Abstract
The importance of the insulin-like growth factor (IGF)-I axis in the regulation of bone size and bone mineral density, two important determinants of bone strength, has been well established from clinical studies involving patients with growth hormone deficiency and IGF-I gene disruption. Data from transgenic animal studies involving disruption and overexpression of components of the IGF-I axis also provide support for a key role for IGF-I in bone metabolism. IGF-I actions in bone are subject to regulation by systemic hormones, local growth factors, as well as mechanical stress. In this review we describe findings from various genetic mouse models that pertain to the role of endocrine and local sources of IGF-I in the regulation of skeletal growth.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Papers of particular interest, published recently, have been highlighted as:• Of importance •• Of major importance
Lefebvre V, Bhattaram P. Vertebrate skeletogenesis. Curr Top Dev Biol. 2010;90:291–317.
Olsen BR, Reginato AM, Wang W. Bone development. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 2000;16:191–220.
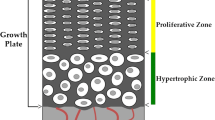
van der Eerden BC, Karperien M, Wit JM. Systemic and local regulation of the growth plate. Endocr Rev. 2003;24:782–801.
Osteoporosis prevention, diagnosis, and therapy. NIH Consens Statement 2000; 17:1–45.
Heaney RP, Abrams S, Dawson-Hughes B, Looker A, Marcus R, Matkovic V, Weaver C. Peak bone mass. Osteoporos Int. 2000;11:985–1009.
Libanati C, Baylink DJ, Lois-Wenzel E, Srinvasan N, Mohan S. Studies on the potential mediators of skeletal changes occurring during puberty in girls. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1999;84:2807–14.
Gafni RI, Baron J. Childhood bone mass acquisition and peak bone mass may not be important determinants of bone mass in late adulthood. Pediatrics. 2007;119 Suppl 2:S131–6.
Hansen MA, Overgaard K, Riis BJ, Christiansen C. Role of peak bone mass and bone loss in postmenopausal osteoporosis: 12 year study. BMJ. 1991;303:961–4.
de Crombrugghe B, Lefebvre V, Behringer RR, Bi W, Murakami S, Huang W. Transcriptional mechanisms of chondrocyte differentiation. Matrix Biol. 2000;19:389–94.
Lefebvre V, Smits P. Transcriptional control of chondrocyte fate and differentiation. Birth Defects Res C Embryo Today. 2005;75:200–12.
Mackie EJ, Tatarczuch L, Mirams M. The growth plate chondrocyte and endochondral ossification. J. Endocrinol. In Press; 2011.
Ohlsson C, Mohan S, Sjogren K, Tivesten A, Isgaard J, Isaksson O, Jansson JO, Svensson J. The role of liver-derived insulin-like growth factor-I. Endocr Rev. 2009;30:494–535.
Olson LE, Ohlsson C, Mohan S. The role of GH/IGF-I-mediated mechanisms in sex differences in cortical bone size in mice. Calcif Tissue Int. 2011;88:1–8.
Walenkamp MJ, Wit JM. Genetic disorders in the GH IGF-I axis in mouse and man. Eur J Endocrinol. 2007;157 Suppl 1:S15–26.
Yakar S, Courtland HW, Clemmons D. IGF-1 and bone: New discoveries from mouse models. J Bone Miner Res. 2010;25:2543–52.
LeRoith D. Clinical relevance of systemic and local IGF-I: lessons from animal models. Pediatr Endocrinol Rev. 2008;5 Suppl 2:739–43.
Mohan S, Baylink DJ. Role of growth hormone/insulin-like growth factor axis. In: Glowacki J, Rosen CJ, Bilezikian JP, editors. The aging skeleton. San Diego: Academic; 1999. p. 209–19.
Ohlsson C, Bengtsson BA, Isaksson OG, Andreassen TT, Slootweg MC. Growth hormone and bone. Endocr Rev. 1998;19:55–79.
Fan Y, Menon RK, Cohen P, Hwang D, Clemens T, DiGirolamo DJ, Kopchick JJ, Le Roith D, Trucco M, Sperling MA. Liver-specific deletion of the growth hormone receptor reveals essential role of growth hormone signaling in hepatic lipid metabolism. J Biol Chem. 2009;284:19937–44.
DiGirolamo DJ, Mukherjee A, Fulzele K, Gan Y, Cao X, Frank SJ, Clemens TL. Mode of growth hormone action in osteoblasts. J Biol Chem. 2007;282:31666–74.
