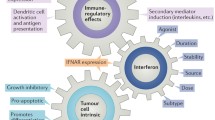
Abstract
Interferons (IFNs), pleiotropic cytokines that regulate antiviral, antitumor, apoptotic, and cellular immune responses, were the first endogenous antiangiogenic regulators identified. In a species-specific manner, IFNs inhibit secretion of such angiogenic factors as basic fibroblast growth factor from tumor cells. The antiangiogenic activity of IFNs is enhanced when they are combined with other antiangiogenic agents, such as tamoxifen and thalidomide.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Folkman J, Merler E, Abernathy C, Williams G: Isolation of a tumor factor responsible for angiogenesis. J Exp Med 1971, 133:275–288.
Folkman J: Anti-angiogenesis: new concept for therapy of solid tumors. Ann Surg 1972, 175:409–416.
Gimbrone MA Jr, Leapman SB, Cotran RS, Folkman J: Tumor dormancy in vivo by prevention of neovascularization. J Exp Med 1972, 136:261–276.
Gospodarowicz D, Bialecki H, Thakral TK: The angiogenic activity of the fibroblast and epidermal growth factor. Exp Eye Res 1979, 28:501–514.
Schweigerer L, Neufeld G, Friedman J, et al.: Capillary endothelial cells express basic fibroblast growth factor, a mitogen that promotes their own growth. Nature 1987, 325:257–259.
Brouty-Boye D, Zetter BR: Inhibition of cell motility by interferon. Science 1980, 208:516–518.
Sidky YA, Borden EC: Inhibition of angiogenesis by interferons: effects on tumor- and lymphocyte-induced vascular responses. Cancer Res 1987, 47:5155–5161.
Norioka K, Mitaka T, Mochizuki Y, et al.: Nakamura H: Interaction of interleukin-1 and interferon-gamma on fibroblast growth factor-induced angiogenesis. Jpn J Cancer Res 1994, 85:522–529.
Voest EE, Kenyon BM, O’Reilly MS, et al.: Inhibition of angiogenesis in vivo by interleukin 12. J Natl Cancer Inst 1995, 87:581–586.
Ezekowitz RAB, Milliken JB, Folkman J: Interferon alfa-2a therapy for life-threatening hemangiomas of infancy. N Engl J Med 1992, 326:1456–1463.
Orchard PJ, Smith CM III, Woods WG, et al.: Treatment of haemangioendotheliomas with alpha interferon. Lancet 1989, 2:565–567.
Marler JJ, Rubin JB, Trede NS, et al.: Successful antiangiogenic therapy of giant cell angioblastoma with interferon alfa 2b: report of 2 cases. Pediatrics 2002, 109:E37.
Bouck N, Stellmach V, Hsu SC: How tumors become angiogenic. In Advances in Cancer Research, vol 69. Edited by Vande Woude G, Klein G. New York: Academic Press; 1997:135–174.
Shing Y, Folkman J, Haudenschild C, et al.: Angiogenesis is stimulated by a tumor-derived endothelial cell growth factor. J Cell Biochem 1985, 29:275–287.
Plouet J, Schilling J, Gospodarowicz D: Isolation and characterization of a newly identified endothelial cell mitogen produced by AtT-20 cells. EMBO J 1989, 8:3801–3806.
Roberts AB, Sporn MB, Assoian RK, et al.: Transforming growth factor type beta: rapid induction of fibrosis and angiogenesis in vivo and stimulation of collagen formation in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 1986, 83:4167–4171.
Yang EY, Moses HL: Transforming growth factor beta 1-induced changes in cell migration, proliferation, and angiogenesis in the chicken chorioallantoic membrane. J Cell Biol 1990, 111:731–741.
Fett JW, Strydom DJ, Lobb FR, et al.: Isolation and characterization of angiogenin, an angiogenic protein from human carcinoma cells. Biochemistry 1985, 24:5480–5487.
Liotta LA, Steeg PS, Stetler-Stevenson WG: Cancer metastasis and angiogenesis: an imbalance of positive and negative regulation. Cell 1991, 64:327–336.
Stetler-Stevenson WG: Matrix metalloproteinases in angiogenesis: a moving target for therapeutic intervention. J Clin Invest 1999, 103:1237–1241.
Torry RJ, Rongish BJ: Angiogenesis in the uterus: potential regulation and relation to tumor angiogenesis. Am J Reprod Immunol 1992, 27:171–179.
Dvorak HF, Nagy JA, Dvorak JT, Dvorak AM: Identification and characterization of the blood vessels of solid tumors that are leaky to circulating macromolecules. Am J Pathol 1988, 133:95–109.
