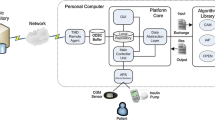
Abstract
Purpose of Review
The review summarizes the current state of the artificial pancreas (AP) systems and introduces various new modules that should be included in future AP systems.
Recent Findings
A fully automated AP must be able to detect and mitigate the effects of meals, exercise, stress and sleep on blood glucose concentrations. This can only be achieved by using a multivariable approach that leverages information from wearable devices that provide real-time streaming data about various physiological variables that indicate imminent changes in blood glucose concentrations caused by meals, exercise, stress and sleep.
Summary
The development of a fully automated AP will necessitate the design of multivariable and adaptive systems that use information from wearable devices in addition to glucose sensors and modify the models used in their model-predictive alarm and control systems to adapt to the changes in the metabolic state of the user. These AP systems will also integrate modules for controller performance assessment, fault detection and diagnosis, machine learning and classification to interpret various signals and achieve fault-tolerant control. Advances in wearable devices, computational power, and safe and secure communications are enabling the development of fully automated multivariable AP systems.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Papers of particular interest, published recently, have been highlighted as: • Of importance •• Of major importance
Albisser AM, Leibel BS, Ewart TG, Davidovac Z, Botz CK, Zingg W. An artificial endocrine pancreas. Diabetes. 1974;23:389–96.
Haidar A, Legault L, Messier V, Mitre TM, Leroux C, Rabasa-Lhoret R. Comparison of dual-hormone artificial pancreas, single-hormone artificial pancreas, and conventional insulin pump therapy for glycaemic control in patients with type 1 diabetes: an open-label randomised controlled crossover trial. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2015;3:17–26.
Thabit H, Tauschmann M, Allen JM, Leelarathna L, Hartnell S, Wilinska ME, et al. Home use of an artificial beta cell in type 1 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2015;373:2129–40.
• Bally L, Thabit H, Kojzar H, Mader JK, Qerimi-Hyseni J, Hartnell S, et al. Day-and-night glycaemic control with closed-loop insulin delivery versus conventional insulin pump therapy in free-living adults with well controlled type 1 diabetes: an open-label, randomised, crossover study. Lancet Diab Endocrinology. 2017;5:261–70. This study demonstrates the improvement of glycemic control with an AP over conventional insulin pump therapy.
Pinsker JE, Lee JB, Dassau E, Seborg, DE, Bradley PK, R. Gondhalekar, R, et al. Randomized crossover comparison of personalized MPC and PID control algorithms for the artificial pancreas. Diabetes Care, 2016; 39:1135–1142.
Dassau E, Brown SA, Basu A, Pinsker JE, Kudva YC, Gondhalekar R, et al. Multicenter outpatient randomized crossover trial of zone-MPC artificial pancreas in type 1 diabetes: effects of initialization strategies. Diabetes. 2015;64:A59–60.
Brown SA, Breton MD, Anderson S, Kollar L, Levy C, Lam D, et al. Artificial pancreas improves glycemic control in a multi-night multicenter outpatient/home study of patients with T1D. Diabetes. 2015;64:A59.
Renard E, Farret A, Kropff J, Bruttomesso D, Messori M, Place J, et al. Day and night closed-loop glucose control in patients with type 1 diabetes under free-living conditions: results of a single-arm 1-month experience compared with a previously reported feasibility study of evening and night at home. Diabetes Care. 2016;39:1151–60.
Kropff J, Del Favero S, Place J, Toffanin C, Visentin R, Monaro M, et al. 2 month evening and night closed-loop glucose control in patients with type 1 diabetes under free-living conditions: a randomised crossover trial. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2015;3:939–47.
Reddy M, Herrero P, El Sharkawy M, Pesl P, Jugnee N, Pavitt D, et al. Metabolic control with the bio-inspired artificial pancreas in adults with type 1 diabetes: a 24-hour randomized controlled crossover study. J. Diabetes Sci. Technol. 2015;10:405–13.