•• Xing W, Govoni K, Donahue LR, Kesavan C, Wergedal J, Long C, Bassett JH, Gogakos A, Wojcicka A, Williams GR, et al. Genetic evidence that thyroid hormone is indispensable for prepubertal IGF-I expression and bone acquisition in mice. J. Bone Miner Res. 2012; 27:1067–79. Reports that TH acting via IGF-dependent and -independent mechanisms plays a more critical role than GH in the regulation of skeletal growth during the prepubertal growth period.
Lakatos P, Foldes J, Nagy Z, Takacs I, Speer G, Horvath C, Mohan S, Baylink DJ, Stern PH. Serum insulin-like growth factor-I, insulin-like growth factor binding proteins, and bone mineral content in hyperthyroidism. Thyroid. 2000;10:417–23.
Lakatos P, Caplice MD, Khanna V, Stern PH. Thyroid hormones increase insulin-like growth factor I content in the medium of rat bone tissue. J Bone Miner Res. 1993;8:1475–81.
O’Shea PJ, Bassett JH, Sriskantharajah S, Ying H, Cheng SY, Williams GR. Contrasting skeletal phenotypes in mice with an identical mutation targeted to thyroid hormone receptor alpha1 or beta. Mol Endocrinol. 2005;19:3045–59.
Styne DM. The regulation of pubertal growth. Horm Res. 2003;60:22–6.
Veldhuis JD, Metzger DL, Martha Jr PM, Mauras N, Kerrigan JR, Keenan B, Rogol AD, Pincus SM. Estrogen and testosterone, but not a nonaromatizable androgen, direct network integration of the hypothalamo-somatotrope (growth hormone)-insulin-like growth factor I axis in the human: evidence from pubertal pathophysiology and sex-steroid hormone replacement. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1997;82:3414–20.
Leung KC, Johannsson G, Leong GM, Ho KK. Estrogen regulation of growth hormone action. Endocr Rev. 2004;25:693–721.
Meinhardt UJ, Ho KK. Modulation of growth hormone action by sex steroids. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf). 2006;65:413–22.
Canalis E. Insulin like growth factors and the local regulation of bone formation. Bone. 1993;14:273–6.
Linkhart TA, Mohan S. Parathyroid hormone stimulates release of insulin-like growth factor-I (IGF-I) and IGF-II from neonatal mouse calvaria in organ culture. Endocrinology. 1989;125:1484–91.
McCarthy TL, Centrella M, Canalis E. Parathyroid hormone enhances the transcript and polypeptide levels of insulin-like growth factor I in osteoblast-enriched cultures from fetal rat bone. Endocrinology. 1989;124:1247–53.
Ishizuya T, Yokose S, Hori M, Noda T, Suda T, Yoshiki S, Yamaguchi A. Parathyroid hormone exerts disparate effects on osteoblast differentiation depending on exposure time in rat osteoblastic cells. J Clin Invest. 1997;99:2961–70.
Bikle DD, Sakata T, Leary C, Elalieh H, Ginzinger D, Rosen CJ, Beamer W, Majumdar S, Halloran BP. Insulin-like growth factor I is required for the anabolic actions of parathyroid hormone on mouse bone. J Bone Miner Res. 2002;17:1570–8.
Miyakoshi N, Kasukawa Y, Linkhart TA, Baylink DJ, Mohan S. Evidence that anabolic effects of PTH on bone require IGF-I in growing mice. Endocrinology. 2001;142:4349–56.
Yamaguchi M, Ogata N, Shinoda Y, Akune T, Kamekura S, Terauchi Y, Kadowaki T, Hoshi K, Chung UI, Nakamura K, et al. Insulin receptor substrate-1 is required for bone anabolic function of parathyroid hormone in mice. Endocrinology. 2005;146:2620–8.
Canalis E. Mechanisms of glucocorticoid action in bone. Curr Osteoporos Rep. 2005;3:98–102.
Cheng SL, Zhang SF, Mohan S, Lecanda F, Fausto A, Hunt AH, Canalis E, Avioli LV. Regulation of insulin-like growth factors I and II and their binding proteins in human bone marrow stromal cells by dexamethasone. J Cell Biochem. 1998;71:449–58.
Chevalley T, Strong DD, Mohan S, Baylink D, Linkhart TA. Evidence for a role for insulin-like growth factor binding proteins in glucocorticoid inhibition of normal human osteoblast-like cell proliferation. Eur J Endocrinol. 1996;134:591–601.
