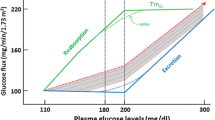
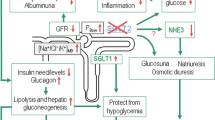
Abstract
In addition to its central role in the development of microvascular complications, hyperglycemia plays an important role in the pathogenesis of type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) by means of glucotoxicity. Thus, effective glycemic control not only reduces the incidence of microvascular complications but also corrects the metabolic abnormalities that contribute to the progression of the disease. Progressive β-cell failure and multiple side effects, including hypoglycemia and weight gain, associated with many current therapies present obstacles to the achievement of optimal and durable glycemic control in subjects with T2DM. Most recently, inhibitors of the renal sodium-glucose cotransporter have been developed to reduce the plasma glucose concentration by producing glucosuria. Because the mechanism of action of these oral antidiabetic agents is independent of β-cell function and tissue sensitivity to insulin, they improve glycemic control while avoiding hypoglycemia and promoting weight loss. In this review, we summarize the available data concerning the mechanism of action, efficacy, and safety of this novel antidiabetic class of therapeutic agents.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Papers of particular interest, published recently, have been highlighted as: •• Of major importance
The Diabetes Control and Complications Trial Research Group. The effect of intensive treatment of diabetes on the development and progression of long-term complications in insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. N Engl J Med. 1993;329:977–86.
UK Prospective Diabetes Study (UKPDS) Group. Intensive blood-glucose control with sulphonylureas or insulin compared with conventional treatment and risk of complications in patients with type 2 diabetes (UKPDS 33). Lancet. 1998;352:837–53.
DeFronzo RA. Banting lecture: from the triumvirate to the ominous octet: a new paradigm for the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus. Diabetes. 2009;58:773–95.
Rossetti L, Giaccari A, DeFronzo RA. Glucose toxicity. Diabetes Care. 1990;13:610–30.
The American Diabetes Association. Standards of medical care in diabetes-2007. Diabetes Care. 2007;30(Supp I):S4–41.
Hoerger TJ, Segel JE, Gregg EW, Saaddine JB. Is glycemic control improving in U.S. adults? Diabetes Care. 2008;31:81–6.
•• Abdul-Ghani MA, Norton L, Defronzo RA. Role of sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT 2) inhibitors in the treatment of type 2 diabetes. Endocr Rev. 2011;32:515–31. This is a recent comprehensive review that summarizes the molecular basis of renal glucose reuptake and the clinical and pathophysiological implications of SGLT2 inhibitors..
Valtin H. Tubular reabsorption. In renal function. Boston: Little, Brown and Company; 1983.
Kamran M, Peterson RG, Dominguez JH. Overexpression of GLUT2 gene in renal proximal tubules of diabetic Zucker rats. J Am Soc Nephrol. 1997;8:943–8.
Farber SJ, Berger EY, Earle DP. Effect of diabetes and insulin of the maximum capacity of the renal tubules to reabsorb glucose. J Clin Invest. 1951;30:125–9.
Thomson SC, Rieg T, Miracle C, Mansoury H, Whaley J, Vallon V, Singh P. Acute and chronic effects of SGLT2 blockade on glomerular and tubular function in the early diabetic rat. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2012;302:R75–83.
Chassis H, Jolliffe N, Smith H. The action of phlorizin on the excretion of glucose, xylose, sucrose, creatinine, and urea by man. J Clin Invest. 1933;12:1083–9.
Vick HD, Deidrich DF. Reevaluation of renal tubular glucose transport inhibition by phlorizin analogs. Am J Physiol. 1973;224:552–7.
Ehrenkranz JR, Lewis NG, Kahn CR, Roth J. Phlorizin: a review. Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 2005;21:31–8.
Li A, Zhang J, Greenberg J, Lee T, Liu J. Discovery of non-glucoside SGLT2 inhibitors. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2011;21:2472–5.
Bhanot S, Murray SF, Booten SL, Chakravarty K, Zanardi T, Henry S, Watts LM, Wancewicz EV, Siwkows A. ISIS 388626, an SGLT2 antisense drug, causes robust and sustained glucosuria in multiple species and is safe and well-tolerated. Diabetes. 2009;58(suppl1):A328.
Kahn BB, DeFronzo RA, Cushman SW, Rossetti L. Normalization of blood glucose in diabetic rats with phlorizin treatment reverses insulin-resistant glucose transport in adipose cells without restoring glucose transporter gene expression. J Clin Invest. 1999;87:561–70.