Cameron F, Ly TT, Forlenza GP, Patek SD, Baysal N, Messer LH, et al. Inpatient clinical trial of a fully closed-loop artificial pancreas using only CGM and accelerometer data for insulin dosing. Diabetes Technol Ther. 2016;18:A23–4.
Ly TT, Roy A, Grosman B, Shin J, Campbell A, Monirabbasi S, et al. Day and night closed-loop control using the integrated medtronic hybrid closed-loop system in type 1 diabetes at diabetes camp. Diabetes Care. 2015;38:1205–11.
Del Favero S, Place J, Kropff J, Messori M, Keith-Hynes P, Visentin R, et al. Multicenter outpatient dinner/overnight reduction of hypoglycemia and increased time of glucose in target with a wearable artificial pancreas using modular model predictive control in adults with type 1 diabetes. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2015;17:468–76.
Del Favero S, Boscari F, Messori M, Rabbone I, Bonfanti R, Sabbion A, et al. Randomized summer camp crossover trial in 5-to 9-year-old children: outpatient wearable artificial pancreas is feasible and safe. Diabetes Care. 2016;39:1180–5.
Renard E, Devries JH, Cobelli C, Magni L, Place J, Kropff J, et al. Reduction of hyper-and hypoglycemia during two months with a wearable artificial pancreas from dinner to breakfast in patients with type 1 diabetes. Diabetes. 2015;64:A237–8.
Russell SJ, El-Khatib FH, Sinha M, et al. Outpatient glycemic control with a bionic pancreas in type 1 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2014;371:313–25.
Russell SJ, Hillard MA, Balliro C, Magyar KL, Selagamsetty R, Sinha M, et al. Day and night glycaemic control with a bionic pancreas versus conventional insulin pump therapy in preadolescent children with type 1 diabetes: a randomised crossover trial. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2016;4:233–43.
Anderson SM, Raghinaru D, Pinsker JE, Boscari F, Renard E, Buckingham BA, et al. Multinational home use of closed-loop control is safe and effective. Diabetes Care. 2016;39:1143–50.
Nimri R, Muller I, Atlas E, Miller S, Kordonouri O, Bratina N, et al. Night glucose control with MD-logic artificial pancreas in home setting: a single blind, randomized crossover trial-interim analysis. Pediatr Diabetes. 2014;15:91–9.
Mauseth R, Lord SM, Hirsch IB, Kircher RC, Matheson DP, Greenbaum CJ. Stress testing of an artificial pancreas system with pizza and exercise leads to improvements in the system’s fuzzy logic controller. J. Diabetes Sci. Technol. 2015;9:1253–9.
Turksoy K, Bayrak ES, Quinn L, Littlejohn E, Cinar A. Multivariable adaptive closed-loop control of an artificial pancreas without meal and activity announcement. Diabetes Technol Ther. 2013;15:386–400.
•• Turksoy K, Quinn LT, Littlejohn E, Cinar A. An integrated multivariable artificial pancreas control system. J. Diabetes Sci. Technol. 2014;8:498–507. This study reports the performance of the multivariable artificial pancreas with a predictive hypoglycemia module in clinical experiments with exercise bouts and no manual entries.
•• Turksoy K, Quinn LT, Littlejohn E, Cinar A. Multivariable adaptive identification and control for artificial pancreas systems. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng. 2014;61:883–91. This study provides the algorithms used in the multivariable artificial pancreas.
Kumareswaran K, Elleri D, Allen JM, Harris J, Xing D, Kollman C, et al. Meta-analysis of overnight closed-loop randomized studies in children and adults with type 1 diabetes: the Cambridge cohort. J Diabetes Sci Technol. 2011;5:1352–62.
Clarke WL, Anderson S, Breton M, Patek S, Kashmer L, Kovatchev B. Closed-loop artificial pancreas using subcutaneous glucose sensing and insulin delivery and a model predictive control algorithm: the Virginia experience. J. Diabetes Sci. Technol. 2009;3:1031–8.
Hovorka R, Allen JM, Elleri D, Chassin LJ, Harris J, Xing D, et al. Manual closed-loop insulin delivery in children and adolescents with type 1 diabetes: a phase 2 randomised crossover trial. Lancet. 2010;375:743–51.
