC, Lijnen HR, Bastelica D, Juhan-Vague I. Adipose tissue and atherothrombosis. Pathophysiol Haemost Thromb. 2003;33(5–6):290–7.
Zelissen PM, Koppeschaar HP, Lips CJ, Hackeng WH. Calcitonin gene-related peptide in human obesity. Peptides. 1991;12(4):861–3.
Baranowska B, Wolinska-Witort E, Martynska L, Chmielowska M, Baranowska-Bik A. Plasma orexin A, orexin B, leptin, neuropeptide Y (NPY) and insulin in obese women. Neuroendocrinol Lett. 2005;26(4):293–6.
Bernecker C, Pailer S, Kieslinger P, Horejsi R, Moller R, Lechner A, et al. GLP-2 and leptin are associated with hyperinsulinemia in non-obese female migraineurs. Cephalalgia. 2010;30(11):1366–74.
Winter AC, Berger K, Buring JE, Kurth T. Body mass index, migraine, migraine frequency and migraine features in women. Cephalalgia. 2009;29(2):269–78.
Silverman K, Evans SM, Strain EC, Griffiths RR. Withdrawal syndrome after the double-blind cessation of caffeine consumption. N Engl J Med. 1992;327(16):1109–14.
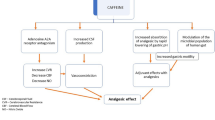
Scher AI, Stewart WF, Lipton RB. Caffeine as a risk factor for chronic daily headache a population-based study. Neurology. 2004;63(11):2022–7.
Hering-Hanit R, Gadoth N. Caffeine-induced headache in children and adolescents. Cephalalgia. 2003;23(5):332–5.
Bigal ME. The paradoxical effects of analgesics and the development of chronic migraine. Arq Nneuropsiquiatria. 2011;69(3):544–51. A review article summarized the association between CM risk and various abortive medications.
De Felice M, Ossipov MH, Wang R, Lai J, Chichorro J, Meng I, et al. Triptan-induced latent sensitization: a possible basis for medication overuse headache. Ann Neurol. 2010;67(3):325–37.
Bigal ME, Serrano D, Buse D, Scher A, Stewart WF, Lipton RB. Acute migraine medications and evolution from episodic to chronic migraine: a longitudinal population‐based study. Headache. 2008;48(8):1157–68.
Starling AJ, Hoffman-Snyder C, Halker RB, Wellik KE, Vargas BB, Dodick DW, et al. Risk of development of medication overuse headache with nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug therapy for migraine: a critically appraised topic. Neurologist. 2011;17(5):297–9.
Katsarava Z, Dzagnidze A, Kukava M, Mirvelashvili E, Djibuti M, Janelidze M, et al. Primary headache disorders in the Republic of Georgia: prevalence and risk factors. Neurology. 2009;73(21):1796–803.
Ashina S, Lyngberg A, Jensen R. Headache characteristics and chronification of migraine and tension-type headache: a population-based study. Cephalalgia. 2010;30(8):943–52.
Bigal ME, Lipton RB. Excessive acute migraine medication use and migraine progression. Neurology. 2008;71(22):1821–8.
Manzoni GC, Lombardi LL, Lana S, Maffezzoni M, Camarda C, Torelli P. Detection of possible factors favouring the evolution of migraine without aura into chronic migraine. Neurol Sci. 2012;33 Suppl 1:S165–7.
Katsarava Z, Schneeweiss S, Kurth T, Kroener U, Fritsche G, Eikermann A, et al. Incidence and predictors for chronicity of headache in patients with episodic migraine. Neurology. 2004;62(5):788–90.
Buchgreitz L, Lyngberg AC, Bendtsen L, Jensen R. Increased pain sensitivity is not a risk factor but a consequence of frequent headache: a population-based follow-up study. Pain. 2008;137(3):623–30.
Louter MA, Bosker JE, van Oosterhout WP, van Zwet EW, Zitman FG, Ferrari MD, et al. Cutaneous allodynia as a predictor of migraine chronification. Brain. 2013;136(Pt 11):3489–96.
Misra UK, Kalita J, Bhoi SK. Allodynia in migraine: clinical observation and role of prophylactic therapy. Clin J Pain. 2013;29(7):577–82.
Bigal M, Ashina S, Burstein R, Reed M, Buse D, Serrano D, et al. Prevalence and characteristics of allodynia in headache sufferers: a population study. Neurology. 2008;70(17):1525–33.
Grande RB, Aaseth K, Gulbrandsen P, Lundqvist C, Russell MB. Prevalence of primary chronic headache in a population-based sample of 30- to 44-year-old persons. Neuroepidemiology. 2008;30(2):76–83.
Hagen K, Zwart JA, Vatten L, Stovner L, Bovim G. Prevalence of migraine and non‐migrainous headache—head‐HUNT, a large population‐based study. Cephalalgia. 2000;20(10):900–6.
Lantéri-Minet M, Auray J-P, El Hasnaoui A, Dartigues J-F, Duru G, Henry P, et al. Prevalence and description of chronic daily headache in the general population in France. Pain. 2003;102(1):143–9.
Park JW, Moon HS, Kim JM, Lee KS, Chu MK. Chronic daily headache in Korea: prevalence, clinical characteristics, medical consultation and management. J Clin Neurol. 2014;10(30):236–43.
Yu S, Liu R, Zhao G, Yang X, Qiao X, Feng J, et al. The prevalence and burden of primary headaches in China: a population‐based door‐to‐door survey. Headache. 2012;52(4):582–91.