Rossetti L, Smith D, Shulman GI, Papachristou D, DeFronzo RA. Correction of hyperglycemia with phlorizin normalizes tissue sensitivity to insulin in diabetic rats. J Clin Invest. 1987;79:1510–5.
Rossetti L, Shulman GI, Zawalich W, DeFronzo RA. Effect of chronic hyperglycemia on in vivo insulin secretion in partially pancreatectomized rats. J Clin Invest. 1987;80:1037–44.
Santer R, Kinner M, Lassen CL, Schneppenheim R, Eggert P, Bald M, Brodehl J, Daschner M, Ehrich JH, Kemper M, Li Volti S, Neuhaus T, Skovby F, Swift PG, Schaub J, Klaerke D. Molecular analysis of the SGLT2 gene in patients with renal glucosuria. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2003;14:2873–82.
Oku A, Ueta K, Nawano M, Arakawa K, Kano-Ishihara T, Matsumoto M, Saito A, Tsujihara K, Anai M, Asano T. Antidiabetic effect of T-1095, an inhibitor of Na(+)-glucose cotransporter, in neonatally streptozotocin-treated rats. Eur J Pharmacol. 2000;391:183–92.
Katsuno K, Fujimori Y, Takemura Y, Hiratochi M, Itoh F, Komatsu Y, Fujikura H, Isaji M. Sergliflozin, a novel selective inhibitor of low-affinity sodium glucose cotransporter (SGLT2), validates the critical role of SGLT2 in renal glucose reabsorption and modulates plasma glucose level. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2007;320:323–30.
Hussey E, Clark R, Amin D, Kipnes M, Semmes R, Odriscoll E, Leong J, Murphy S, Dobbins R, Nunez D. Early clinical studies to assess safety, tolerability, pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of single dose of sergliflozin, a novel inhibitor of renal glucose reabsorption in healthy volunteers and subjects with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Diabetes. 2007;56(Suppl1):A189.
Hussey E, Dobbins R, Stolz R, Stockman N, Semmes R, Murray S, Nunez D. A double-blind randomized repeat dose study to assess safety, tolerability, pharmacokineticks and pharmacodynamics of three times daily dosing of sergliflozin, a novel inhibitor of renal glucose reabsorption in healthy overweight and obese subjects. Diabetes. 2007;56(Suppl1):A491.
Fujimori Y, Katsuno K, Nakashima I, Ishikawa-Takemura Y, Fujikura H, Isaji M. Remogliflozin etabonate, in a novel category of selective low-affinity sodium glucose cotransporter (SGLT2) inhibitors, exhibits antidiabetic efficacy in rodent models. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2008;327:268–76.
Dobbins RL, Kapur A, Kapitza C, O’connor-Semmes RL, Tao W, Hussey EK. Remogliflozin etabonate, a selective inhibitor of the sodium-glucose transporter 2 (SGLT2) reduces serum glucose in type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) patients. Diabetes. 2009;58 suppl 1:A573.
http://www.pharmaceutical-business-review.com/news/glaxosmithkline_discontinues_ development_of_remogliflozin_090703.
•• http://www.fda.gov/downloads/AdvisoryCommittees/CommitteesMeetingMaterials/Drugs/EndocrinologicandMetabolicDrugsAdvisoryCommittee/UCM262996.pdf This site contains the entire package for the FDA submission of dapagliflozin with a summary of the clinical efficacy and adverse events observed in phase 1, 2, and 3 of studies.
Komoroski B, Vachharajani N, Feng Y, Li L, Kornhauser D, Pfister M. Dapagliflozin, a novel, selective SGLT2 inhibitor, improved glycemic control over 2 weeks in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Clin Pharm Ther. 2009;85:513.
Obermeier M, Yao M, Khanna A, Koplowitz B, Zhu M, Li W, Komoroski B, Kasichayanula S, Discenza L, Washburn W, Meng W, Ellsworth BA, Whaley JM, Humphreys WG. In vitro characterization and pharmacokinetics of dapagliflozin (BMS-512148), a potent sodium-glucose cotransporter type II inhibitor, in animals and humans. Am Soc Pharmacol Exp Therapeut. 2010;38:405–14.
List J, Woo V, Morales E, Tang W, Fiedorek FT. Sodium-glucose cotransport inhibition with dapagliflozin in type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2009;32:650–7.