Belardelli F, Gresser I, Maury C, et al.: Antitumor effects of interferon in mice injected with interferon-sensitive and interferon-resistant Friend leukemia cells. III. Inhibition of growth and necrosis of tumors implanted subcutaneously. Int J Cancer 1983, 31:649–653.
Dvorak HF, Gresser I: Microvascular injury in pathogenesis of interferon-induced necrosis of subcutaneous tumors in mice. J Natl Cancer Inst 1989, 81:497–502.
Sato N, Nariuchi H, Tsuruoka N, et al.: Actions of TNF and IFN-gamma on angiogenesis in vitro. J Invest Dermatol 1990, 95:85S-89S.
Maheshwari RK, Srikantan V, Bhartiya D, et al.: Differential effects of interferon gamma and alpha on in vitro model of angiogenesis. J Cell Physiol 1991, 146:164–169.
Sinkovics JG: Kaposi’s sarcoma: its ‘oncogenes’ and growth factors. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol 1991, 11:87–107.
Sepp NT, Li LJ, Lee KH, et al.: Basic fibroblast growth factor increases expression of the alpha v beta 3 integrin complex on human microvascular endothelial cells. J Invest Dermatol 1994, 103:295–299.
Singh RK, Gutman M, Bucana CD, et al.: Interferons alpha and beta down-regulate the expression of basic fibroblast growth factor in human carcinomas. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 1995, 92:4562–4566.
Dinney CP, Bielenberg DR, Perrotte P, et al.: Inhibition of basic fibroblast growth factor expression, angiogenesis, and growth of human bladder carcinoma in mice by systemic interferon-alpha administration. Cancer Res 1998, 58:808–814. IFN suppressed bFGF expression in tumor cells, resulting in decreased tumor blood vessels.
Bielenberg DR, Bucana CD, Sanchez R, et al.: Molecular regulation of UVB-induced cutaneous angiogenesis. J Invest Dermatol 1998, 111:864–872.
Chang E, Boyd A, Nelson CC, et al.: Successful treatment of infantile hemangiomas with interferon-alpha-2b. J Pediatr Hematol Oncol 1997, 19:237–244.
Kaban LB, Mulliken JB, Ezekowitz RA, et al.: Antiangiogenic therapy of a recurrent giant cell tumor of the mandible with interferon alfa-2a. Pediatrics 1999, 103:1145–1149. IFN can induce complete regression of tumors other than hemangioblastomas.
Niemela M, Maenpaa H, Salven P, et al.: Interferon alpha-2a therapy in 18 hemangioblastomas. Clin Cancer Res 2001, 7:510–516.
Bielenberg DR, Bucana CD, Sanchez R, et al.: Progressive growth of infantile cutaneous hemangiomas is directly correlated with hyperplasia and angiogenesis of adjacent epidermis and inversely correlated with expression of the endogenous angiogenesis inhibitor, IFN-beta. Int J Oncol 1999, 14:401–408. In hemangiomas, VEGF is associated with tumor growth, whereas high IFN-β levels are associated with tumor regression.
Di Raimondo F, Palumbo GA, Molica S, Giustolisi R: Angiogenesis in chronic myeloproliferative diseases. Acta Haematol 2001, 106:177–183.
Gohji K, Fidler IJ, Tsan R, et al.: Human recombinant interferons-beta and -gamma decrease gelatinase production and invasion by human KG-2 renal-carcinoma cells. Int J Cancer 1994, 58:380–384.
Ma Z, Qin H, Benveniste EN: Transcriptional suppression of matrix metalloproteinase-9 gene expression by IFN-gamma and IFN-beta: critical role of STAT-1alpha. J Immunol 2001, 167:5150–5159.
Strieter RM, Kunkel SL, Elner VM, et al.: Interleukin-8: a corneal factor that induces neovascularization. Am J Pathol 1992, 141:1279–1284.
Koch AE, Polverini PJ, Kunkel SL, et al.: Interleukin-8 as a macrophage-derived mediator of angiogenesis. Science 1992, 258:1798–1801.
Singh RK, Gutman M, Llansa N, Fidler IJ: Interferon-beta prevents the upregulation of interleukin-8 expression in human melanoma cells. J Interferon Cytokine Res 1996, 16:577–584.
Folkman J: Seminars in Medicine of the Beth Israel Hospital, Boston: Clinical applications of research on angiogenesis. N Engl J Med 1995, 333:1757–1763.