Steil GM, Palerm CC, Kurtz N, Voskanyan G, Roy A, Paz S, et al. The effect of insulin feedback on closed loop glucose control. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2011;96:1402–8.
Breton M, Farret A, Bruttomesso D, Anderson S, Magni L, Patek S, et al. Fully integrated artificial pancreas in type 1 diabetes modular closed-loop glucose control maintains near normoglycemia. Diabetes. 2012;61:2230–7.
Weinzimer SA, Steil GM, Swan KL, Dziura J, Kurtz N, Tamborlane WV. Fully automated closed-loop insulin delivery versus semiautomated hybrid control in pediatric patients with type 1 diabetes using an artificial pancreas. Diabetes Care. 2008;31:934–9.
Agrawal P, Welsh JB, Kannard B, Askari S, Yang Q, Kaufman FR. Usage and effectiveness of the low glucose suspend feature of the medtronic paradigm Veo insulin pump. J Diabetes Sci Technol. 2011;5:1137–41.
Cengiz E, Swan KL, Tamborlane WV, Steil GM, Steffen ST, Weinzimer SA. Is an automatic pump suspension feature safe for children with type 1 diabetes? An exploratory analysis with a closed-loop system. Diabetes Technol Ther. 2009;11:207–10.
Bergenstal R, Buckingham B, Garg S, Weinzimer SA, Brazg R, Ilany J, et al. Pivotal trial of a hybrid closed-loop system in type 1 diabetes (T1D), in American Diabetes Association 2016 Meeting, 2016 (New Orleans, LA; June 10–14).
Medtronic: Minimed 670G System. https://www.medtronicdiabetes.com/loop-blog/important-update-minimed-670g-availability-priority-access-program/. Accessed 3 Jul 2017.
Dexcom. https://www.dexcom.com. Accessed 3 Jul 2017.
Medtronic. https://www.medtronicdiabetes.com/products/enlite-sensor. Accessed 3 Jul 2017.
Senseonics. http://ous.eversensediabetes.com/products/eversense-sensor/. Accessed 3 Jul 2017.
Tandem Diabetes Care. https://www.tandemdiabetes.com. Accessed 3 Jul 2017.
Insulet-Omnipod. https://www.myomnipod.com/about-insulet/. Accessed 3 Jul 2017.
Roche Diabetes Care. https://www.accu-chek.com/node/8731/support. Accessed 3 Jul 2017.
DiaTribe. https://diatribe.org/bigfoot-biomedical-acquires-asante-snap-pump-technology. Accessed 3 Jul 2017.
• Klonoff DC, Zimliki CL, Stevens A, Beaston P, Pinkos A, Choe SY, et al. Innovations in technology for the treatment of diabetes: clinical development of the artificial pancreas (an autonomous system). J Diabetes Sci Technol. 2011;5:804–26. This publication illustrates the state-of-the-art and future challenges as the surge is AP research was accelerating.
Kowalski A, Lum JW. Juvenile diabetes research foundation artificial pancreas consortium update. J Diabetes Sci Tech. 2009;3:1224–6.
National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (NIDDK), https://www.nih.gov/news-events/news-releases/four-pivotal-nih-funded-artificial-pancreas-research-efforts-begin. Accessed 3 Jul 2017.
Bigfoot Biomedical https://www.bigfootbiomedical.com/first-clinical-trial/. Accessed 3 Jul 2017.
•• Kowalski A. Pathway to artificial pancreas systems revisited: moving downstream. Diabetes Care. 2015;38:1036–43. doi:10.2337/dc15-0364. This publication provides an excellent summary of the progress made in the past 10 years and provides a strategic road map for future research.
• Breton MD, Brown SA, Karvetski CH, Kollar L, Topchyan KA, Anderson SM, et al. Adding heart rate signal to a control-to-range artificial pancreas system improves the protection against hypoglycemia during exercise in type 1 diabetes. Diabetes Technol Ther. 2014;16:506–11. This study demonstrates the benefits of using additional measurements in enhancing the performance of an artificial pancreas during structured exercise.
