Abstract
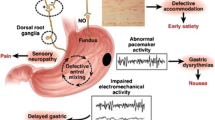
The worldwide epidemic of type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) is a substantial economic and social burden. Although gastroparesis associated with type 1 diabetes mellitus (T1DM) has been recognized for years, only recently have studies shown that patients with T2DM also have high rates of gastroparesis. Individuals with T2DM constitute 90% to 95% of the diabetic population. Unique characteristics that distinguish this population are obesity, insulin resistance, and associated comorbidities. These features highlight the importance of investigating gastric emptying in individuals with T2DM and upper gastrointestinal symptoms. The purpose of this review is to examine the literature pertaining to diabetes and the effect of diabetes on gastric neuromuscular function, with a focus on T2DM. An understanding of gastric motility in T2DM is important to diagnose gastroparesis, to treat upper gastrointestinal symptoms, and to restore normal gastric motility, which may lead, in turn, to improved glucose control.
Similar content being viewed by others
References and Recommended Reading
WHO Diabetes Fact Sheet http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs12/en/index.html Accessed February 6, 2007.
CDC: National Diabetes Fact Sheet http://www.cdc.gov/diabetes/pubs/estimates05.htm#top Accessed February 6, 2007.
Diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Care 2006, 29(Suppl 1):S43–S48.
Rundles R: Diabetic neuropathy: general review with report of 125 cases. Medicine 1945, 24:111–160.
Kassander P: Asymptomatic gastric retention in diabetics (gastroparesis diabeticorum). Ann Intern Med 1958, 48:797–812.
Wooten RL, Meriwether TW III: Diabetic gastric atony: a clinical study. JAMA 1961, 176:1082–1087.
Feldman M, Schiller LR: Disorders of gastrointestinal motility associated with diabetes mellitus. Ann Intern Med 1983, 98:378–384.
Schvarcz E, Palmer M, Ingberg CM et al.: Increased prevalence of upper gastrointestinal symptoms in long-term type 1 diabetes mellitus. Diabet Med 1996, 13:478–481.
Maleki D, Locke GR III, Camilleri M, et al.: Gastrointestinal tract symptoms among persons with diabetes mellitus in the community. Arch Intern Med 2000, 160:2808–2816.
Janatuinen E, Pikkarainen P, Laakso M, Pyorala K: Gastrointestinal symptoms in middle-aged diabetic patients. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1993, 28:427–432.
Bytzer P, Talley NJ, Leemon M, et al.: Prevalence of gastrointestinal symptoms associated with diabetes mellitus: a population-based survey of 15,000 adults. Arch Intern Med 2001, 161:1989–1996.
Enck P, Rathmann W, Spiekermann M, et al.: Prevalence of gastrointestinal symptoms in diabetic patients and non-diabetic subjects. Z Gastroenterol 1994, 32:637–641.
Ko GT, Chan WB, Chan JC, et al.: Gastrointestinal symptoms in Chinese patients with Type 2 diabetes mellitus. Diabet Med 1999, 16:670–674.
Spangeus A, El-Salhy M, Suhr O, et al.: Prevalence of gastrointestinal symptoms in young and middle-aged diabetic patients. Scand J Gastroenterol 1999, 34:1196–1202.
Ricci JA, Siddique R, Stewart WF, et al.: Upper gastrointestinal symptoms in a U.S. national sample of adults with diabetes. Scand J Gastroenterol 2000, 35:152–159.
Leatherdale BA, Green DJ, Harding LK, et al.: Guar and gastric emptying in non-insulin dependent diabetes. Acta Diabetol Lat 1982, 19:339–343.
Sasaki H, Nagulesparan M, Dubois A, et al.: Hypergastrinemia in obese noninsulin-dependent diabetes: a possible reflection of high prevalence of vagal dysfunction. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 1983, 56:744–750.
Horowitz M, Harding PE, Maddox AF, et al.: Gastric and oesophageal emptying in patients with type 2 (non-insulin-dependent) diabetes mellitus. Diabetologia 1989, 32:151–159.
Chang CS, Kao CH, Wang YS, et al.: Discrepant pattern of solid and liquid gastric emptying in Chinese patients with type II diabetes mellitus. Nucl Med Commun 1996, 17:60–65.
Tung CF, Chang CS, Chen GH, et al.: Comprehensive gastric emptying study for type-II diabetes mellitus dyspeptic patients. Scand J Gastroenterol 1997, 32:884–887.
Annese V, Bassotti G, Caruso N, et al.: Gastrointestinal motor dysfunction, symptoms, and neuropathy in noninsulin-dependent (type 2) diabetes mellitus. J Clin Gastroenterol 1999, 29(2):171–177.
Moldovan C, Dumitrascu DL, Demian L, et al.: Gastroparesis in diabetes mellitus: an ultrasonographic study. Rom J Gastroenterol 2005, 14:19–22.
Aylett P: Gastric emptying and change of blood glucose level, as affected by glucagon and insulin. Clin Sci 1962, 22:171–178.
