Abstract
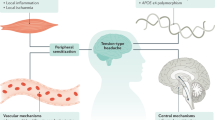
Tension-type headache (TTH) is the most common and most socioeconomically costly headache. Yet our knowledge regarding TTH pathophysiological mechanisms is still in its early stages. Psychological stress and weak coping mechanisms may initiate and propagate physiological pain via activation of second messengers in downstream substrates involved in pain. It seems that peripheral mechanisms are predominant in the episodic type (ETTH), whereas central mechanisms are involved in the chronic type (CTTH) of tension headache. The conversion from ETTH to CTTH is most relevant to the clinician and the patient, as CTTH is the most debilitating. This paper focuses and summarizes our current understanding of central sensitization, the process by which this conversion occurs in TTH, and proposes an integrated model to explain how ETTH progresses into CTTH in genetically susceptible individuals.
Similar content being viewed by others
References and Recommended Reading
Headache Classification Subcommittee of the International Headache Society: The International Classification of Headache Disorders, 2nd edn. Cephalalgia 2004, 24(Supp 1):1–150.
Lyngberg AC, Rasmussen BK, Jørgensen T, Jensen R: Has the prevalence of migraine and tension-type headache changed over a 12-year period? A Danish population survey. Eur J Epidemiol 2005, 20:243–249.
Rasmussen BK, Jensen R, Schroll M, Olesen J: Epidemiology of headache in a general population. A prevalence study. J Clin Epidemiol 1991, 44:1147–1157.
Jensen R, Symon D: Epidemiology of tension-type headaches. In The Headaches, edn 3. Edited by Olesen J, Goadsby PJ, Ramadan N, et al. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 2005:621–624.
Lyngberg AC, Rasmussen BK, Jørgensen T, Jensen R: Incidence of primary headache: a Danish epidemiologic follow-up study. Am J Epidemiol 2005, 161:1066–1073.
Spierings EL, Ranke AH, Honkoop PC: Precipitating and aggravating factors of migraine versus tension-type headache. Headache 2001, 41:554–558.
Clark GT, Sakai S, Merrill R, et al.: Cross-correlation between stress, pain, physical activity, and temporalis muscle EMG in tension-type headache. Cephalalgia 1995, 15:511–518.
Lyngberg AC, Rasmussen BK, Jørgensen T, Jensen R: Prognosis of migraine and tension-type headache: a population-based follow-up study. Neurology 2005, 65:580–585.
Russel MB, Saltyete-Benth J, Levi N: Are infrequent episodic, frequent episodic, and chronic-tension headache inherited? A population based study of 11, 199 twin pairs. J Headache Pain 2006, 7:119–126.
Ostergaard S, Russell MB, Bendtsen L, Olesen J: Comparison of first degree relatives and spouses of people with chronic tension headache. BMJ 1997, 314:1092–1093.
Jensen R, Rasmussen BK, Pedersen B, Olesen J: Muscle tenderness and pressure pain thresholds in headache. A population study. Pain 1993, 52:193–199.
Jensen R, Bendtsen L, Olesen J: Muscular factors are of importance in tension type headache. Headache 1998, 38:10–17.
Jensen R: An analysis of spontaneous tension-type headaches: an analysis of tenderness, pain thresholds and EMG. Pain 1995, 64:251–256.
Mork H, Ashina M, Bendtsen L, et al.: Possible mechanisms of pain perception in patients with episodic tension-type headache: a new experimental model of myofascial pain. Cephalalgia 2004, 24:466–475.
Ashina M, Stallknecht B, Bendtsen L, et al.: Tender points are not sites of ongoing inflammation: in vivo evidence in patients with chronic tension-type headache. Cephalalgia 2003, 23:109–116.
Ashina M, Stallknecht B, Bendtsen L, et al.: In vivo evidence of altered skeletal muscle blood flow in chronic tension-type headache. Brain 2002, 125:320–326.
Schoenen J, Gerard P, De Pasqua V, Juprelle M: EMG activity in pericranial muscles during postural variation and mental activity in healthy volunteers and patients with chronic tension type headache. Headache 1991, 31:321–324.
Rollnik JD, Karst M, Fink M, Dengler R: Botulinum toxin type A and EMG: a key to the understanding of chronic tension-type headaches? Headache 2001, 41:985–989.
Sarkar S, Aziz Q, Woolf CJ, et al.: Contribution of central sensitization to the development of non-cardiac chest pain. Lancet 2000, 356:1154–1159.
Schoenen J, Bottin D, Hardy F, Gerard P: Cephalic and extracephalic pressure pain threshold in chronic tensiontype headache. Pain 1991, 47:145–149.
Bendtsen L, Jensen R, Olesen J: Decreased pain detection and tolerance thresholds in chronic tension-type headache. Arch Neurol 1996, 53:373–376.
