Abstract
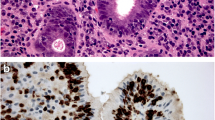
High-grade dysplasia is the last stage before the development of adenocarcinoma. Despite the fact that the lesion is not yet invasive, it has tremendous potential to become malignant. The approach to the disease has clinicians divided between immediate intervention with surgical resection or continued endoscopic surveillance proof of the unclear natural history. Much knowledge has been acquired recently regarding application of surveillance and outcomes of esophageal resection. Also, many endoscopic techniques for treating high-grade dysplasia have been studied in depth. Results on their safety, efficacy, and complication rates have recently become available. This review analyzes the progress in the understanding and treatment of high-grade dysplasia during the past 24 to 36 months and examines how this new information plays a role in the disease’s treatment algorithm.
Similar content being viewed by others
References and Recommended Reading
Wu PC, Posner MC: The role of surgery in the management of esophageal cancer. Lancet Oncol 2003, 4:481–488.
Falk GW: Barrett’s esophagus. Gastroenterology 2002, 122:1569–1591.
Spechler SJ: Clinical practice. Barrett’s esophagus. N Engl J Med 2002, 346:836–842.
Flejou JF, Svrcek M: Barrett’s oesophagus—a pathologist’s view. Histopathology 2007, 50:3–14.
Weston AP, Sharma P, Topalovski M, et al.: Long-term follow-up of Barrett’s high-grade dysplasia. Am J Gastroenterol 2000, 95:1888–1893.
Reid BJ, Blount PL, Feng Z, Levine DS: Optimizing endoscopic biopsy detection of early cancers in Barrett’s high-grade dysplasia. Am J Gastroenterol 2000, 95:3089–3096.
Altorki NK, Skinner DB: Adenocarcinoma in Barrett’s esophagus. Semin Surg Oncol 1990, 6:274–278.
Riddell RH, Goldman H, Ransohoff DF, et al.: Dysplasia in inflammatory bowel disease: standardized classification with provisional clinical applications. Hum Pathol 1983, 14:931–968.
Geboes K, Van Eyken P: The diagnosis of dysplasia and malignancy in Barrett’s osophagus. Histopathology 2000, 37:99–107.
Overholt BF, Lightdale CJ, Wang KK, et al.: Photodynamic therapy with porfimer sodium for ablation of high-grade dysplasia in Barrett’s esophagus: international, partially blinded, randomized phase III trial. Gastrointest Endosc 2005, 62:488–498.
Ormsby AH, Petras RE, Henricks WH, et al.: Observer variation in the diagnosis of superficial oesophageal adenocarcinoma. Gut 2002, 51:671–676.
Weston AP, Krmpotich PT, Cherian R, et al.: Prospective long-term endoscopic and histological follow-up of short segment Barrett’s esophagus: comparison with traditional long segment Barrett’s esophagus. Am J Gastroenterol 1997, 92:407–413.
Weston AP, Sharma P, Mathur S, et al.: Risk stratification of Barrett’s esophagus: updated prospective multivariate analysis. Am J Gastroenterol 2004, 99:1657–1666.
Avidan B, Sonnenberg A, Schnell TG, et al.: Hiatal hernia size, Barrett’s length, and severity of acid reflux are all risk factors for esophageal adenocarcinoma. Am J Gastroenterol 2002, 97:1930–1936.
Buttar NS, Wang KK, Sebo TJ, et al.: Extent of high-grade dysplasia in Barrett’s esophagus correlates with risk of adenocarcinoma. Gastroenterology 2001, 120:1630–1639.
Tharavej C, Hagen JA, Peters JH, et al.: Predictive factors of coexisting cancer in Barrett’s high-grade dysplasia. Surg Endosc 2006, 20:439–443.
Chow WH, Blaser MJ, Blot WJ, et al.: An inverse relation between cagA+ strains of Helicobacter pylori infection and risk of esophageal and gastric cardia adenocarcinoma. Cancer Res 1998, 58:588–590.
Reid BJ, Levine DS, Longton G, et al.: Predictors of progression to cancer in Barrett’s esophagus: baseline histology and flow cytometry identify low-and high-risk patient subsets. Am J Gastroenterol 2000, 95:1669–1676.
Levine DS, Haggitt RC, Blount PL, et al.: An endoscopic biopsy protocol can differentiate high grade dysplasia from early adenocarcinoma in Barrett’s esophagus. Gastroenterology 1993, 105:40–50.
Sampliner RE; Practice Parameters Committee of the American College of Gastroenterology: Updated guidelines for the diagnosis, surveillance, and therapy of Barrett’s esophagus. Am J Gastroenterol 2002, 97:1888–1895.
Tytgat GN, Bartelink H, Bernards R, et al.: Cancer of the esophagus and gastric cardia: recent advances. Dis Esophagus 2004, 17:10–26.
