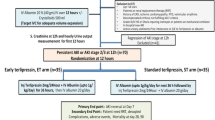
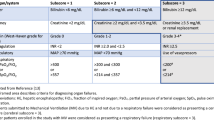
Abstract
Liver support systems aim to provide temporary support of liver function while maintaining extra-hepatic function in patients with liver failure. Important advances have been achieved in the design of artificial and bio-artificial devices, but the current systems are far from meeting the ideal. Artificial devices provide detoxification through different dialysis procedures, whereas bio-artificial devices add synthetic functions by incorporating a cellular component into the system. Overall, liver support systems have consistently shown beneficial effects on the pathophysiology of liver failure, especially in acute-on-chronic liver failure. However, these beneficial effects have not been translated into an improvement of survival. Our review discusses the current evidence, paying special attention to the clinical aspects of (bio)-artificial liver support devices.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Papers of particular interest, published recently, have been highlighted as: • Of importance •• Of major importance
Kim WR, Brown Jr RS, Terrault NA, El-Serag H. Burden of liver disease in the United States: summary of a workshop. Hepatology. 2002;36:227–42.
Palmes D, Skawran S, Spiegel HU. Acute liver failure: from bench to bedside. Transplant Proc. 2005;37:1628–31.
Palmes D, Qayumi AK, Spiegel HU. Liver bridging techniques in the treatment of acute liver failure. J Invest Surg. 2000;13:299–311.
Rajvanshi P, Larson AM, Kowdley KV. Temporary support for acute liver failure. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2002;35:335–44.
Allen JW, Hassanein T, Bhatia SN. Advances in bioartificial liver devices. Hepatology. 2001;34:447–55.
• Carpentier B, Gautier A, Legallais C. Artificial and bioartificial liver devices: present and future. Gut 2009;58:1690–1702. In this article, the rationale and technical features of different ALS devices are extensively reviewed.
Millis J, Kramer D, O’Grady J. Results of phase I trial of the extracorporeal liver assist device in acute liver failure. Am J Transplant. 2001;1:391.
Ellis AJ, Hughes RD, Wendon JA, et al. Pilot-controlled trial of the extracorporeal liver assist device in acute liver failure. Hepatology. 1996;24:1446–51.
Demetriou AA, Brown Jr RS, Busuttil RW, et al. Prospective, randomized, multicenter, controlled trial of a bioartificial liver in treating acute liver failure. Ann Surg. 2004;239:660–7. discussion 667–670.
Jalan R, Williams R. Bio-artificial liver support for acute liver failure: should we be using it to treat patients? Transplantation. 2002;73:165–6.
Faybik P, Hetz H, Baker A, et al. Extracorporeal albumin dialysis in patients with Amanita phalloides poisoning. Liver Int. 2003;23 Suppl 3:28–33.
Felldin M, Friman S, Backman L, et al. Treatment with the molecular adsorbent recirculating system in patients with acute liver failure. Transplant Proc. 2003;35:822–3.
Guo LM, Liu JY, Xu DZ, Li BS, et al. Application of molecular adsorbents recirculating system to remove NO and cytokines in severe liver failure patients with multiple organ dysfunction syndrome. Liver Int. 2003;23 Suppl 3:16–20.
Isoniemi H. Current Indications for Albumin Dialysis: Acute Hepatic Failure. 4th International Symposium on Albumin Dialysis in Liver Disease, Rostock- Warnemunde, September 2002.
Novelli G, Rossi M, Pretagostini R, et al. A 3-year experience with molecular adsorbent recirculating system (MARS): our results on 63 patients with hepatic failure and color Doppler US evaluation of cerebral perfusion. Liver Int. 2003;23 Suppl 3:10–5.
Schmidt LE, Wang LP, Hansen BA, Larsen FS. Systemic hemodynamic effects of treatment with the molecular adsorbents recirculating system in patients with hyperacute liver failure: a prospective controlled trial. Liver Transpl. 2003;9:290–7.
Saliba F, Camus C, Durand F, et al. Randomized controlled multicenter trial evaluating the efficacy and safety of albumin dialysis with MARS in patients with fulminant and subfulminant hepatic failure. Hepatology. 2008;48:LB4.
Kantola T, Maklin S, Koivusalo AM, et al. Cost-utility of molecular adsorbent recirculating system treatment in acute liver failure. World J Gastroenterol. 2010;16:2227–34.
Mitzner SR, Stange J, Klammt S, et al. Improvement of hepatorenal syndrome with extracorporeal albumin dialysis MARS: results of a prospective, randomized, controlled clinical trial. Liver Transpl. 2000;6:277–86.
Wong F, Raina N, Richardson R. Molecular adsorbent recirculating system is ineffective in the management of type 1 hepatorenal syndrome in patients with cirrhosis with ascites who have failed vasoconstrictor treatment. Gut. 2010;59:381–6.
Heemann U, Treichel U, Loock J, et al. Albumin dialysis in cirrhosis with superimposed acute liver injury: a prospective, controlled study. Hepatology. 2002;36:949–58.
Hassanein TI, Tofteng F, Brown Jr RS, et al. Randomized controlled study of extracorporeal albumin dialysis for hepatic encephalopathy in advanced cirrhosis. Hepatology. 2007;46:1853–62.
Ferenci P, Kramer L. MARS and the failing liver-Any help from the outer space? Hepatology. 2007;46:1682–4.