Göbel H, Weigle L, Kropp P, Soyka D: Pain sensitivity and pain reactivity of pericranial muscles in migraine and tension type headache. Cephalalgia 1992, 12:142–151.
Bigal ME, Ashina S, Burstein, et al.: Prevalence and characteristics of allodynia in headache sufferers. Neurology 2008, 70:1525–1533.
Ashina S, Bendtsen L, Ashina M, et al.: Evidence for generalized muscular and cutaneous hyperalgesia in patients with chronic tension-type headache [abstract]. Presented at the 14th International Headache Research Seminar. Copenhagen, Denmark; March 11–13, 2005.
Langemark M, Jensen K, Jensen TS, Olesen J: Pressure pain thresholds and thermal nociceptive thresholds in chronic tension type headache. Pain 1989, 38:203–210.
Urban MO, Gebhart GF: Supraspinal contributions to hyperalgesia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 1999, 96:7687–7692.
Langemark M, Bach FW, Jensen TS, Olesen J: Decreased nociceptive flexion reflex threshold in chronic tension-type headache. Arch Neurol 1993, 50:1061–1064.
Ji RR, Kohno T, Moore KA, Woolf CJ: Central sensitization and LTP: do pain and memory share similar mechanisms? Trends Neurosci 2003, 26:696–705.
Munhoz CD, Garcia-Bueno B, Madrigal JLM, et al.: Stress-induced neuroinflammation: mechanisms and new pharmacological targets. Braz J Med Biol Res 2008, 41:1038–1046.
Le Doaré K, Akerman S, Holland PR, et al.: Occipital afferent activation of second order neurons in the trigeminocervical complex in rats. Neurosci Lett 2006, 403:73–77.
Alam Z, Coombes N, Waring RH, et al.: Plasma levels of neuroexcitatory amino acids in patients with migraine or tension headache. J Neurol Sci 1998, 156:102–106.
Mazzotta G, Sarchielli P, Gaggioli A, Gallai V: Study of pressure pain and cellular concentration of neurotransmitters related to nociception in episodic tension-type headache patients. Headache 1997, 37:565–571.
Bendtsen L, Jensen R, Hindberg I, et al.: Serotonin metabolism in chronic tension-type headache. Cephalalgia 1997, 17:843–848.
Olesen J: The role of nitric oxide in migraine, tension-type headache and cluster headache. Pharmacol Ther 2008, 120:157–171.
Ashina M, Lassen LH, Bendtsen L, et al.: Effect of inhibition of nitric oxide synthase on chronic tension-type headache: a randomized crossover trial. Lancet 1999, 353:287–289.
Ashina M, Simonsen H, Bendtsen L, et al.: Glyceryl trinitrate may trigger endogenous nitric oxide production in patients with chronic tension-type headache. Cephalagia 2004, 24:967–972.
Holthusen H, Arndt JO: Nitric oxide evokes pain at nociceptors of the paravascular tissue and veins in humans. J Physiol 1995, 487(Pt 1):253–258.
Lambert GA, Hoskin KL, Zagami AS: Nitrergic and glutamatergic neuronal mechanisms at the trigeminovascular first-order synapse. Neuropharmacology 2004, 47:92–105.
Wu J, Lin Q, Lu Y, et al.: Changes in nitric oxide synthase isoforms in the spinal cord of rat following induction of chronic arthritis. Exp Brain Res 1998, 118:457–465.
Ashina M, Bendtsen L, Jensen R, et al.: Possible mechanisms of action of nitric oxide synthase inhibitors in chronic tension type headache. Brain 1999, 122:1629–1635.
Ashina M, Bendtsen L, Jensen R, et al.: Plasma levels of calcitonin gene-related peptide in chronic tension-type headache. Neurology 2000, 55:1335–1340.
Schoenen J: Tension-type headache and fibromyalgia: what’s common, what’s different? Neurol Sci 2004, 25:S157–S159.
Bendtsen L, Jensen R, Olesen J: Qualitatively altered nociception in chronic myofascial pain. Pain 1996, 65:259–264.
Thompson SWN, King AE, Woolf CJ: Activity-dependent changes in rat ventral horn neurons in vitro: summation of prolonged afferent evoked postsynaptic depolarizations produce a D-APV sensitive windup. Eur J Neurosci 1990, 2:638–649.
Tegeder I, Niederberger E, Vetter G, et al.: Effects of selective COX-1 and -2 inhibition on formalin-evoked nociceptive behavior and prostaglandin E2 release in the spinal cord. J Neurochem 2001, 79:777–786.
Classey JD, Knight YE, Goadsby PJ: The NMDA receptor antagonist MK-801 reduces Fos-like immunoreactivity within the trigeminocervical complex following superior sagittal sinus stimulation in the cat. Brain Res 2001, 907:117–124.
Bartsch T, Goadsby PJ: Increased responses in trigeminocervical nociceptive neurons to cervical input after stimulation of the dura mater. Brain 2003, 126:1801–1813.