• Jacobs PG, Resalat N, El Youssef J, Reddy R, Branigan D, Preiser N, et al. Incorporating an exercise detection, grading, and hormone dosing algorithm into the artificial pancreas using accelerometry and heart rate. J. Diabetes Sci. Technol. 2015;9:1175–84. This study demonstrates the benefits of using additional measurements in enhancing the performance of an artificial pancreas during structured exercise.
Dasanayake IS, Bevier WC, Castorino K, Pinsker JE, Seborg DE, Doyle FJ, et al. Early detection of physical activity for people type 1 diabetes mellitus. J. Diabetes Sci. Technol. 2015;9:1236–45.
• Stenerson M, Cameron F, Payne SR, Payne SL, Ly TT, Wilson DM, et al. The impact of accelerometer use in exercise-associated hypoglycemia prevention in type 1 diabetes. J. Diabetes Sci. Technol. 2015;9:80–5. This study demonstrates the benefits of using additional measurements in enhancing the performance of an artificial pancreas during structured exercise.
Cichosz SL, Frystyk J, Hejlesen OK, Tarnow L, Fleischer J. A novel algorithm for prediction and detection of hypoglycemia based on continuous glucose monitoring and heart rate variability in patients with type 1 diabetes. J. Diabetes Sci. Technol. 2014;9:731–7.
Cameron F, Ly TT, Forlenza GP, Patek SD, Baysal N, Messer LH, et al. Inpatient clinical trial of a fully closed-loop artificial pancreas using only CGM and accelerometer data for insulin dosing. Diabetes Technology Therapeutics. 2016;18:A23–4.
• Turksoy K, Bayrak ES, Quinn L, Littlejohn E, Rollins D, Cinar A. Hypoglycemia early alarm systems based on multivariable models. Ind Eng Chem Res. 2013;52:12329–36. doi:10.1021/ie3034015. This study demonstrates the benefits of a hypoglycemia prediction algorithm based on recursively updated multivariable glucose concentration estimation models.
•• Turksoy K, Hajizadeh I, Samadi S, Feng J, Sevil M, Park, et al. Real-time insulin bolusing for unannounced meals with artificial pancreas. Control Eng Pract. 2017;59:159–64. This study illustrates the performance of adding an algorithm that detects rapid rises in glucose levels and provides insulin boluses when no activities that would reduce glucose levels are occurring.
Palerm CC, Zisser H, Jovanovic L, Doyle FJ. A run-to-run control strategy to adjust basal insulin infusion rates in type 1 diabetes. J Process Control. 2008;18:258–65. doi:10.1016/j.jprocont.2007.07.010.
Srinivasan B, Primus CJ, Bonvin D, Ricker NL. Run-to-run optimization via control of generalized constraints. Control Eng Pract. 2001;9:911–9.
Magni L, Forgione M, Toffanin C, Dalla Man C, Kovatchev B, De Nicolao G, et al. Run-to-run tuning of model predictive control for type 1 diabetes subjects: in silico trial. J Diabetes Sci Technol. 2009;3:1091–8. doi:10.1177/193229680900300512.
Toffanin C, Visentin R, Messori M, Di Palma F, Magni L, Cobelli C. Towards a run-to-run adaptive artificial pancreas: in silico results. IEEE Trans Biomed Engng. 2017; doi:10.1109/TBME.2017.2652062.
• Toffanin C, Messori M, Cobelli C, Magni L. Automatic adaptation of basal therapy for type 1 diabetic patients: a run-to-run approach. Biomedical Signal Processing and Control. 2017;31:539–49. This study illustrates the benefits of updating the model to improve controller performance.
Eren-Oruklu M, Cinar A, Quinn L, Smith D. Estimation of future glucose concentrations with subject-specific recursive linear models. Diabetes Technol Ther. 2009;11:243–53.
Boiroux D, Duun-Henriksen AK, Schmidt S, Nørgaard K, Poulsen NK, Madsen H, et al. Adaptive control in an artificial pancreas for people with type 1 diabetes. Control Eng Pract. 2017;58:332–42.