Jux C, Leiber K, Hugel U, Blum W, Ohlsson C, Klaus G, Mehls O. Dexamethasone impairs growth hormone (GH)-stimulated growth by suppression of local insulin-like growth factor (IGF)-I production and expression of GH- and IGF-I-receptor in cultured rat chondrocytes. Endocrinology. 1998;139:3296–305.
Knutsen R, Honda Y, Strong DD, Sampath TK, Baylink DJ, Mohan S. Regulation of insulin-like growth factor system components by osteogenic protein-1 in human bone cells. Endocrinology. 1995;136:857–65.
McCarthy TL, Centrella M. Local IGF-I expression and bone formation. Growth Horm IGF Res. 2001;11:213–9.
Mohan S, Baylink DJ. IGF system components and their role in bone metabolism. In: Rosenfeld RG, Roberst C, editors. IGFs in health and diseases. New Jersey: Humana Press; 1999. p. 457–96.
Tremollieres FA, Strong DD, Baylink DJ, Mohan S. Insulin-like growth factor II and transforming growth factor beta 1 regulate insulin-like growth factor I secretion in mouse bone cells. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh). 1991;125:538–46.
Zhang X, Sobue T, Hurley MM. FGF-2 increases colony formation, PTH receptor, and IGF-1 mRNA in mouse marrow stromal cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2002;290:526–31.
Baker J, Liu JP, Robertson EJ, Efstratiadis A. Role of insulin-like growth factors in embryonic and postnatal growth. Cell. 1993;75:73–82.
Liu JP, Baker J, Perkins AS, Robertson EJ, Efstratiadis A. Mice carrying null mutations of the genes encoding insulin-like growth factor I (Igf-1) and type 1 IGF receptor (Igf1r). Cell. 1993;75:59–72.
Mohan S, Richman C, Guo R, Amaar Y, Donahue LR, Wergedal J, Baylink DJ. Insulin-like growth factor regulates peak bone mineral density in mice by both growth hormone-dependent and -independent mechanisms. Endocrinology. 2003;144:929–36.
Sjogren K, Bohlooly YM, Olsson B, Coschigano K, Tornell J, Mohan S, Isaksson OG, Baumann G, Kopchick J, Ohlsson C. Disproportional skeletal growth and markedly decreased bone mineral content in growth hormone receptor −/− mice. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2000;267:603–8.
Mohan S, Baylink DJ. Impaired skeletal growth in mice with haploinsufficiency of IGF-I: genetic evidence that differences in IGF-I expression could contribute to peak bone mineral density differences. J Endocrinol. 2005;185:415–20.
Bikle D, Majumdar S, Laib A, Powell-Braxton L, Rosen C, Beamer W, Nauman E, Leary C, Halloran B. The skeletal structure of insulin-like growth factor I-deficient mice. J Bone Miner Res. 2001;16:2320–9.
Camacho-Hubner C, Woods KA, Clark AJ, Savage MO. Insulin-like growth factor (IGF)-I gene deletion. Rev Endocr Metab Disord. 2002;3:357–61.
Walenkamp MJ, Karperien M, Pereira AM, Hilhorst-Hofstee Y, van Doorn J, Chen JW, Mohan S, Denley A, Forbes B, van Duyvenvoorde HA, et al. Homozygous and heterozygous expression of a novel insulin-like growth factor-I mutation. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2005;90:2855–64.
Rajaram S, Baylink DJ, Mohan S. Insulin-like growth factor-binding proteins in serum and other biological fluids: regulation and functions. Endocr Rev. 1997;18:801–31.
Sjogren K, Liu JL, Blad K, Skrtic S, Vidal O, Wallenius V, LeRoith D, Tornell J, Isaksson OG, Jansson JO, et al. Liver-derived insulin-like growth factor I (IGF-I) is the principal source of IGF-I in blood but is not required for postnatal body growth in mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1999;96:7088–92.
Yakar S, Liu JL, Stannard B, Butler A, Accili D, Sauer B, LeRoith D. Normal growth and development in the absence of hepatic insulin-like growth factor I. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1999;96:7324–9.
•• Yakar S, Rosen CJ, Bouxsein ML, Sun H, Mejia W, Kawashima Y, Wu Y, Emerton K, Williams V, Jepsen K, et al. Serum complexes of insulin-like growth factor-1 modulate skeletal integrity and carbohydrate metabolism. FASEB J. 2009;23:709–19. Uses triple knockout mice that lack liver-derived IGF-I, IGFBP-3, and ALS to demonstrate the importance of the circulating IGF regulatory complex in defining skeletal status.