Hoskin KL, Zagami A, Goadsby PJ: Stimulation of the middle meningeal artery leads to Fos expression in the trigeminocervical nucleus: a comparative study of monkey and cat. J Anat 1999, 194:579–588.
Neugebauer V, Li W, Bird GC, et al.: Synaptic plasticity in the amygdala in a model of arthritic pain: differential roles of metabotropic glutamate receptors 1 and 5. J Neurosci 2003, 23:52–63.
Wei F, Zhuo M: Potentiation of sensory responses in the anterior cingulate cortex following digit amputation in the anaesthetized rat. J Physiol 2001, 532:823–833.
Schmidt-Wilcke T, Leinisch E, Straube A, et al.: Gray matter decrease in patients with chronic tension type headache. Neurology 2005, 65:1483–1486.
Clark GT, Sakai S, Merrill R, et al.: Cross-correlation between stress, pain, physical activity, and temporalis muscle EMG in tension-type headache. Cephalalgia 1995, 15:511–518.
Madrigal JL, Garcia-Bueno B, Caso JR, et al.: Stressinduced oxidative changes in brain. CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets 2006, 5:561–568.
Madrigal JL, Moro MA, Lizasoain I, et al.: Inducible nitric oxide synthase expression in brain cortex after acute restraint stress is regulated by nuclear factor kappaB-mediated mechanisms. J Neurochem 2001, 76:532–538.
Munhoz CD, Lepsch LB, Kawamoto EM, et al.: Chronic unpredictable stress exacerbates lipopolysaccharide-induced activation of nuclear factor kappaB in the frontal cortex and hippocampus via glucocorticoid secretion. J Neurosci 2006, 26:3813–3820.
Holroyd K, O’Donnell F, Stensland M, et al.: Management of chronic tension-type headache with tricyclic antidepressant medication, stress management therapy, and their combination: a randomized controlled trial. JAMA 2001, 285:2208–2215.
Spiegel K, Kalb R, Pasternak G: Analgesic activity of tricyclic antidepressants. Ann Neurol 1983, 13:462–465.
Ashina S, Bendtsen L, Jensen R: Analgesic effect of amitriptyline in chronic tension-type headache is not directly related to serotonin reuptake inhibition. Pain 2004, 108:108–114.
Sawynok J, Esser M, Reid A: Antidepressants as analgesics: an overview of central and peripheral mechanisms of action. J Psychiatry Neurosci 2001, 26:21–29.
Watanabe Y, Saito H, Abe K: Tricyclic antidepressants block NMDA receptor-mediated synaptic responses and induction of long-term potentiation in rat hippocampal slices. Neuropharmacology 1993, 32:479–486.
Bendtsen L, Jensen R: Amitriptyline reduces myofascial tenderness in patients with chronic tension-type headache. Cephalalgia 2000, 20:603–610.
Bendtsen L, Jensen R: Mirtazapine is effective in the prophylactic treatment of chronic tension-type headache. Neurology 2004, 62:1706–1711.
Westenberg HG: Pharmacology of antidepressants: selectivity or multiplicity? J Clin Psych 1999, 60(Suppl 17):4–8.
Lassen LH, Ashina M, Christiansen I, et al.: Nitric oxide synthase inhibition: a new principle in the treatment of migraine attacks. Cephalalgia 1998, 18:27–32.
Juhasz G, Zsombok T, Modos EA, et al.: NO-induced migraine attack: strong increase in plasma calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP) concentration and negative correlation with platelet serotonin release. Pain 2003, 106:461–470.
Goadsby PJ, Edvinsson L: The trigeminovascular system and migraine: studies characterizing cerebrovascular and neuropeptide changes seen in humans and cats. Ann Neurol 1993, 33:48–56.
Goadsby PJ: New targets in the acute treatment of headache. Curr Opin Neurol 2005, 18:283–288.
Shields KG, Kaube H, Goadsby PJ: GABA receptors modulate trigeminovascular nociceptive transmission in the ventroposteromedial (VPM) thalamic nucleus of the rat. Cephalalgia 2003, 23:728.
Lindelof K, Bendtsen L: Memantine for prophylaxis of chronic tension-type headache: a double-blind, randomized, crossover clinical trial. Cephalalgia 2008, 29:314–321.
Goadsby PJ, Hoskin KL, Storer RJ, et al.: Adenosine (A1) receptor agonists inhibit trigeminovascular nociceptive transmission. Brain 2002, 125:1392–1401.
Sawynok J, Liu XJ: Adenosine in the spinal cord and periphery: release and regulation of pain. Prog Neurobio 2003, 69:313–340.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, Y. Advances in the pathophysiology of tension-type headache: From stress to central sensitization. Current Science Inc 13, 484–494 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11916-009-0078-x
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11916-009-0078-x