Relf M, LeJeune S, Scott PA, et al.: Expression of the angiogenic factors vascular endothelial cell growth factor, acidic and basic fibroblast growth factor, tumor growth factor beta-1, platelet-derived endothelial cell growth factor, placenta growth factor, and pleiotrophin in human primary breast cancer and its relation to angiogenesis. Cancer Res 1997, 57:963–969.
Mayer-Ezell R, Tichauer M, Terracina G, et al.: Angiogenic factor levels in human tumor xenografts [abstract]. Proc Am Soc Cancer Res 2002, 43:25.
Uchida K, Takahashi A, Miyao N, et al.: Juvenile hemangioma of the testis: analysis of expression of angiogenic factors. Urology 1997, 49:285–286.
Gagliardi A, Collins DC: Inhibition of angiogenesis by antiestrogens. Cancer Res 1993, 53:533–535.
Blackwell KL, Haroon ZA, Shan S, et al.: Tamoxifen inhibits angiogenesis in estrogen receptor-negative animal models. Clin Cancer Res 2000, 6:4359–4364.
Lindner DJ, Borden EC: Effects of tamoxifen and interferonbeta or the combination on tumor-induced angiogenesis. Int J Cancer 1997, 71:456–461.
Minischetti M, Vacca A, Ribatti D, et al.: TNP-470 and recombinant human interferon-alpha2a inhibit angiogenesis synergistically. Br J Haematol 2000, 109:829–837. IFNs have synergistic antiangiogenic activity when combined with other agents.
Parangi S, O`Reilly M, Christofori G, et al.: Antiangiogenic therapy of transgenic mice impairs de novo tumor growth. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 1996, 93:2002–2007.
Albini A, Marchisone C, Del Grosso F, et al.: Inhibition of angiogenesis and vascular tumor growth by interferonproducing cells: a gene therapy approach. Am J Pathol 2000, 156:1381–1393.
Slaton JW, Perrotte P, Inoue K, et al.: Interferon-alphamediated down-regulation of angiogenesis-related genes and therapy of bladder cancer are dependent on optimization of biological dose and schedule. Clin Cancer Res 1999, 5:2726–2734. Raises the important question of what is the optimal antiangiogenic dose of IFN.
Singh RK, Bucana CD, Gutman M, et al.: Organ site-dependent expression of basic fibroblast growth factor in human renal cell carcinoma cells. Am J Pathol 1994, 145:365–374.
Gutman M, Singh RK, Xie K, et al.: Regulation of interleukin-8 expression in human melanoma cells by the organ environment. Cancer Res 1995, 55:2470–2475.
Lyden D, Hattori K, Dias S, et al.: Impaired recruitment of bone-marrow-derived endothelial and hematopoietic precursor cells blocks tumor angiogenesis and growth. Nat Med 2001, 7:1194–1201. Stem cell precursors are an important component of neo-vessel formation within growing tumors.
Borden EC: Interferons. In Cancer Medicine. Edited by Holland JF, Frei EF III, Bast RC, et al. Baltimore: Williams & Wilkins; 1997:1199–1212.
Cao G, Su J, Lu W, et al.: Adenovirus-mediated interferon-beta gene therapy suppresses growth and metastasis of human prostate cancer in nude mice. Cancer Gene Ther 2001, 8:497–505. Production of IFN-β embedded by a plasmid trans gene may be an effective method to block tumor angiogenesis.
Bostrom PJ, Uotila P, Rajala P, et al.: Interferon-alpha inhibits cyclooxygenase-1 and stimulates cyclooxygenase-2 expression in bladder cancer cells in vitro. Urol Res 2001, 29:20–24.
Regulier E, Paul S, Marigliano M, et al.: Adenovirus-mediated delivery of antiangiogenic genes as an antitumor approach. Cancer Gene Ther 2001, 8:45–54.
Arenberg DA, White ES, Burdick MD, et al.: Improved survival in tumor-bearing SCID mice treated with interferon-gammainducible protein 10 (IP-10/CXCL10). Cancer Immunol Immunother 2001, 50:533–538. One role of the IFN-stimulated gene IP-10 appears to be inhibition of angiogenesis in a human non-small-cell lung cancer model.
Feldman AL, Friedl J, Lans TE, et al.: Retroviral gene transfer of interferon-inducible protein 10 inhibits growth of human melanoma xenografts. Int J Cancer 2002, 99:149–153.
Wen Y, Yan DH, Wang B, et al.: p202, an interferon-inducible protein, mediates multiple antitumor activities in human pancreatic cancer xenograft models. Cancer Res 2001, 61:7142–7147.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lindner, D.J. Interferons as antiangiogenic agents. Curr Oncol Rep 4, 510–514 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11912-002-0065-4
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11912-002-0065-4