Yakar S, Rosen CJ, Beamer WG, Ackert-Bicknell CL, Wu Y, Liu JL, Ooi GT, Setser J, Frystyk J, Boisclair YR, et al. Circulating levels of IGF-1 directly regulate bone growth and density. J Clin Invest. 2002;110:771–81.
Stratikopoulos E, Szabolcs M, Dragatsis I, Klinakis A, Efstratiadis A. The hormonal action of IGF1 in postnatal mouse growth. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2008;105:19378–83.
• Nordstrom SM, Tran JL, Sos BC, Wagner KU, Weiss EJ. Liver-derived IGF-I contributes to GH-dependent increases in lean mass and bone mineral density in mice with comparable levels of circulating GH. Mol Endocrinol. 2011;25:1223–30. Reports a significant role for growth hormone-dependent hepatic IGF-I in regulating bone density.
Mohan S, Bautista CM, Wergedal J, Baylink DJ. Isolation of an inhibitory insulin-like growth factor (IGF) binding protein from bone cell-conditioned medium: a potential local regulator of IGF action. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1989;86:8338–42.
Zhao G, Monier-Faugere MC, Langub MC, Geng Z, Nakayama T, Pike JW, Chernausek SD, Rosen CJ, Donahue LR, Malluche HH, et al. Targeted overexpression of insulin-like growth factor I to osteoblasts of transgenic mice: increased trabecular bone volume without increased osteoblast proliferation. Endocrinology. 2000;141:2674–82.
Jiang J, Lichtler AC, Gronowicz GA, Adams DJ, Clark SH, Rosen CJ, Kream BE. Transgenic mice with osteoblast-targeted insulin-like growth factor-I show increased bone remodeling. Bone. 2006;39:494–504.
Devlin RD, Du Z, Buccilli V, Jorgetti V, Canalis E. Transgenic mice overexpressing insulin-like growth factor binding protein-5 display transiently decreased osteoblastic function and osteopenia. Endocrinology. 2002;143:3955–62.
Miyakoshi N, Richman C, Kasukawa Y, Linkhart TA, Baylink DJ, Mohan S. Evidence that IGF-binding protein-5 functions as a growth factor. J Clin Invest. 2001;107:73–81.
Miyakoshi N, Richman C, Qin X, Baylink DJ, Mohan S. Effects of recombinant insulin-like growth factor-binding protein-4 on bone formation parameters in mice. Endocrinology. 1999;140:5719–28.
Qin X, Wergedal JE, Rehage M, Tran K, Newton J, Lam P, Baylink DJ, Mohan S. Pregnancy-associated plasma protein-A increases osteoblast proliferation in vitro and bone formation in vivo. Endocrinology. 2006;147:5653–61.
Richman C, Baylink DJ, Lang K, Dony C, Mohan S. Recombinant human insulin-like growth factor-binding protein-5 stimulates bone formation parameters in vitro and in vivo. Endocrinology. 1999;140:4699–705.
Zhang M, Xuan S, Bouxsein ML, von Stechow D, Akeno N, Faugere MC, Malluche H, Zhao G, Rosen CJ, Efstratiadis A, et al. Osteoblast-specific knockout of the insulin-like growth factor (IGF) receptor gene reveals an essential role of IGF signaling in bone matrix mineralization. J Biol Chem. 2002;277:44005–12.
Govoni KE, Wergedal JE, Florin L, Angel P, Baylink DJ, Mohan S. Conditional deletion of insulin-like growth factor-I in collagen type 1alpha2-expressing cells results in postnatal lethality and a dramatic reduction in bone accretion. Endocrinology. 2007;148:5706–15.
Govoni KE, Lee SK, Chung YS, Behringer RR, Wergedal JE, Baylink DJ, Mohan S. Disruption of insulin-like growth factor (IGF)-I expression in type II{alpha}I collagen expressing cells reduces bone length and width in mice. Physiol Genomics. 2007;30(3):354–62. Epub 2007 May 22.
Wang Y, Cheng Z, Elalieh HZ, Nakamura E, Nguyen MT, Mackem S, Clemens TL, Bikle DD, Chang W. IGF-1R signaling in chondrocytes modulates growth plate development by interacting with the PTHrP/Ihh pathway. J Bone Miner Res. 2011;26:1437–46.
