Abstract
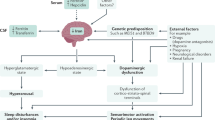
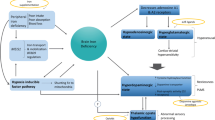
This update on restless legs syndrome (RLS) focuses on its pathophysiology, genetics, health impact, and treatment. Although symptoms are exquisitely responsive to dopaminergics, clear delineation of dopaminergic pathology has not emerged. Rather, heuristic models of alterations in spinal sensorimotor circuits and central nervous system iron deficiency are gaining more attention. Genome-wide association studies have recently identified polymorphisms in three genes with no obvious relationship to dopamine that account for 70% of the population risk for RLS. A single variant in the BTBD9 gene on chromosome 6 contributes to 50% of the population risk. Although the functions of BTBD9 remain uncertain, its biological plausibility is evidenced by its dose-dependent relationship to periodic limb movements of sleep, decrements in iron stores, and ethnic differences in RLS prevalence. RLS is also implicated in cardiovascular morbidity. Despite these advances in our knowledge, there remain unanswered questions about the pathophysiology of RLS as well as its genetics, health-related significance, and treatment.
Similar content being viewed by others
References and Recommended Reading
Stefansson H, Rye DB, Hicks A, et al.: a genetic risk factor for periodic limb movements in sleep. N Engl J Med 2007, 357:639–647.
Allen RP, Walters AS, Montplaisir J, et al.: Restless legs syndrome prevalence and impact: REST general population study. Arch Intern Med 2005, 165:1286–1292.
O’Keeffe ST, Egan D, Myers A, Redmond S: The frequency and impact of restless legs syndrome in primary care. Ir Med J 2007, 100:539–542.
Winkelman JW, Finn L, Young T: Prevalence and correlates of restless legs syndrome symptoms in the Wisconsin Sleep Cohort. Sleep Med 2006, 7:545–552.
Picchietti D, Allen RP, Walters AS, et al.: Restless legs syndrome: prevalence and impact in children and adolescents—the Peds REST study. Pediatrics 2007, 120:253–266.
Nichols DA, Allen RP, Grauke JH, et al.: Restless legs syndrome symptoms in primary care: a prevalence study. Arch Intern Med 2003, 163:2323–2329.
Earley CJ, Allen RP, Beard JL, et al.: Insight into the pathophysiology of restless legs syndrome. J Neurosci Res 2000, 62:623–628.
Winkelman J, Chertow G, Lazarus J: Restless legs syndrome in end-stage renal disease. Am J Kidney Dis 1996, 28:372–378.
Hening WA, Caivano CK: Restless legs syndrome: a common disorder in patients with rheumatologic conditions. Semin Arthritis Rheum 2007 Oct 29 (Epub ahead of print).
Merlino G, Fratticci L, Valente M, et al.: Association of restless legs syndrome in Type 2 diabetes. Sleep 2007, 30:866–871.
Gomez-Esteban JC, Zarranz JJ, Tijero B, et al.: Restless legs syndrome in Parkinson’s disease. Mov Disord 2007, 22:1912–1916.
Trotti LM, Rye DB: Functional anatomy and treatment of RLS/PLMS emerging after spinal cord lesions [abstract]. Sleep 2007, 30:A306.
Gemignani F, Marbini A, Di Giovanni G, et al.: Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease type 2 with restless legs syndrome. Neurology 1999, 52:1064–1066.
Abele M, Burk K, Laccone F, et al.: Restless legs syndrome in spinocerebellar ataxia types 1, 2, and 3. J Neurol 2001, 248:311–314.
Manconi M, Fabbrini M, Bonanni E, et al.: High prevalence of restless legs syndrome in multiple sclerosis. Eur J Neurol 2007, 14:534–539.
Akpinar S: Restless legs syndrome treatment with dopaminergic drugs. Clin Neuropharmacol 1987, 10:69–79.
Connor JR, Boyer PJ, Menzies SL, et al.: Neuropathological examination suggests impaired brain iron acquisition in restless legs syndrome. Neurology 2003, 61:304–309.
Wetter TC, Eisensehr I, Trenkwalder C: Functional neuroimaging studies in restless legs syndrome. Sleep Med 2004, 5:401–406.
Godau J, Wevers AK, Gaenslen A, et al.: Sonographic abnormalities of brainstem structures in restless legs syndrome. Sleep Med 2007 Nov 15 (Epub ahead of print).
Schmidauer C, Sojer M, Seppi K, et al.: Transcranial ultrasound shows nigral hypoechogenicity in restless legs syndrome. Ann Neurol 2005, 58:630–634.
Winkelmann J, Polo O, Provini F, et al.: Genetics of restless legs syndrome (RLS): state-of-the-art and future directions. Mov Disord 2007, 22:S449–S458.
Desautels A, Turecki G, Montplaisir J, et al.: Evidence for a genetic association between monoamine oxidase A and restless legs syndrome. Neurology 2002, 59:215–219.
Rye DB, Freeman AA: Dopamine in behavioral state control. In Neurochemistry of Sleep and Wakefulness. Edited by Monti JM, Pandi-Perumal SR, Sinton CM. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press; 2008:79–221.