Cameron F, Niemeyer G, Wilson DM, Bequette BW, Benassi KS, Clinton P, et al. Inpatient trial of an artificial pancreas based on multiple model probabilistic predictive control with repeated large unannounced meals. Diabetes Technol Ther. 2014;16:728–34. doi:10.1089/dia.2014.0093.
• Turksoy K, Samadi S, Feng J, Littlejohn E, Quinn L, Cinar A. Meal detection in patients with type 1 diabetes: a new module for the multivariable adaptive artificial pancreas control system. IEEE J Biomed Health Inform. 2016;20:47–54. doi:10.1109/JBHI.2015.2446413. This study illustrates detection of rapid increases of glucose levels and meals based on compartmental models and reduction of peak glucose values.
Turksoy K, Kilkus J, Hajizadeh I, Samadi S, Feng J, Sevil M, et al. Hypoglycemia detection and carbohydrate suggestion in an artificial pancreas. J Diabetes Sci Technol. 2016;10:1236–44.
• Samadi S, Turksoy K, Hajizadeh I, Feng J, Sevil M, Cinar A. Meal detection and carbohydrate estimation using continuous glucose sensor data. IEEE J Biomed Health Inform. 2017;21:619–27. doi:10.1109/JBHI.2017.2677953. This study illustrates detection of rapid increases of glucose levels and meals based on qualitative trend analysis and fuzzy logic, estimation of meal sizes, and reduction of peak glucose values.
Riddell MC, Zaharieva DP, Yavelberg L, Cinar A, Jamnik VK. Exercise and the development of the artificial pancreas one of the more difficult series of hurdles. J. Diabetes Sci. Technol. 2015;9:1217–26.
Colberg S. Diabetic athlete’s handbook. Human Kinetics; 2009.
• Riddell MC, Gallen IW, Smart CE, Taplin CE, Adolfsson P, Lumb AN, et al. Exercise management in type 1 diabetes: a consensus statement. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2017;5:377–90. This paper provides valuable information about management of glucose during and after exercise.
Yardley JE, Colberg SR. Update on Management of Type 1 diabetes and type 2 diabetes in athletes. Curr Sports Med Rep. 2017;16:38–44.
• Turksoy K, Paulino TML, Zaharieva DP, Yavelberg L, Jamnik, Riddell MC, et al. Classification of physical activity: information to artificial pancreas control systems in real time. J. Diabetes Sci. Technol. 2015;9:1200–7. This study provides an algorithm for classifying the type of exercise (aerobic or resistance) in real time to inform the artificial pancreas for proper adjustment of insulin infusion rates depending on the type of exercise.
Ben Brahim N, Place J, Renard E, Breton MD. Identification of main factors explaining glucose dynamics during and immediately after moderate exercise in patients with type 1 diabetes. J. Diabetes Sci. Technol. 2015;9:1185–91.
•• Turksoy K, Monforti C, Park M, Griffith G, Quinn L, Cinar A. Use of wearable sensors and biometric variables in an artificial pancreas system. Sensors. 2017;17. doi:10.3390/s17030532. This study provides information about informative physiological variables about physical activities for use in multivariable artificial pancreas systems that can be more effective during and after exercise.
Colberg SR, Laan R, Dassau E, Kerr D. Physical activity and type 1 diabetes time for a rewire? J. Diabetes Sci. Technol. 2015;9:609–18.
Dadlani V, Levine JA, McCrady-Spitzer SK, Dassau E, Kudva YC. Physical activity capture technology with potential for incorporation into closed-loop control for type 1 diabetes. J. Diabetes Sci. Technol. 2015;9:1208–16.
Kudva YC, Carter RE, Cobelli C, Basu R, Basu A. Closed-loop artificial pancreas systems: physiological input to enhance next-generation devices. Diabetes Care. 2014;37:1184–90.
Fahey AJ, Paramalingam N, Davey RJ, Davis EA, Jones TW, Fournier PA. The effect of a short sprint on postexercise whole-body glucose production and utilization rates in individuals with type 1 diabetes mellitus. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2012;97:4193–200.
