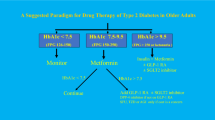
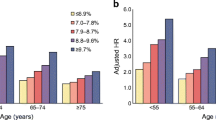
Abstract
As the number of older adults increases in the United States and worldwide, management of patients with multiple coexisting chronic diseases has become a critical component in health care. Management of diabetes is particularly challenging in this population due to significant risks of microvascular and macrovascular diseases on the one hand, and complications of the treatment strategies (e.g., hypoglycemia) with intensive control on the other hand. To provide a balanced approach to diabetes in the elderly, a comprehensive and holistic strategy, with consideration of overall health, functional status, psychosocial environment, financial resources and, finally but most importantly, quality of life is needed. Understanding the unique challenges faced by older adults with diabetes and issues pertaining to antidiabetes medications with aging is an important first step in the direction of better and tailored care of this burgeoning population.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Papers of particular interest, published recently, have been highlighted as:•• Of major importance
•• Prevention CDC. National diabetes fact sheet: national estimates and general information on diabetes and prediabetes in the United States. US Department of Health and Human Services, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, 2011. This article shows the burden of diabetes in the older population. The current data show much higher prevalence of both diagnoses and undiagnosed diabetes in people over 65 years of age.
American Diabetes Association. Economic consequences of diabetes mellitus in the U.S. in 1997. Diabetes Care 1998;21(2):296–309.
Brown AF, Mangione CM, Saliba D, Sarkisian CA. Guidelines for improving the care of the older person with diabetes mellitus. J Am Geriatr Soc 2003;51(5 Suppl Guidelines):S265-80.
Sinclair AJ, Girling AJ, Bayer AJ. Cognitive dysfunction in older subjects with diabetes mellitus: impact on diabetes self-management and use of care services. All Wales Research into Elderly (AWARE) Study. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2000;50(3):203–12.
Kaufman DW, Kelly JP, Rosenberg L, Anderson TE, Mitchell AA. Recent patterns of medication use in the ambulatory adult population of the United States: the Slone survey. Jama. 2002;287(3):337–44.
Sergi G, De Rui M, Sarti S, Manzato E. Polypharmacy in the elderly: can comprehensive geriatric assessment reduce inappropriate medication use? Drugs Aging. 2011;28(7):509–18.
•• Budnitz DS, Lovegrove MC, Shehab N, Richards CL. Emergency hospitalizations for adverse drug events in older Americans. N Engl J Med 2011;365(21):2002–12. This article is important in underscoring significant cost of commonly prescribed medications in older adults due to adverse reaction. It also shows that improving the management with antidiabetic medications has potential to reduce hospitalization in older adults.
Araki A, Ito H. Diabetes mellitus and geriatric syndromes. Geriatr Gerontol Int. 2009;9(2):105–14.
Munshi M. Managing the "geriatric syndrome" in patients with type 2 diabetes. Consult Pharm. 2008;23(Suppl B):12–6.
Munshi M, Grande L, Hayes M, et al. Cognitive dysfunction is associated with poor diabetes control in older adults. Diabetes Care. 2006;29(8):1794–9.
Egede LE. Effect of comorbid chronic diseases on prevalence and odds of depression in adults with diabetes. Psychosom Med. 2005;67(1):46–51.
Blaum CS, Ofstedal MB, Langa KM, Wray LA. Functional status and health outcomes in older americans with diabetes mellitus. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2003;51(6):745–53.
Chelliah A, Burge MR. Hypoglycaemia in elderly patients with diabetes mellitus: causes and strategies for prevention. Drugs Aging. 2004;21(8):511–30.
Bourdel-Marchasson I, Berrut G. Caring the elderly diabetic patient with respect to concepts of successful aging and frailty. Diabetes Metab 2005;31 Spec No 2:5 S13-5S9.
Knowler WC, Barrett-Connor E, Fowler SE, et al. Reduction in the incidence of type 2 diabetes with lifestyle intervention or metformin. N Engl J Med. 2002;346:393–403.
Morley JE. The elderly Type 2 diabetic patient: special considerations. Diabet Med. 1998;15 Suppl 4:S41–6.
Cryer PE, Davis SN, Shamoon H. Hypoglycemia in diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2003;26(6):1902–12.
Leese GP, Wang J, Broomhall J, et al. Frequency of severe hypoglycemia requiring emergency treatment in type 1 and type 2 diabetes: a population-based study of health service resource use. Diabetes Care. 2003;26(4):1176–80.
Munshi MN, Segal AR, Suhl E, et al. Frequent hypoglycemia among elderly patients with poor glycemic control. Arch Intern Med. 2011;171(4):362–4.
Bruno JJ, Ellis JJ. Herbal use among US elderly: 2002 National Health Interview Survey. Ann Pharmacother. 2005;39(4):643–8.
Orwig D, Brandt N, Gruber-Baldini AL. Medication management assessment for older adults in the community. Gerontologist. 2006;46(5):661–8.
Field TS, Gurwitz JH, Avorn J, et al. Risk factors for adverse drug events among nursing home residents. Arch Intern Med. 2001;161(13):1629–34.
Bressler R, Bahl JJ. Principles of drug therapy for the elderly patient. Mayo Clin Proc. 2003;78(12):1564–77.
McLean AJ, Le Couteur DG. Aging biology and geriatric clinical pharmacology. Pharmacol Rev. 2004;56(2):163–84.
Bailey CJ, Kodack M. Patient adherence to medication requirements for therapy of type 2 diabetes. Int J Clin Pract. 2011;65(3):314–22.
Asche C, LaFleur J, Conner C. A review of diabetes treatment adherence and the association with clinical and economic outcomes. Clin Ther. 2011;33(1):74–109.
•• Lipska KJ, Bailey CJ, Inzucchi SE. Use of metformin in the setting of mild-to-moderate renal insufficiency. Diabetes Care 2012;34(6):1431–7. This article is a systemic review of the literature assessing use of metformin in mild to moderate renal insufficiency. Metformin is an attractive agent to use in elderly due to low risk of hypoglycemia. This article may help clinicians to make better decisions when they are faced with older adults with mild to moderate renal insufficiency who are on metformin or who need to start metformin.
•• American Geriatrics Society Updated Beers Criteria for Potentially Inappropriate Medication Use in Older Adults. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2012 Feb 29. doi: 10.1111/j.1532-5415.2012.03923.x. This article is a systematic and comprehensive review of drug-related problems and adverse drug events in older adults. Recent update has included an antidiabetic medication and sliding scale insulin strategy as "potentially inappropriate medications" for older adults. It is important to review this article to understand which drugs should be avoided in older adults.
Nathan DM. Insulin treatment in the elderly diabetic patient. Clin Geriatr Med. 1990;6(4):923–31.
Segal AR, Munshi MN. Insulin therapy for older adults with diabetes. Geriatrics and aging. 2008;11(6):357–62.
Velussi M. Lispro insulin treatment in comparison with regular human insulin in type 2 diabetic patients living in nursing homes. Diabetes Nutr Metab. 2002;15(2):96–100.
Disclosure
Conflicts of interest: M. Munshi: has received grant support from Sanofi-Aventis; M. Maguchi: none; A. Segal: none.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Munshi, M.N., Maguchi, M. & Segal, A.R. Treatment of Type 2 Diabetes in the Elderly. Curr Diab Rep 12, 239–245 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11892-012-0269-4
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11892-012-0269-4