Fendrich K, Vennemann M, Pfaffenrath V, Evers S, May A, Berger K, et al. Headache prevalence among adolescents—the German DMKG headache study. Cephalalgia. 2007;27(4):347–54.
Wang S-J, Fuh J-L, Lu S-R. Chronic daily headache in adolescents: an 8-year follow-up study. Neurology. 2009;73(6):416–22.
Queiroz L, Peres M, Kowacs F, Piovesan E, Ciciarelli M, Souza J, et al. Chronic daily headache in Brazil: a nationwide population‐based study. Cephalalgia. 2008;28(12):1264–9.
Hagen K, Vatten L, Stovner L, Zwart JA, Krokstad S, Bovim G. Low socio‐economic status is associated with increased risk of frequent headache: a prospective study of 22 718 adults in Norway. Cephalalgia. 2002;22(8):672–9.
Arruda MA, Guidetti V, Galli F, Albuquerque RC, Bigal ME. Frequency of headaches in children is influenced by headache status in the mother. Headache. 2010;50(6):973–80.
Cevoli S, Sancisi E, Grimaldi D, Pierangeli G, Zanigni S, Nicodemo M, et al. Family history for chronic headache and drug overuse as a risk factor for headache chronification. Headache. 2009;49(3):412–8.
Russell M, Østergaard S, Bendtsen L, Olesen J. Familial occurrence of chronic tension‐type headache. Cephalalgia. 1999;19(4):207–10.
Shin H-E, Han S-J, Lee K-S, Park J-W. Polymorphism of the glutamate transporter protein EAAT2 and migraine transformation into chronic daily headache. J Clin Neurol. 2011;7(3):143–7. A genetic association study for the migraine transformation to CDH.
Terrazzino S, Sances G, Balsamo F, Viana M, Monaco F, Bellomo G, et al. Role of 2 common variants of 5HT2A gene in medication overuse headache. Headache. 2010;50(10):1587–96.
Stewart W, Scher A, Lipton R. Stressful life events and risk of chronic daily headache: results from the frequent headache epidemiology study. Cephalalgia. 2001;21:279.
Tietjen G, Brandes J, Digre KB, Baggaley S, Martin V, Recober A, et al. History of childhood maltreatment is associated with comorbid depression in women with migraine. Neurology. 2007;69(10):959–68.
Reynolds DJ, Hovanitz CA. Life event stress and headache frequency revisited. Headache. 2000;40(2):111–8.
De Benedittis G, Lorenzetti A, Fieri A. The role of stressful life events in the onset of chronic primary headache. Pain. 1990;40(1):65–75.
De Benedittis G, Lorenzetti A. The role of stressful life events in the persistence of primary headache: major events vs. daily hassles. Pain. 1992;51(1):35–42.
De Leeuw R, Schmidt JE, Carlson CR. Traumatic stressors and post‐traumatic stress disorder symptoms in headache patients. Headache. 2005;45(10):1365–74.
Scher A, Stewart W, Buse D, Krantz D, Lipton R. Major life changes before and after the onset of chronic daily headache: a population‐based study. Cephalalgia. 2008;28(8):868–76.
Passchier J, Schouten J, Donk J, Romunde L. The association of frequent headaches with personality and life events. Headache. 1991;31(2):116–21.
Juang KD, Wang SJ, Fuh JL, Lu SR, Chen YS. Association between adolescent chronic daily headache and childhood adversity: a community‐based study. Cephalalgia. 2004;24(1):54–9.
Kay D, Kerr T, Lassman L. Brain trauma and the postconcussional syndrome. Lancet. 1971;298(7733):1052–5.
Walker WC, Seel RT, Curtiss G, Warden DL. Headache after moderate and severe traumatic brain injury: a longitudinal analysis. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2005;86(9):1793–800.
Alves WM, Colohan AR, O’Leary TJ, Rimel RW, Jane JA. Understanding posttraumatic symptoms after minor head injury. J Head Trauma Rehabil. 1986;1(2):1–12.
Yamaguchi M. Incidence of headache and severity of head injury. Headache. 1992;32(9):427–31.
Jensen OK, Nielsen FF. The influence of sex and pre-traumatic headache on the incidence and severity of headache after head injury. Cephalalgia. 1990;10(6):285–93.
Moscato D, Peracchi MI, Mazzotta G, Savi L, Battistella PA. Post-traumatic headache from moderate head injury. J Headache Pain. 2005;6(4):284–6.
Weiss HD, Stern BJ, Goldberg J. Post‐traumatic migraine: chronic migraine precipitated by minor head or neck trauma. Headache. 1991;31(7):451–6.
Scher AI, Lipton RB, Stewart W. Risk factors for chronic daily headache. Curr Pain Headache Rep. 2002;6(6):486–91.
Couch JR, Lipton RB, Stewart WF, Scher AI. Head or neck injury increases the risk of chronic daily headache a population-based study. Neurology. 2007;69(11):1169–77.
Compliance with Ethics Guidelines
ᅟ
Conflict of Interest
Dr. Soo-Jin Cho and Dr. Min Kyung Chu each declare no potential conflicts of interest.
Human and Animal Rights and Informed Consent
This article does not contain any studies with human or animal subjects performed by any of the authors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This article is part of the Topical Collection on Chronic Daily Headache
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cho, SJ., Chu, M.K. Risk Factors of Chronic Daily Headache or Chronic Migraine. Curr Pain Headache Rep 19, 465 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11916-014-0465-9
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11916-014-0465-9