Abstract
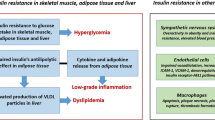
Selective insulin resistance influences pathogenesis and treatment of type 2 diabetes and metabolic syndrome. Downregulation of the antiatherogenic pathway and maintained activity of the proatherogenic and cancerogenic pathways lead to atherosclerosis and cancer. Exogenous insulin added to “compensatory” hyperinsulinemia might worsen the primary end points, resulting in potential increase in cardiovascular and cancer events in spite of improvement of surrogate metabolic end points. Conversely, metformin can improve primary and surrogate end points.
Similar content being viewed by others
References and Recommended Reading
Reaven GM: Banting lecture 1988. Role of insulin resistance in human disease. Diabetes 2003, 37:1595–1607.
DeFronzo RA, Bonadonna RC, Ferrannini E: Pathogenesis of NIDDM. A balanced overview. Diabetes Care 1992, 15:318–368.
Cusi K, Maezono K, Osman A, et al.: Insulin resistance differentially affects PI 3-kinase and MAP-kinase-mediated signalling in human muscle. J Clin Invest 2000, 105:311–320.
Montagnani M, Golovchenco I, Kim I, et al.: Inhibition of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase enhances mitogenic actions of insulin in endothelial cells. J Biol Chem 2002, 277:1794–1799.
Wang CCL, Goalstone ML, Draznin B: Molecular mechanism of insulin resistance that impact cardiovascular biology. Diabetes 2004, 53:2735–2740.
Draznin B: Molecular mechanisms of insulin resistance: serine phosphorylation of insulin receptor substrate-1 and increased expression of p85? The two sides of a coin. Diabetes 2006, 55:2392–2397.
Giovannucci E: The role of insulin resistance and hyperinsulinemia in cancer causation. Curr Med Chem-Immun Endoc & Metab Agents 2005, 5:53–60.
Goldstein JL, Brown MS: Regulation of the mevalonate pathway. Nature 1990, 343:425–430.
Ness GC, Chambers CM: Feedback and hormonal regulation of hepatic 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase: the concept of cholesterol buffering capacity. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med 2000, 224:8–19.
Siperstein MD: Role of cholesterogenesis and isoprenoid synthesis in DNA replication and cell growth. J Lipid Res 1984, 25:1462–1468.
Muis MJ, Bots ML, Grobbee DE, Stolk RP: Insulin treatment and cardiovascular disease: friend or foe? A point of view. Diabet Med 2004, 22:118–126.
Stettler C, Alleman S, Jüni P, et al.: Glycemic control and macrovascular disease in types 1 and 2 diabetes mellitus: meta-analysis of randomized trials. Am Heart J 2006, 152:27–38.
Garcia MJ, McNamara P, Gordon T, Kannell WB: Morbidity and mortality in diabetics in the Framingham population. Sixteen year follow-up study. Diabetes 1974, 23:105–111.
Janka HU, Ziegler AG, Standl E, Menhert H: Daily insulin dose as a predictor of macrovascular disease in insulin treated non-insulin-dependent diabetics. Diabete Metab 1987, 13:359–364.
Kleinman JC, Donahue RP, Harris M, et al.: Mortality among diabetics in a national sample. Am J Epidemiol 1988, 128:389–401.
Nelson RG, Sievers ML, Knowler WC, et al.: Low incidence of coronary heart disease in Pima Indians despite high prevalence of non-insulin-dependent diabetes. Circulation 1990, 81:987–995.
Muggeo M, Verlato G, Bonora E, et al.: The Verona diabetes study: a population-based survey on known diabetes mellitus prevalence and 5-year all-cause mortality. Diabetologia 1995, 38:318–325.
Colwell J, Abraira C, Henderson W, et al.: VA Cooperative Study on glycemic control and complications in type II diabetes (VACSDM): micro and macrovascular events. Diabetologia 1996, 39(Suppl 1):A34.
Abraira C, Colwell J, Nuttall F, et al.: Cardiovascular events and correlates in the Veteran Affairs Diabetes Feasibility Trial. Veteran Affairs Cooperative Study on glycemic control and complications in type II diabetes. Arch Intern Med 1997, 7:181–188.
Faglia E, Favales F, Quarantiello A, et al.: are insulin-treated type 2 subjects at higher risk for foot ulcers? Diabetes Care 1999, 22:1379–1380.
Bruno G, Merletti F, Boffetta P, et al.: Impact of glycaemic control, hypertension and insulin treatment on general and cause-specific mortality: an Italian population-based cohort of Type II (non-insulin-dependent) diabetes mellitus. Diabetologia 1999, 42:297–301.
Saito I, Folsom AR, Brancati FL, et al.: Nontraditional risk factors for coronary heart disease incidence among persons with diabetes: the Atherosclerosis risk in communities (ARIC) study. Ann Intern Med 2000, 133:81–91.