Yardley JE, Kenny GP, Perkins BA, Riddell MC, Malcolm J, Boulay P, et al. Effects of performing resistance exercise before versus after aerobic exercise on glycemia in type 1 diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2012;35:669–75.
Gettman LR, Pollock ML. Circuit weight training: a critical review of its physiological benefits. Phys Sports Med. 1981;9:44–60.
Stanforth D, Stanforth PR, Hoemeke ME. Physiologic and metabolic responses to a body pump workout. J Strength Cond Res. 2000;14:144–50.
Marcovecchio ML, Chiarelli F, The effects of acute and chronic stress on diabetes control. Sci Signal. 2012; 5(247). doi:10.1126/scisignal.2003508.
Gonder-Frederick LA, Carter WR, Cox DJ, Clarke WL. Environmental stress and blood glucose change in insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Health Psychol. 1990;9:503–15.
Hanson SL, Pichert JW. Perceived stress and diabetes control in adolescents. Health Psychol. 1986;5:439–52.
Halford WK, Cuddihy S, Mortimer RH. Psychological stress and blood glucose regulation in type I diabetic patients. Health Psychol. 1990;9:516–28.
Chida Y, Hamer M. An association of adverse psychosocial factors with diabetes mellitus: a meta-analytic review of longitudinal cohort studies. Diabetologia. 2008;51:2168–78.
Hilliard ME, Joyce P, Hessler D, Butler AM, Anderson BJ, Jaser S. Stress and A1c among people with diabetes across the lifespan. Curr. Diab. Rep. 2016;16:1–10.
Baucom KJW, Queen TL, Wiebe DJ, Turner SL, Wolfe KL, Godbey EI, et al. Depressive symptoms, daily stress, and adherence in late adolescents with type 1 diabetes. Health Psychol. 2015;34:522–30.
Frenzel MP, McCaul KD, Glasgow RE, Schafer LC. The relationship of stress and coping to regimen adherence and glycemic control of diabetes. J Soc Clin Psychol. 1988;6:77–87.
Surwit RS, Schneider MS. Role of stress in the etiology and treatment of diabetes mellitus. Psychosom Med. 1993;55:380–93.
Moberg E, Kollind M, Lins PE, Adamson U. Acute mental stress impairs insulin sensitivity in IDDM patients. Diabetologia. 1994;37:247–51.
Colberg SR, Edelman S. 50 secrets of the longest living people with diabetes. Da Capo Press, 2008.
Riazi A, Pickup J, Bradley C. Daily stress and glycaemic control in type 1 diabetes: individual differences in magnitude, direction, and timing of stress-reactivity. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2004;66:237–44.
Kelly MM, Tyrka AR, Anderson GM, Price LH, Carpenter LL. Sex differences in emotional and physiological responses to the Trier Social Stress Test. J Behav Ther Exp Psychiatry. 2008;39:87–98.
Kajantie E, Phillips DIW. The effects of sex and hormonal status on the physiological response to acute psychosocial stress. Psychoneuroendocrinology. 2006;31:151–78.
Wiesli P, Schmid C, Kerwer O, Nigg-Koch C, Klaghofer R, Seifert B, et al. Acute psychological stress affects glucose concentrations in patients with type 1 diabetes following food intake but not in the fasting state. Diabetes Care. 2005;28:1910–5.
Perkins BA, Riddell MC, Campaigne BN, et al. Type 1 diabetes and exercise: using the insulin pump to maximum advantage. Can J Diabetes. 2006;30:72–9.
Gonder-Frederick LA, Grabman JH, Kovatchev B, Brown SA, Patek S, Basu A, et al. Is psychological stress a factor for incorporation into future closed-loop systems? J. Diabetes Sci. Technol. 2016;10:640–6.
Perfect MM, Patel PG, Scott RE, Wheeler MD, Patel C, Griffin K, et al. Sleep, glucose, and daytime functioning in youth with type 1 diabetes. Sleep. 2012;35:81–8.