•• Banares R, Nevens F, Larsen FS, et al. Extracorporeal albumin dialysis with the molecular adsorbent recirculating system in acute-on-chronic liver failure: The RELIEF trial. Hepatology 2012 (Epub ahead of print). Large randomized clinical trial comparing albumin dialysis (MARS device) plus SMT versus SMT alone in patients with acutely decompensated cirrhosis.
•• Kribben A, Gerken G, Haag S, et al. Effects of fractionated plasma separation and adsorption on survival in patients with acute-on-chronic liver failure. Gastroenterology 2012;142:782–789. Large randomized clinical trial comparing FPSA (Prometheus device) plus SMT versus SMT alone in patients with acutely decompensated cirrhosis.
•• Stutchfield BM, Simpson K, Wigmore SJ. Systematic review and meta-analysis of survival following extracorporeal liver support. Br J Surg 2011;98:623–631. Systematic review with meta-analysis of the use of ALS in patients with ALF and ACLF.
• Baptista PM, Siddiqui MM, Lozier G, et al. The use of whole organ decellularization for the generation of a vascularized liver organoid. Hepatology 2011;53:604–617. This paper provides information about the generation of biological decellularized matrix in small animal as scaffolds able to be recellularized.
Kantola T, Koivusalo AM, Parmanen S, Hockerstedt K, Isoniemi H. Survival predictors in patients treated with a molecular adsorbent recirculating system. World J Gastroenterol. 2009;15:3015–24.
Matsubara S, Okabe K, Ouchi K, et al. Continuous removal of middle molecules by hemofiltration in patients with acute liver failure. Crit Care Med. 1990;18:1331–8.
Agarwal R, Farber MO. Is continuous veno-venous hemofiltration for acetaminophen-induced acute liver and renal failure worthwhile? Clin Nephrol. 2002;57:167–70.
Clemmesen JO, Kondrup J, Nielsen LB, Larsen FS, Ott P. Effects of high-volume plasmapheresis on ammonia, urea, and amino acids in patients with acute liver failure. Am J Gastroenterol. 2001;96:1217–23.
Sadamori H, Yagi T, Inagaki M, et al. High-flow-rate haemodiafiltration as a brain-support therapy proceeding to liver transplantation for hyperacute fulminant hepatic failure. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2002;14:435–9.
Mori T, Eguchi Y, Shimizu T, et al. A case of acute hepatic insufficiency treated with novel plasmapheresis plasma diafiltration for bridge use until liver transplantation. Ther Apher. 2002;6:463–6.
O'Grady JG, Gimson AE, O'Brien CJ, et al. Controlled trials of charcoal hemoperfusion and prognostic factors in fulminant hepatic failure. Gastroenterology. 1988;94:1186–92.
Ash SR. Hemodiabsorption in treatment of acute hepatic failure and chronic cirrhosis with ascites. Artif Organs. 1994;18:355–62.
Stange J, Hassanein TI, Mehta R, Mitzner SR, Bartlett RH. The molecular adsorbents recycling system as a liver support system based on albumin dialysis: a summary of preclinical investigations, prospective, randomized, controlled clinical trial, and clinical experience from 19 centers. Artif Organs. 2002;26:103–10.
Evenepoel P, Laleman W, Wilmer A, et al. Detoxifying capacity and kinetics of prometheus–a new extracorporeal system for the treatment of liver failure. Blood Purif. 2005;23:349–58.
Rifai K, Ernst T, Kretschmer U, Haller H, Manns MP, Fliser D. Removal selectivity of Prometheus: a new extracorporeal liver support device. World J Gastroenterol. 2006;12:940–4.
Lanjuan L, Qian Y, Jianrong H, et al. Severe hepatitis treated with an artificial liver support system. Int J Artif Organs. 2001;24:297–303.
Ash SR. Extracorporeal blood detoxification by sorbents in treatment of hepatic encephalopathy. Adv Ren Replace Ther. 2002;9:3–18.
Sen S, Davies NA, Mookerjee RP, et al. Pathophysiological effects of albumin dialysis in acute-on-chronic liver failure: a randomized controlled study. Liver Transpl. 2004;10:1109–19.
El Banayosy A, Kizner L, Schueler V, et al. First use of the molecular adsorbent recirculating system technique on patients with hypoxic liver failure after cardiogenic shock. ASAIO J. 2004;50:332–7.
Laleman W, Wilmer A, Evenepoel P, et al. Effect of the molecular adsorbent recirculating system and Prometheus devices on systemic haemodynamics and vasoactive agents in patients with acute-on-chronic alcoholic liver failure. Crit Care. 2006;10:R108.
Dethloff T, Tofteng F, Frederiksen HJ, et al. Effect of Prometheus liver assist system on systemic hemodynamics in patients with cirrhosis: a randomized controlled study. World J Gastroenterol. 2008;14:2065–71.
Disclosure
Rafael Bañares has received consultant honoraries from Gambro. No potential conflicts of interest relevant to this article were reported for María-Vega Catalina and Javier Vaquero.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This article is part of the Topical Collection on Liver
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bañares, R., Catalina, MV. & Vaquero, J. Liver Support Systems: Will They Ever Reach Prime Time?. Curr Gastroenterol Rep 15, 312 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11894-013-0312-x
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11894-013-0312-x