MacGregor IL, Gueller R, Watts HD, Meyer JH: The effect of acute hyperglycemia on gastric emptying in man. Gastroenterology 1976, 70:190–196.
Fraser RJ, Horowitz M, Maddox AF, et al.: Hyperglycaemia slows gastric emptying in type 1 (insulin-dependent) diabetes mellitus. Diabetologia. 1990, 33:675–680.
Schvarcz E, Palmer M, Aman J, et al.: Physiological hyperglycemia slows gastric emptying in normal subjects and patients with insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Gastroenterology 1997, 113:60–66.
Velchik MG, Reynolds JC, Alavi A: The effect of meal energy content on gastric emptying. J Nucl Med 1989, 30:1106–1110.
Jones KL, Horowitz M, Carney BI, et al.: Gastric emptying in early noninsulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. J Nucl Med 1996, 37:1643–1648.
Iber FL, Parveen S, Vandrunen M, et al.: Relation of symptoms to impaired stomach, small bowel, and colon motility in long-standing diabetes. Dig Dis Sci 1993, 38:45–50.
Chang CS, Lien HC, Yeh HZ, et al.: Effect of cisapride on gastric dysrhythmia and emptying of indigestible solids in type-II diabetic patients. Scand J Gastroenterol 1998, 33:600–604.
Koch KL, Stern RM, Stewart WR, Vasey MW: Gastric emptying and gastric myoelectrical activity in patients with diabetic gastroparesis: effect of long-term domperidone treatment. Am J Gastroenterol 1989, 84:1069–1075.
Horowitz M, O’Donovan D, Jones KL, et al.: Gastric emptying in diabetes: clinical significance and treatment. Diabet Med 2002, 19:177–194.
Zhao J, Frokjaer JB, Drewes AM, et al.: Upper gastrointestinal sensory-motor dysfunction in diabetes mellitus. World J Gastroenterol 2006, 12:2846–2857.
Bytzer P, Talley NJ, Hammer J, et al.: GI symptoms in diabetes mellitus are associated with both poor glycemic control and diabetic complications. Am J Gastroenterol 2002, 97:604–611.
Rathmann W, Enck P, Frieling T, Gries FA: Visceral afferent neuropathy in diabetic gastroparesis. Diabetes Care 1991, 14:1086–1089.
Buysschaert M, Moulart M, Urbain JL, et al.: Impaired gastric emptying in diabetic patients with cardiac autonomic neuropathy. Diabetes Care 1987, 10:448–452.
Migdalis L, Thomaides T, Chairopoulos C, et al.: Changes of gastric emptying rate and gastrin levels are early indicators of autonomic neuropathy in type II diabetic patients. Clin Auton Res 2001, 11:259–263.
Yoshida MM, Schuffler MD, Sumi SM: There are no morphologic abnormalities of the gastric wall or abdominal vagus in patients with diabetic gastroparesis. Gastroenterology 1988, 94:907–914.
Barnett JL, Owyang C: Serum glucose concentration as a modulator of interdigestive gastric motility. Gastroenterology 1988, 94:739–744.
Fraser R, Horowitz M, Dent J: Hyperglycaemia stimulates pyloric motility in normal subjects. Gut. 1991, 32(5):475–478.
Jebbink RJ, Samsom M, Bruijs PP, et al.: Hyperglycemia induces abnormalities of gastric myoelectrical activity in patients with type I diabetes mellitus. Gastroenterology 1994, 107:1390–1397.
Sogabe M, Okahisa T, Tsujigami K, et al.: Ultrasonographic assessment of gastric motility in diabetic gastroparesis before and after attaining glycemic control. J Gastroenterol 2005, 40:583–590.
Holzapfel A, Festa A, Stacher-Janotta G, et al.: Gastric emptying in type II (non-insulin-dependent) diabetes mellitus before and after therapy readjustment: no influence of actual blood glucose concentration. Diabetologia 1999, 42:1410–1412.
Smith U: Gastric emptying in type 2 diabetes: quick or slow? Diabet Med 1996, 13(Suppl 5):S31–S33.
Phillips WT, Schwartz JG, McMahan CA: Rapid gastric emptying of an oral glucose solution in type 2 diabetic patients. J Nucl Med 1992, 33:1496–1500.
Schwartz JG, Green GM, Guan D, et al.: Rapid gastric emptying of a solid pancake meal in type II diabetic patients. Diabetes Care 1996, 19:468–471.
Frank JW, Saslow SB, Camilleri M, et al.: Mechanism of accelerated gastric emptying of liquids and hyperglycemia in patients with type II diabetes mellitus. Gastroenterology 1995, 109:755–765.
Bertin E, Schneider N, Abdelli N, et al.: Gastric emptying is accelerated in obese type 2 diabetic patients without autonomic neuropathy. Diabetes Metab 2001, 27:357–364.
Weytjens C, Keymeulen B, Van Haleweyn C, et al.: Rapid gastric emptying of a liquid meal in long-term type 2 diabetes mellitus. Diabet Med 1998, 15:1022–1027.