Lean JM, Jagger CJ, Chambers TJ, Chow JW. Increased insulin-like growth factor I mRNA expression in rat osteocytes in response to mechanical stimulation. Am J Physiol. 1995;268:E318–27.
Lean JM, Mackay AG, Chow JW, Chambers TJ. Osteocytic expression of mRNA for c-fos and IGF-I: an immediate early gene response to an osteogenic stimulus. Am J Physiol. 1996;270:E937–45.
Triplett JW, O’Riley R, Tekulve K, Norvell SM, Pavalko FM. Mechanical loading by fluid shear stress enhances IGF-1 receptor signaling in osteoblasts in a PKCzeta-dependent manner. Mol Cell Biomech. 2007;4:13–25.
Xing W, Baylink D, Kesavan C, Hu Y, Kapoor S, Chadwick RB, Mohan S. Global gene expression analysis in the bones reveals involvement of several novel genes and pathways in mediating an anabolic response of mechanical loading in mice. J Cell Biochem. 2005;96:1049–60.
Cheng M, Zaman G, Rawlinson SC, Mohan S, Baylink DJ, Lanyon LE. Mechanical strain stimulates ROS cell proliferation through IGF-II and estrogen through IGF-I. J Bone Miner Res. 1999;14:1742–50.
Cheng MZ, Rawlinson SC, Pitsillides AA, Zaman G, Mohan S, Baylink DJ, Lanyon LE. Human osteoblasts’ proliferative responses to strain and 17beta-estradiol are mediated by the estrogen receptor and the receptor for insulin-like growth factor I. J Bone Miner Res. 2002;17:593–602.
Rawlinson SC, Mohan S, Baylink DJ, Lanyon LE. Exogenous prostacyclin, but not prostaglandin E2, produces similar responses in both G6PD activity and RNA production as mechanical loading, and increases IGF-II release, in adult cancellous bone in culture. Calcif Tissue Int. 1993;53:324–9.
Gross TS, Srinivasan S, Liu CC, Clemens TL, Bain SD. Noninvasive loading of the murine tibia: an in vivo model for the study of mechanotransduction. J Bone Miner Res. 2002;17:493–501.
Sakata T, Halloran BP, Elalieh HZ, Munson SJ, Rudner L, Venton L, Ginzinger D, Rosen CJ, Bikle DD. Skeletal unloading induces resistance to insulin-like growth factor I on bone formation. Bone. 2003;32:669–80.
Sakata T, Wang Y, Halloran BP, Elalieh HZ, Cao J, Bikle DD. Skeletal unloading induces resistance to insulin-like growth factor-I (IGF-I) by inhibiting activation of the IGF-I signaling pathways. J Bone Miner Res. 2004;19:436–46.
Kapur S, Mohan S, Baylink DJ, Lau KH. Fluid shear stress synergizes with insulin-like growth factor-I (IGF-I) on osteoblast proliferation through integrin-dependent activation of IGF-I mitogenic signaling pathway. J Biol Chem. 2005;280:20163–70.
Lau KH, Kapur S, Kesavan C, Baylink DJ. Up-regulation of the Wnt, estrogen receptor, insulin-like growth factor-I, and bone morphogenetic protein pathways in C57BL/6J osteoblasts as opposed to C3H/HeJ osteoblasts in part contributes to the differential anabolic response to fluid shear. J Biol Chem. 2006;281:9576–88.
•• Long RK, Nishida S, Kubota T, Wang Y, Sakata T, Elalieh HZ, Halloran BP, Bikle DD. Skeletal unloading-induced insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1) nonresponsiveness is not shared by platelet-derived growth factor: the selective role of integrins in IGF-1 signaling. J Bone Miner Res. 2011;26:2948–58. Reports that skeletal unloading causes bone loss that is associated with impaired IGF-I but not PDGF signaling.
•• Kesavan C, Wergedal JE, Lau KH, Mohan S. Conditional disruption of IGF-I gene in type 1alpha collagen-expressing cells shows an essential role of IGF-I in skeletal anabolic response to loading. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 301:E1191–7. Reports that locally produced IGF-I is critically involved in mediating bone formation response to mechanical strain in mice.
Acknowledgments
Financial support was received from funding agencies in the United States (NIH grant AR048139 and VA merit review grant).
Disclosures
No potential conflicts of interest relevant to this article were reported.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mohan, S., Kesavan, C. Role of Insulin-like Growth Factor-1 in the Regulation of Skeletal Growth. Curr Osteoporos Rep 10, 178–186 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11914-012-0100-9
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11914-012-0100-9