Feupe SF, Frias PF, Mednick SC, Mcdevitt EA, Heintzman ND. Nocturnal continuous glucose and sleep stage data in adults with type 1 diabetes in real-world conditions. J. Diabetes Sci. Technol. 2013;7:1337–45.
Jauch-Chara K, Schmid SM, Hallschmid M, Born J, Schultes B. Altered neuroendocrine sleep architecture in patients with type 1 diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2008;31:1183–8.
Yeshayahu Y, Mahmud FH. Altered sleep patterns in adolescents with type 1 diabetes: implications for insulin regimen. Diabetes Care. 2010;33:e142.
Estrada CL, Danielson KK, Drum ML, Lipton RB. Insufficient sleep in young patients with diabetes and their families. Biol Res Nurs. 2012;14:48–54.
Koren D, O’Sullivan KL, Mokhlesi B. Metabolic and glycemic sequelae of sleep disturbances in children and adults. Curr Diab Rep. 2015;15:1–10.
Jaser SS, Ellis D. Sleep in adolescents and young adults with type 1 diabetes: associations with diabetes management and glycemic control. Heal Psychol Behav Med. 2016;4:49–55.
McDonough RJ, Clements MA, DeLurgio SA, Patton SR. Sleep duration and its impact on adherence in adolescents with type 1 diabetes mellitus Pediatr. Diabetes. 2016;18:262–70.
Turner SL, Queen TL, Butner J, Wiebe D, Berg CA. Variations in daily sleep quality and type 1 diabetes management in late adolescents. J Pediatr Psychol. 2016;41:661–9.
Barnard K, James J, Kerr D, Adolfsson P, Runion A, Serbedzija G. Impact of chronic sleep disturbance for people living with type 1 diabetes. J Diabetes Sci Technol. 2016;10:762–7.
Sherr JL, Collazo MP, Cengiz E, Michaud C, Carria L, Steffen AT, et al. Safety of nighttime 2-hour suspension of basal insulin in pump-treated type 1 diabetes even in the absence of low glucose. Diabetes Care. 2014;37:773–9.
Buckingham B, Chase HP, Dassau E, Cobry E, Clinton P, Gage V, et al. Prevention of nocturnal hypoglycemia using predictive alarm algorithms and insulin pump suspension. Diabetes Care. 2010;33:1013–7.
Beck RW, Raghinaru D, Wadwa RP, Chase HP, Maahs DM, Buckingham BA. Frequency of morning ketosis after overnight insulin suspension using an automated nocturnal predictive low glucose suspend system. Diabetes Care. 2014;37:1224–9.
Buckingham BA, Raghinaru D, Cameron F, Bequette BW, Chase HP, Maahs DM, et al. Predictive low-glucose insulin suspension reduces duration of nocturnal hypoglycemia in children without increasing ketosis. Diabetes Care. 2015;38:1197–204.
Baysal N, Cameron F, Buckingham BA, Wilson DM, Chase HP, Maahs DM, et al. A novel method to detect pressure-induced sensor attenuations (PISA) in an artificial pancreas. J Diabetes Sci Technol. 2014;8:1091–6. doi:10.1177/1932296814553267.
Feng J, Turksoy K, Samadi S, Hajizadeh I, Littlejohn E, Cinar A. Hybrid online sensor error detection and functional redundancy for systems with time-varying parameters. J Process Control. 2017. Accepted for publication.
Turksoy K. Iman Hajizadeh I, Littlejohn E, Cinar A. Multivariate statistical monitoring of sensor faults of a multivariable artificial pancreas. IFAC World Congress, 2017.
Forlenza G, Chernavvsky D, DeBoer M, Robic J, Kovatchev B, Wadwa RP, et al. The artificial pancreas improves glycemic control during extended exercise at ski camp in adolescents with type 1 diabetes. Diabetes Technol Ther. 2017 (2017 ATTD Supplement) 19:A-47.
Sevil M, Hajizadeh I, Samadi S, Feng J, Lazaro C, Frantz N, et al. Social and competition stress detection with wristband physiological signals. 2017 I.E. 14th International Conference on Wearable and Implantable Body Sensor Networks (BSN), 2017. 39–42.