Parkman HP, Hasler WL, Fisher RS: American Gastroenterological Association technical review on the diagnosis and treatment of gastroparesis. Gastroenterology 2004, 127:1592–1622.
Tougas G, Eaker EY, Abell TL, et al.: Assessment of gastric emptying using a low fat meal: establishment of international control values. Am J Gastroenterol 2000, 95:1456–1462.
Kuo B MR, Koch K, Chey WD, et al.: SmartPill, a novel ambulatory diagnostic test for measuring gastric emptying in health and disease [abstract]. Presented at Digestive Disease Week; Los Angeles, CA; May 20–25, 2006.
Koch KL: Electrogastrography: physiological basis and clinical application in diabetic gastropathy. Diabetes Technol Ther 2001, 3:51–62.
Abell TL, Bernstein VK, Cutts T, et al.: Treatment of gastroparesis: a multidisciplinary clinical review. Neurogastroenterol Motil 2006, 18:263–283.
Kong MF, Horowitz M: Gastric emptying in diabetes mellitus: relationship to blood-glucose control. Clin Geriatr Med 1999, 15:321–338.
Groop LC, Luzi L, DeFronzo RA, Melander A: Hyperglycaemia and absorption of sulphonylurea drugs. Lancet 1989, 2:129–130.
Schwartz JG, Guan D, Green GM, Phillips WT: Treatment with an oral proteinase inhibitor slows gastric emptying and acutely reduces glucose and insulin levels after a liquid meal in type II diabetic patients. Diabetes Care 1994, 17:255–262.
Phillips WT, Schwartz JG, McMahan CA: Reduced postprandial blood glucose levels in recently diagnosed non-insulin-dependent diabetics secondary to pharmacologically induced delayed gastric emptying. Dig Dis Sci 1993, 38:51–58.
Gonlachanvit S, Hsu CW, Boden GH, et al.: Effect of altering gastric emptying on postprandial plasma glucose concentrations following a physiologic meal in type-II diabetic patients. Dig Dis Sci 2003, 48:488–497.
Thompson RG, Gottlieb A, Organ K, et al.: Pramlintide: a human amylin analogue reduced postprandial plasma glucose, insulin, and C-peptide concentrations in patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabet Med 1997, 14:547–555.
Willms B, Werner J, Holst JJ, et al.: Gastric emptying, glucose responses, and insulin secretion after a liquid test meal: effects of exogenous glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1)-(7–36) amide in type 2 (noninsulin-dependent) diabetic patients. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 1996, 81:327–332.
Gentilcore D, Chaikomin R, Jones KL, et al.: Effects of fat on gastric emptying of and the glycemic, insulin, and incretin responses to a carbohydrate meal in type 2 diabetes. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2006, 91:2062–2067.
Monnier L, Lapinski H, Colette C: Contributions of fasting and postprandial plasma glucose increments to the overall diurnal hyperglycemia of type 2 diabetic patients: variations with increasing levels of HbA(1c). Diabetes Care 2003, 26:881–885.
Talley NJ: Diabetic gastropathy and prokinetics. Am J Gastroenterol 2003, 98:264–271.
Petrakis IE, Vrachassotakis N, Sciacca V, et al.: Hyperglycaemia attenuates erythromycin-induced acceleration of solid-phase gastric emptying in idiopathic and diabetic gastroparesis. Scand J Gastroenterol 1999, 34:396–403.
Ueno N, Inui A, Asakawa A, et al.: Erythromycin improves glycaemic control in patients with type II diabetes mellitus. Diabetologia 2000, 43:411–415.
Asakawa H, Hayashi I, Fukui T, Tokunaga K: Effect of mosapride on glycemic control and gastric emptying in type 2 diabetes mellitus patients with gastropathy. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 2003, 61:175–182.
Horowitz M, Jones KL, Harding PE, Wishart JM: Relationship between the effects of cisapride on gastric emptying and plasma glucose concentrations in diabetic gastroparesis. Digestion 2002, 65:41–46.
Lehmann R, Honegger RA, Feinle C, et al.: Glucose control is not improved by accelerating gastric emptying in patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus and gastroparesis, a pilot study with cisapride as a model drug. Exp Clin Endocrinol Diabetes 2003, 111:255–261.
Koch KL: Nausea and vomiting. In Therapy of Digestive Disorders. Edited by Wolfe MM. Philadelphia: WB Saunders Company; 2006:1003–1016.
van der Voort IR, Becker JC, Dietl KH, et al.: Gastric electrical stimulation results in improved metabolic control in diabetic patients suffering from gastroparesis. Exp Clin Endocrinol Diabetes. 2005, 113:38–42.
Rees DA, Alcolado JC: Animal models of diabetes mellitus. Diabet Med 2005, 22, 359–370.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Intagliata, N., Koch, K.L. Gastroparesis in type 2 diabetes mellitus: Prevalence, etiology, diagnosis, and treatment. Curr Gastroenterol Rep 9, 270–279 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11894-007-0030-3
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11894-007-0030-3