Jamieson GG, Mathew G, Ludemann R, et al.: Postoperative mortality following oesophagectomy and problems in reporting its rate. Br J Surg 2004, 91:943–947.
Bailey SH, Bull DA, Harpole DH, et al.: Outcomes after esophagectomy: a ten-year prospective cohort. Ann Thorac Surg 2003, 75:217–222.
Williams VA, Watson TJ, Herbella FA, et al.: Esophagectomy for high grade dysplasia is safe, curative, and results in good alimentary outcome. J Gastrointest Surg 2007, 11:1589–1597.
Patti MG, Corvera CU, Glasgow RE, Way LW: A hospital’s annual rate of esophagectomy influences the operative mortality rate. J Gastrointest Surg 1998, 2:186–192.
Swisher SG, Deford L, Merriman KW, et al.: Effect of operative volume on morbidity, mortality, and hospital use after esophagectomy for cancer. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 2000, 119:1126–1132.
Chang LC, Oelschlager BK, Quiroga E, et al.: Long-term outcome of esophagectomy for high-grade dysplasia or cancer found during surveillance for Barrett’s esophagus. J Gastrointest Surg 2006, 10:341–346.
Smithers BM, Gotley DC, Martin I, Thomas JM: Comparison of outcomes between open and minimally invasive esophagectomy. Ann Surg 2007, 245:232–240.
Braghetto I, Csendes A, Cardemil G, et al.: Open transthoracic or transhiatal esophagectomy versus minimally invasive esophagectomy in terms of morbidity, mortality and survival. Surg Endosc 2006, 20:1681–1686.
Peyre CG, DeMeester SR, Rizzetto C, et al.: Vagal-sparing esophagectomy. The ideal operation for intramucosal adenocarcinoma and Barrett with high-grade dysplasia. Ann Surg 2007, 246:665–674.
Feith M, Stein HJ, Siewert JR: Pattern of lymphatic spread of Barrett’s cancer. World J Surg 2003, 27:1052–1057.
Seewald S, Ang TL, Soehendra N: Endoscopic mucosal resection of Barrett’s oesophagus containing dysplasia or intramucosal cancer. Postgrad Med J 2007, 83:367–372.
Ell C, May A, Gossner L, et al.: Endoscopic mucosal resection of early cancer and high grade dysplasia in Barrett’s esophagus. Gastroenterology 2000, 118:670–677.
May A, Gossner L, Pech O, et al.: Local endoscopic therapy for intraepithelial high grade neoplasia and early adenocarcinoma in Barrett’s esophagus: acute phase and intermediate results of a new treatment approach. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol 2002, 14:1085–1091.
Conio M, Repici A, Cestari R, et al.: Endoscopic mucosal resection for high-grade dysplasia and intramucosal carcinoma in Barrett’s esophagus: an Italian experience. World J Gastroenterol 2005, 11:6650–6655.
Prasad GA, Buttar NS, Wongkeesong LM, et al.: Significance of neoplastic involvement of margins obtained by endoscopic mucosal resection in Barrett’s esophagus. Am J Gastroenterol 2007, 102:2380–2386.
Johnston MH, Eastone JA, Horwhat JD, et al.: Cryoablation of Barrett’s esophagus: a pilot study. Gastrointest Endosc 2005, 62:842–848.
Mino-Kenudson M, Ban S, Ohana M, et al.: Buried dysplasia and early adenocarcinoma arising in Barrett esophagus after porfimer-photodynamic therapy. Am J Surg Pathol 2007, 31:403–409.
Prasad GA, Wang KK, Buttar NS, et al.: Long-term survival following endoscopic and surgical treatment of high-grade dysplasia in Barrett’s esophagus. Gastroenterology 2007, 132:1226–1233.
Ganz RA, Utley DS, Stern RA, et al.: Complete ablation of esophageal epithelium with a balloon-based bipolar electrode: a phased evaluation in the porcine and in the human esophagus. Gastrointest Endosc 2004, 60:1002–1010.
Sharma VK, Wang KK, Overholt BF, et al.: Balloon-based, circumferential, endoscopic radiofrequency ablation of Barrett’s esophagus: 1-year follow-up of 100 patients. Gastrointest Endosc 2007, 65:185–195.
Roorda AK, Marcus SN, Triadafilopoulos G: Early experience with radiofrequency energy ablation therapy for Barrett’s esophagus with and without dysplasia. Dis Esophagus 2007, 20:516–522.
Smith CD, Bejarano PA, Melvin WS, et al.: Endoscopic ablation of intestinal metaplasia containing high-grade dysplasia in esophagectomy patients using a balloon-based ablation system. Surg Endosc 2007, 21:560–569.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Palazzo, F., Fisichella, P.M. & Patti, M.G. Management of high-grade dysplasia. Curr Gastroenterol Rep 10, 240–245 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11894-008-0050-7
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11894-008-0050-7