Ferrannini E, Ramos SJ, Tang W, Salsali A, List JF. Dapagliflozin monotherapy in T2DM patients with inadequate glycemic control by diet and exercise: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, multicenter phase III trial. Diabetes Care. 2010;33:2217–24.
Wilding JPH, Norwood P, Tjoen C, Bastien A, List JF, Fiedorek FT. A study of dapagliflozin in patients with type 2 diabetes receiving high doses of insulin plus insulin sensitizers. Applicability of a novel insulin-independent treatment. Diabetes Care. 2009;32:1656–62.
Zhang L, Feng Y, List J, Kasichayanula S, Pfister M. Dapagliflozin treatment in patients with different stages of type 2 diabetes mellitus: effects on glycaemic control and body weight. Diabetes Obes Metabol. 2010;12:510–6.
Nauck MA, Del Prato S, Meier JJ, Durán-García S, Rohwedder K, Elze M, Parikh SJ. Dapagliflozin versus glipizide as add-on therapy in patients with type 2 diabetes who have inadequate glycemic control with metformin: a randomized, 52-week, double-blind, active-controlled noninferiority trial. Diabetes Care. 2011;34:2015–22.
Baily CJ, Gross JI, Yadav M, Iqbal N, Mansfield TA, List JF. Sustained efficacy of dapagliflozin when added to metformin in type 2 diabetes inadequately controlled by metformin monotherapy. Diabetologia. 2011;54(Suppl1):A146.
Del Prato S, Nauck M, Rohwedder K, Theuerkauf A, Langkilde AM, Parikh S. Long term efficacy and safety of ass-on dapagliflozin vs add-on glipizide in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus inadequately controlled with metformin: 2 year results. Diabetologia. 2011;54(Suppl1):A852.
Sha S, Devineni D, Ghosh A, Polidori D, Chien S, Wexler D, Shalayda K, Demarest K. Rothenberg PCanagliflozin, a novel inhibitor of sodium glucose co-transporter 2, dose dependently reduces calculated renal threshold for glucose excretion and increases urinary glucose excretion in healthy subjects. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2011;13:669–72.
Inagaki N, Kondo K, Iwasaki T, Maruyama N, Susuta Y, Sakai M, Kuki H. Canagliflozin, a novel inhibitor of sodium glucose co-transporter 2 (SGLT2) improves glycemic control and reduces body weight in Japanese type 2 diabetes Mellitus (T2DM). Diabetes. 2011;60(suppl):A999.
Rosensotck J, Arbit D, Usiskin K, Capuano G, Canovatchel W. Canagliflozin an inhibitor of sodium glucose co-transporter 2 (SGLT2), improves glycemic control and lowers body weight in subjects with type 2 diabetes (T2D) on metformin. Diabetes. 2010;59 suppl 1:A21.
Devineni D, Morrow L, Hompesch M, Skee D, Vandebosch A, Murphy J, Ways K, Schwartz S. Canagliflozin improves glycemic control over 28 days in subjects with type 2 diabetes not optimally controlled on insulin. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2012[ahead of print].
Polidori D, Zhao Y, Sha S, Canovatchel W. Canagliflozin treatment improves beta cell function in subject with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes. 2010;59 suppl 1:A176.
Grempler R, Thomas L, Eckhardt M, Himmelsbach F, Sauer A, Sharp DE, Bakker RA, Mark M, Klein T, Eickelmann P. Empagliflozin, a novel selective sodium glucose cotransporter-2 (SGLT-2) inhibitor: characterisation and comparison with other SGLT-2 inhibitors. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2012;14:83–90.
Koiwai K, Seman L, Yamamura N, Macha S, Taniguchi A, Negishi T, Sesoko S, Dugi KA. Safety, tolerability, pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of single doses of BI 10773, a sodium-glucose co-transporter inhibitor (SGLT2), in Japanese healthy volunteers. Diabetes. 2010;59 suppl 1:2175PO.
Heise T, Seewaldt-Becker E, Macha S, Hantel S, Huber K, Pinnetti S, Seman L, Hans-Juergen W. BI 10773, a sodium-glucose co-transporter inhibitor (SGLT-2), is safe and efficacious following 4-week treatment in patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes. 2010;59(suppl):629P.
Rosenstock J, Jelaska A, Seman L, Pinnetti S, Hantel S, Woerle HJ. Efficacy and safety of BI 10773, a new sodium glucose cotransporter-2 (SGLT-2) inhibitor, in type 2 diabetes inadequately controlled on metformin. Diabetes. 2011;60(suppl):989P.