Garcia-Borreguero D, Larrosa D, Granizo JJ, et al.: Circadian variation in neuroendocrine response to 1-dopa in patients with restless legs syndrome. Sleep 2004, 27:669–673.
Happe S, Bachmann CG, Helmschmied K, et al.: Growth hormone response to low-dose apomorphine in restless legs syndrome. Growth Horm IGF Res 2007, 17:323–327.
Earley CJ, Hyland K, Allen RP: Circadian changes in CSF dopaminergic measures in restless legs syndrome. Sleep Med 2006, 7:263–268.
Clemens S, Rye DB, Hochmann S: Restless legs syndrome: revisiting the dopamine hypothesis from the spinal cord perspective. Neurology 2006, 67:125–130.
Bara-Jimenez W, Aksu M, Graham B, et al.: Periodic limb movements in sleep: state-dependent excitability of the spinal flexor reflex. Neurology 2000, 54:1609–1616.
Hogl B, Frauscher B, Seppi K, et al.: Transient restless legs syndrome after spinal anesthesia. Neurology 2002, 59:1705–1707.
Qu S, Le W, Zhang X, et al.: Locomotion is increased in A11-lesioned mice with iron deprivations: a possible animal model for restless legs syndrome. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 2007, 66:383–388.
Trenkwalder C, Hogl B, Benes H, Kohnen R: Augmentation in restless legs syndrome is associated with low ferritin. Sleep Med 2007 Oct 5 (Epub ahead of print).
Erikson KM, Jones BC, Hess EJ, et al.: Iron deficiency decreases dopamine D1 and D2 receptors in the rat brain. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 2001, 69:409–418.
Desai AV, Cherkas LF, Spector TD, Williams AJ: Genetic influences in self-reported symptoms of obstructive sleep apnoea and restless legs: a twin study. Twin Res 2004, 7:589–595.
Ondo WG, Vuong KD, Wang Q: Restless legs syndrome in monozygotic twins: clinical correlates. Neurology 2000, 55:1404–1406.
Chen S, Ondo WG, Rao S, et al.: Genomewide linkage scan identifies a novel susceptibility locus for restless legs syndrome on chromosome 9p. Am J Hum Genet 2004, 74:876–885.
Pichler I, Hicks AA, Pramstaller PP: Restless legs syndrome: an update on genetics and future perspectives. Clin Genet 2008, 73:297–305
Winkelmann J, Schormair B, Lichtner P, et al.: Genome-wide association study of restless legs syndrome identifies common variants in three genomic regions. Nat Genet 2007, 39:1000–1006.
Winkelman JW: Periodic limb movements in sleep—endophenotype for restless legs syndrome? N Engl J Med 2007, 357:703–705.
Kushida C, Martin M, Nikam P, et al.: Burden of restless legs syndrome on health-related quality of life. Qual Life Res 2007, 16:617–624.
Benz RL, Pressman MR, Hovick ET, Peterson DD: Potential novel predictors of mortality in end-stage renal disease patients with sleep disorders. Am J Kidney Dis 2000, 35:1221–1223.
Winkelman JW, Shahar E, Sharief I, Gottlieb DJ.: Association of restless legs syndrome and cardiovascular disease in the Sleep Heart Health Study. Neurology 2008, 70:35–42.
Billars L, Hicks A, Bliwise D, et al.: Hypertension risk and PLMS in restless legs syndrome [abstract]. Sleep 2007, 30:A297–A298.
Littner MR, Kushida C, Anderson WM, et al.: Practice parameters for the dopaminergic treatment of restless legs syndrome and periodic limb movement disorder. Sleep 2004, 27:557–559.
Happe S, Trenkwalder C: Role of dopamine receptor agonists in the treatment of restless legs syndrome. CNS Drugs 2004, 18:27–36.
Driver-Dunckley ED, Noble BN, Hentz JG, et al.: Gambling and increased sexual desire with dopaminergic medications in restless legs syndrome. Clin Neuropharmacol 2007, 30:249–255.
Garcia-Borreguero D, Allen RP, Kohnen R, et al.: Diagnostic standards for dopaminergic augmentation of restless legs syndrome. Sleep Med 2007, 8:520–530.
Earley CJ, Allen RP: Restless legs syndrome augmentation associated with tramadol. Sleep Med 2006, 7:592–593.
Garcia-Borreguero D, Allen RP, Benes H, et al.: Augmentation as a treatment complication of restless legs syndrome: concept and management. Mov Disord 2007, 22(Suppl 18):S476–S484.
Bartell S, Zallek S: Intravenous magnesium sulfate may relieve restless legs syndrome in pregnancy. J Clin Sleep Med 2006, 2:187–188.
Pennestri MH, Montplaisir J, Colombo R, et al.: Nocturnal blood pressure changes in patients with restless legs syndrome. Neurology 2007, 68:1213–1218.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Trotti, L.M., Bhadriraju, S. & Rye, D.B. An update on the pathophysiology and genetics of restless legs syndrome. Curr Neurol Neurosci Rep 8, 281–287 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11910-008-0044-8
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11910-008-0044-8