• Haidar A, Legault L, Matteau-Pelletier L, Messier V, Dallaire M, Ladouceur M, et al. Outpatient overnight glucose control with dual-hormone artificial pancreas, single-hormone artificial pancreas, or conventional insulin pump therapy in children and adolescents with type 1 diabetes: an open-label, randomised controlled trial. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2015;3:595–604. This study provides a good comparison of single (insulin) and dual-hormone (insulin/glucagon) artificial pancreas performance.
Castle JR, El Youssef J, Bakhtiani PA, Cai Y, Stobbe JM, Branigan D, et al. Effect of repeated glucagon doses on hepatic glycogen in type 1 diabetes: implications for a bihormonal closed-loop system. Diabetes Care. 2015;38:2115–9.
Feng J, Turksoy K, Cinar A. Performance assessment of model-based artificial pancreas control systems. In: Kirchsteiger H, Jorgensen JB, Renard E, del Re L, editors. Prediction methods for blood glucose concentration. New York: Springer; 2016. p. 243–65.
• Hajizadeh I, Rashid M, Turksoy K, Samadi S, Frantz N, Sevil M, Cengiz E, et al. Plasma insulin estimation in people with type 1 diabetes mellitus. Ind Eng Chem Res. 2017. Accepted for publication. This study provides an algorithm to estimate plasma insulin concentration from CGM readings in real time to replace insulin-on-board estimates based on aggregate patient data.
• Gondhalekar R, Dassau E, Doyle FJ. Periodic zone-MPC with asymmetric costs for outpatient-ready safety of an artificial pancreas to treat type 1 diabetes. Automatica. 2016;71:237–46. This study provides an enhancement of model-predictive artificial pancreas control systems by adjusting the cost function for different ranges of glucose concentrations and modifying the aggressiveness of the control actions as needed.
Chakrabarty A, Zavitsanou S, Doyle FJ, Dassau E. Event-triggered model predictive control for embedded artificial pancreas systems, IEEE Trans BME, 2017.
Tidepool. http://tidepool.org. Accessed 3 Jul 2017.
Diabetes Mine. http://www.healthline.com/diabetesmine. Accessed 3 Jul 2017.
diaTribe. https://diatribe.org. Accessed 3 Jul 2017.
diyps.org. https://diyps.org/2014/02/07/a-diy-artificial-pancreas-system/. Accessed 3 Jul 2017.
TypeZero Technologies http://typezero.com. Accessed 3 Jul 2017.
Beta Bionics. https://www.betabionics.org. Accessed 3 Jul 2017.
Pacific Diabetes Technologies. http://pacificdt.com. Accessed 3 Jul 2017.
ClinicalDiabetes.gov. https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/results?term=artificial+pancreas&cond=Diabetes&Search=Apply&recrs=a&recrs=d&age_v=&gndr=&type=&rslt=. Accessed 24 Jul 2017.
Acknowledgments
The multivariable artificial pancreas research is supported by the National Institutes of Health (NIH) under grants 1DP3DK101077-01 and 1DP3DK101075-01 and by Juvenile Diabetes Research Foundation International (JDRF) under grant 17-2013-472.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
Ali Cinar reports grants from National Institutes of Health, grants from Juvenile Diabetes Research Foundation, during the conduct of the study; In addition, Dr. Cinar has a patent AUTOMATIC INSULIN PUMPS USING RECURSIVE MULTIVARIABLE MODELS AND ADAPTIVE CONTROL ALGORITHMS issued, and a patent MULTIVARIABLE ARTIFICIAL PANCREAS SYSTEM pending.
Human and Animal Rights and Informed Consent
This article does not contain any studies with human or animal subjects performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
This article is part of the Topical Collection on Therapies and New Technologies in the Treatment of Type 1 Diabetes
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cinar, A. Multivariable Adaptive Artificial Pancreas System in Type 1 Diabetes. Curr Diab Rep 17, 88 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11892-017-0920-1
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11892-017-0920-1