Kashiwagi A, Utsuno A, Kazuta K, Yoshida S, Kageyama S. ASP1941, a novel, selective SGLT2 inhibitor, was effective and safe in Japanese healthy volunteers and patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Diabetes. 2010;59 suppl 1:A21.
Takinami A, Takinami Y, Kazuta K, Yoshida S, Utsuno A, Nagase I, Kashiwagi A. Ipragliflozin improved glycemic control with additional benefit of reduction of body weight and blood pressure in Japanese patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus BRIGHTEN Study. Diabetologia. 2011;54(suppl):A149.
Freiman J, Ruff DA, Frazier KS, Combs K, Turnage A, Shadoan M, Powell D, Zambrowicz B, Brown P. LX4211, a dual SGLT2/SGLT1 inhibtor, shows rapid and significant improvements in glycemic control over 28 days in patients with type 2 diabetes (T2DM). Diabetes 2010;59(suppl 1), (late breaking abstract).
Seino Y, Sasaki T, Fukatsu A, Samukawa Y, Sakai S, Watanabe T. TS-071, a novel and selective SGLT2 inhibitor, improved glycemic control and decreased body weight in 12-week study of Japanese patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Diabetes. 2011;60(suppl):P998.
Nucci G, Amin NB, Wang X, Lee DS, Rusnak JM. The sodium glucose co-transported PF04971729, provides multifaced improvement in diabetic patients inadequately controlled on metformin. Diabetologia. 2011;54(suppl):A850.
Kadokura T, Ishikawa H, Nakajo I, Yoshida S, Utsuno A, Smulders RA, Morozumi K. The effect of renal impairment on the pharmacokinetics and urinary glucose excretion of the SGLT2 inhibitor ipragliflozin in Japanese type 2 diabetes mellitus patients. Diabetologia. 2011;54(suppl):A847.
Vallon V, Richter K, Blantz RC, Thomson S, Osswald H. Glomerular hyperfiltration in experimental diabetes mellitus: potential role of tubular reabsorption. J Am Soc Nephrol. 1999;10:2569–76.
Thomson SC, Vallon V, Blantz RC. Kidney function in early diabetes: the tubular hypothesis of glomerular filtration. Am J Physiol. 2004;286:F8–18.
Noonan WT, Shapiro VM, Banks RO. Renal glucose reabsorption during hypertonic glucose infusion in female streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Life Sci. 2001;68:2967–77.
Dominguez JH, Camp K, Maianu L, Feister H, Garvey WT. Molecular adaptations of GLUT1 and GLUT2 in renal proximal tubules of diabetic rats. Am J Physiol. 1994;266:F283–90.
Nelson RG, Bennett PH, Beck GJ, Tan M, Knowler WC, Mitch WE, Hirschman GH, Myers BD. Development and progression of renal disease in Pima Indians with non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Diabetic Renal Disease Study Group. N Engl J Med. 1996;335:1636–42.
Tuttle KR, Bruton JL, Perusek MC, Lancaster JL, Kopp DT, DeFronzo RA. Effect of strict glycemic control on renal hemodynamic response to amino acids and renal enlargement in insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. N Engl J Med. 1991;324:1626–32.
Arakawa K, Ishihara T, Oku A, Nawano M, Ueta K, Kitamura K, Matsumoto M, Saito A. Improved diabetic syndrome in C57BL/KsJ-db/db mice by oral administration of the Na(+)-glucose cotransporter inhibitor T-1095. Br J Pharmacol. 2001;132:578–86.
Parikh S, Johnsson K, Ptaszynska A, Schmitz B, Sugg J, List JF. Characterization of urinary tract infection in the setting of pharmacologically induced glucosuria. Diabetologia. 2011;54(suppl):A841.
Disclosure
Conflicts of interest: M.A. Abdul-Ghani:none; L. Norton:none; R.A. DeFronzo: has board membership with Amylin, Takeda, Boehringer Ingelheim, Novo Nordisk, and Bristol-Myers Squibb; has received grant support from Amylin and Takeda, is a member of the Novo Nordisk speakers bureau.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Abdul-Ghani, M.A., Norton, L. & DeFronzo, R.A. Efficacy and Safety of SGLT2 Inhibitors in the Treatment of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Curr Diab Rep 12, 230–238 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11892-012-0275-6
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11892-012-0275-6