Shichiri M, Kishikawa H, Ohkubo Y, Wake N: Long-term results of the Kumamoto study on optimal diabetes control in type 2 diabetic patients. Diabetes Care 2000, 23(Suppl 2):B21–B29.
Nichols GA, Gullion CM, Koro CE, et al.: Risk of congestive heart failure after initiation of anti-hyperglycemic therapy. Diabetologia 2003, 46:A364.
Kronmal RA, Barzilay JI, Tracy RP, et al.: The relationship of fasting serum radioimmune insulin levels to incident coronary heart disease in an insulin-treated diabetic cohort. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2004, 89:2852–2858.
Smooke S, Horwich TB, Fonarow GC: Insulin-treated diabetes is associated with a marked increase in mortality in patients with advanced heart failure. Am Heart J 2005, 149:168–174.
Tseng C-H: Exogenous insulin use and hypertension in adult patients with diabetes mellitus. Arch Intern Med 2006, 166:1184–1189.
Kronmal RA, Barzilay JL, Smith NL, et al.: Mortality in pharmacologically treated older adults with diabetes: the Cardiovascular Health Study 1989–2001. PLoS Med 2006, 3:e400.
Yang YX, Hennessy S, Lewis JD: Insulin therapy and colorectal cancer risk among type 2 diabetes mellitus patients. Gastroenterology 2004, 127:1044–1050.
Renehan AG, Shalet SM: Diabetes, insulin therapy, and colorectal cancer [editorial]. BMJ 2005, 330:551–552.
Bowker SL, Majumdar SR, Veugelers P, Johnson JA: Increased cancer-related mortality for patients with type 2 diabetes who use sulfonylureas or insulin. Diabetes Care 2006, 23:441–442.
DeFronzo RA: Pharmacologic therapy for type 2 diabetes mellitus. Ann Intern Med 1999, 31:281–303.
Ballani P, Tran MT, Navar MD, Davidson MB: Clinical experience with U-500 regular insulin in obese, markedly insulin resistant type 2 diabetic patients. Diabetes Care 2006, 29:2504–2505.
Gerstein HC: Glycosylated haemoglobin: finally ready for prime time as cardiovascular risk factor. Ann Intern Med 2004, 141:475–476.
Dandona P, Aljada A, Mohanty P: The anti-inflammatory and potential anti-atherogenic effect of insulin: a new paradigm. Diabetologia 2002, 45:924–930.
Dandona P, Aljada A, Mohanty P, et al.: Insulin suppresses plasma concentration of vascular endothelial growth factor and matrix metalloproteinase-9. Diabetes Care 2003, 26:3310–3314.
Madonna R, Pandolfi A, Massaro M, et al.: Insulin enhances vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 expression in human cultured endothelial cells through a pro-atherogenic pathway mediated by p38 mitogen-activated protein-kinase. Diabetologia 2004, 47:532–536.
Rossouw JE, Anderson GL, Prentice RL, et al.: Risk and benefits of estrogen plus progestin in healthy postmenopausal women: principal results from the Women’s Health Initiative randomized controlled trial. JAMA 2002, 288:321–333.
Lenzer J: FDA advisers warn: COX 2 inhibitors increase risk of heart attack and stroke. BMJ 2005, 330:440.
Herrington DM, Howard TD: From presumed benefit to potential harm—hormone therapy and heart disease. N Engl J Med 2003, 349:519–521.
Effects of intensive blood glucose control with metformin on complications in overweight patients with type 2 diabetes (UKPDS 34). UK Prospective Diabetes Study (UKPDS) Group. Lancet 1998, 352:854–865.
Zhou G, Myers R, Li Y, et al.: Role of AMP-activated protein kinase in mechanism of metformin action. J Clin Invest 2001, 108:1167–1174.
Muntoni S: Inhibition of fatty acid oxidation by biguanides: implications for metabolic physiopathology. Adv Lipid Res 1974, 12:311–377.
Muntoni S: Metformin and fatty acids. Diabetes Care 1999, 22:179–180.
Essop MF, Opie LH: Metabolic therapy for heart failure. Eur Heart J 2004, 25:1765–1768.
Muntoni S: Metformin and heart failure: innocent until proven guilty. Diabetes Care 2006, 29:751–752.
von Lewinski D, Bruns S, Walther S, et al.: Insulin causes [Ca2+]i-dependent and [Ca2+]i-independent positive inotropic effects in failing human myocardium. Circulation 2005, 111:2588–2595.
Gandhy GY, Nuttall GA, Abel MD, et al.: Intensive intraoperative insulin therapy versus conventional glucose management during cardiac surgery: a randomized trial. Ann Intern Med 2007, 146:233–243.
Muntoni S, Muntoni SA: Insulin treatment in the absence of dependence. Available at http://www.annals.org/cgi/eletters/146/4/233#15139. Accessed February 28, 2008.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Muntoni, S., Muntoni, S. & Draznin, B. Effects of chronic hyperinsulinemia in insulin-resistant patients. Curr Diab Rep 8, 233–238 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11892-008-0040-z
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11892-008-0040-z